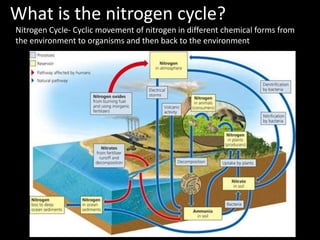
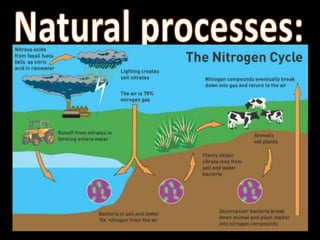
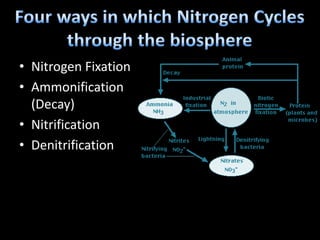
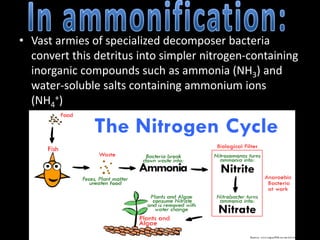
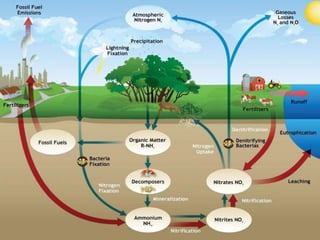
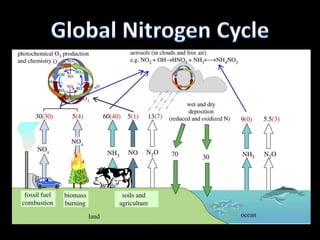
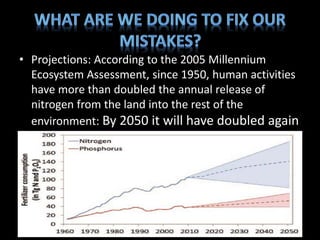
The nitrogen cycle describes the movement of nitrogen through the environment. It involves nitrogen fixation by bacteria, ammonification by decomposers, nitrification by soil bacteria, and denitrification by bacteria in waterlogged soils that converts nitrogen back to its gaseous form. Human activities such as fossil fuel combustion, use of nitrogen fertilizers, and livestock ranching have significantly increased the global nitrogen cycle, causing issues like smog, acid rain, eutrophication, and increased greenhouse gas emissions. While some seek solutions, many nations prioritize food production over environmental impacts.