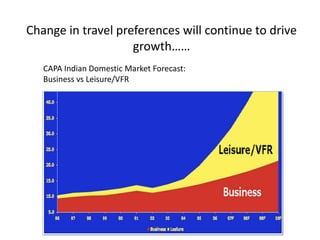
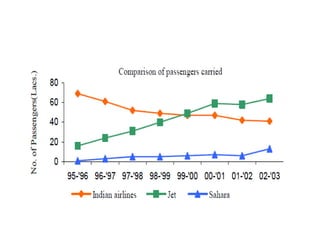
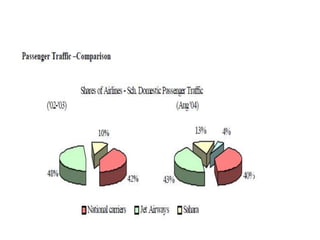
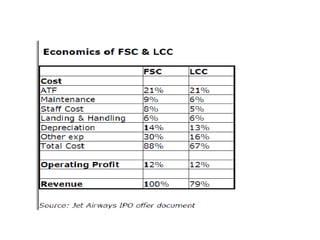
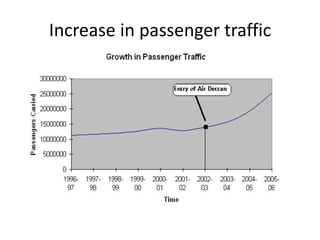
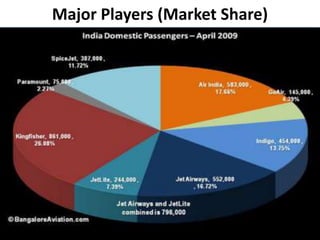
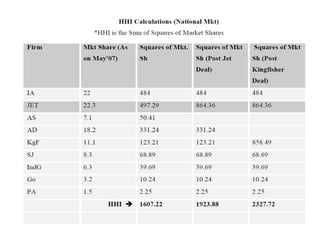
The Indian aviation industry has grown significantly over the past decade, with passenger traffic growing around 15% annually. However, growth slowed to 0.7% in 2009. The vision is for 280 million passengers by 2020. Private carriers were introduced in the 1990s and led to intense price competition through discounted fares like Apex. Low-cost carriers like Air Deccan further drove down prices. Major carriers have consolidated through mergers and acquisitions, like Jet Airways acquiring Air Sahara and Kingfisher Airlines acquiring a stake in Air Deccan. The industry now faces opportunities for further growth but also threats from economic slowdowns and infrastructure limitations.