This document provides an introduction to the Engineering Economics course ECO 300. It outlines the lecture plan, recommended textbooks, and foundational concepts of engineering economics. The key points are:
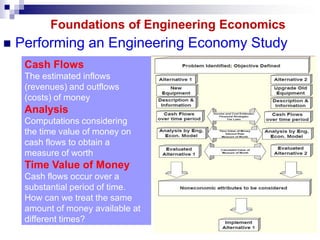
1) Engineering economics applies economic principles to engineering problems to analyze costs and compare alternative capital projects or engineering solutions.
2) The course will cover cost estimation, quantification of profitability, process optimization, and financial management over 16 weeks.
3) Engineering economics uses mathematical techniques to simplify economic comparisons and assist with decision-making regarding how to best invest limited capital over time. Sensitivity analysis is used to account for uncertainty in estimates.