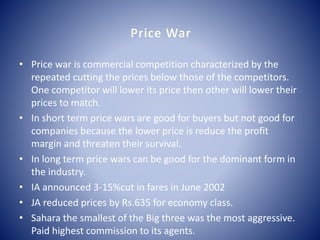
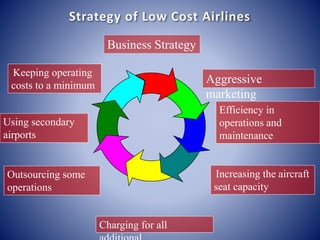
The document discusses the history and development of the airline industry in India. It describes how Indian Airlines was initially the sole player, but competition increased in the 1990s with the entry of Jet Airways and Air Sahara. All three airlines engaged in price wars in 2002 by cutting fares and introducing various promotional schemes to attract customers. This led to unprecedented growth in air travel accessibility for the Indian population.