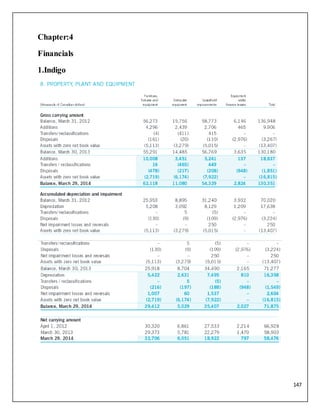
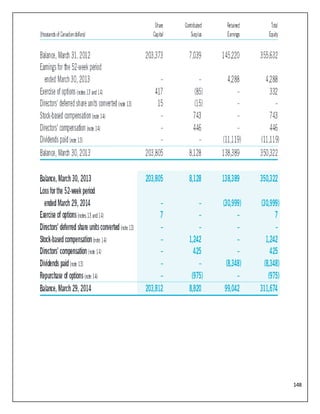
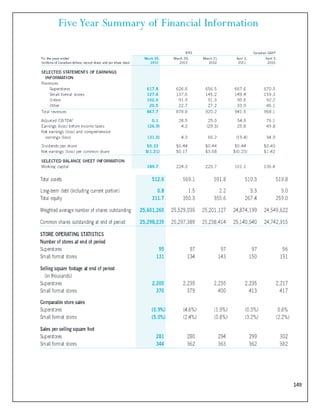
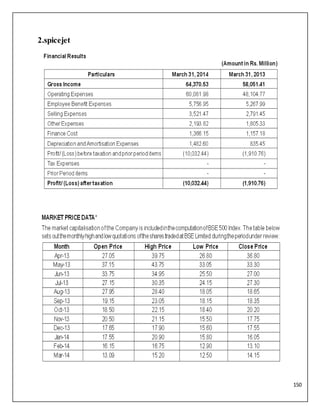
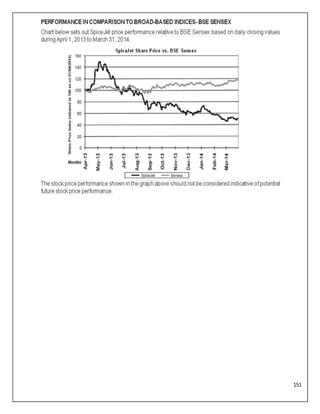
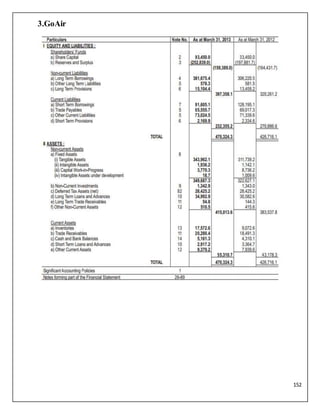
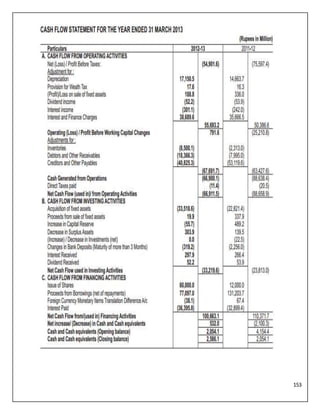
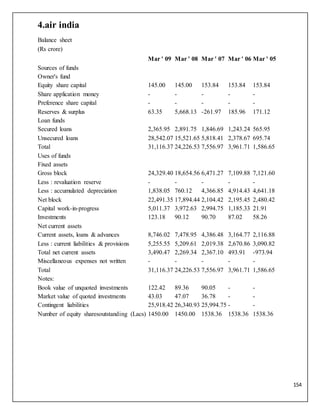
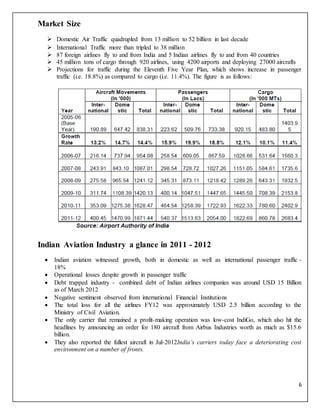
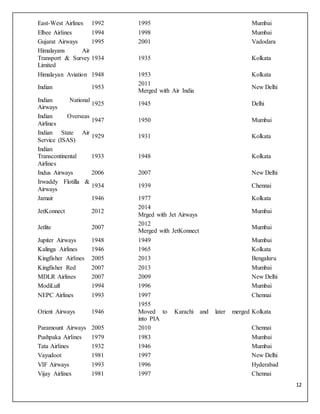
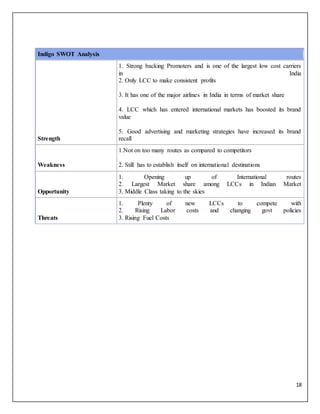
The document is a project report analyzing the Indian aviation industry, detailing its historical development, market dynamics, and competitive landscape. Key players in the industry include Indigo, SpiceJet, and Air India, with a focus on operational challenges, market growth, and financials. The report highlights the industry's transition from government control to privatization, recent trends in passenger traffic, and ongoing competition from both airlines and alternative transport modes.




























![42
Etihad deal. The stock had fallen by 18% in a period of one week. Economic Times reported that "The
froth that developed around Jet stock was largely deal driven and has now fizzled away."
In August 2014, Jet Airways announced that it is discontinuing its low fare arm JetKonnect and JetLite
making Jet Airways 3rd full service airline in India besides Air India and Vistara (proposed)
Jet Airways Boeing 777-300ER atSan Francisco International Airport
Corporate affairs and Identity
Jet Airways's head office is located in the Siroya Centre in Andheri, Mumbai. Jet Airways's head office
was previously located in the S.M. Centre, a rented, unmarked six-storey building in Andheri. In 2008
Robyn Meredith of Forbes stated that the complex was "as shabby as [Jet Airways] CEO NareshGoyal's
home is posh" and that the complex was "In need of a fresh coat of paint". The complex was 15 minutes
driving time from ChhatrapatiShivaji International Airport. In 2013, it was announced that Etihad
Airways would buy a 24% stake in the airline through preferential allotment of shares.
Subsidiaries
JetLite
JetLite was a wholly owned subsidiary of Jet Airways. It was established as Sahara Airlines on 20
September 1991 and began operations on 3 December 1993 with two Boeing 737-200 aircraft. Initially
services were primarily concentrated in the northern sectors of India, keeping Delhi as its base, and then
operations were extended to cover all the country. Sahara Airlines was rebranded as Air Sahara on 2
October 2000. On 12 April 2007 Jet Airways took over Air Sahara and on 16 April 2007 Air Sahara was
renamed as JetLite. JetLite operated a fleet of mixed owned–leased Boeing 737 Next Generation aircraft
and Bombardier CRJ-200ER. JetLite ceased operations on 25 March 2012 after merger with Jet
Konnect. The Bombardier jets were phased out but the Boeings remained in service and operated for
JetKonnect. JetLite offered a buy on board service called JetCafé, offering food for purchase.
JetKonnect
JetKonnect, formerly Jet Airways Konnect, the low-cost brand of Jet Airways, was launched on 8 May
2009. It operated a fleet of Boeing 737 Next Generation aircraft. The rationale for launching Jet Konnect
was to close down loss-making routes and divert the planes to more profitable routes with
higher passenger load factors. Jet already ran a low-cost airline named JetLite. According to Jet
Airways, the decision to launch a low-cost brand instead of expanding the existing JetLite was taken to
avoid the regulatory delays associated with moving excess aircraft and assets from Jet Airways to
JetLite, which have separate operating codes. Jet Connect offers a no frills flight where meals and other
refreshments have to be purchased on board. To identify if the flight is a full service or Connect the
flight numbers for Connect are in the series 9W 2000-2999. Jet Airways merged the Jet Lite brand into
Jet Connect on 25 March 2012. Jet Airways offered eight business class seats in Connect to cash in on
Kingfisher Airlines' woes. In December 2012, Jet Airways placed an order for 5 ATR 72-600 aircraft to](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-42-320.jpg)
![43
"enhance regional connectivity." The first aircraft was delivered the same month, leased from GECAS
and was operated for JetKonnect.
Jet Airways announced on 11 August 2014 that it would phase out Jet Konnect by the end of the year as
part of plans to reposition itself as a uniform full-service operator., on 1 December 2014 Jet Connect
was fully merged with Jet Airways.
Destinations
Jet Airways serves 47 domestic destinations and 22 international destinations, a total of 69 in 19
countries across Asia, Europe and North America. Short-haul destinations are served using Boeing 737
Next Generation. ATR 72-500s are used only on domestic regional routes, while long-haul routes are
served using its Airbus A330-200 and Boeing 777-300ER aircraft. London, England was the airline's
first long-haul destination and was launched in 2005. Since 2007 Jet Airways has had a scissors hub
at Brussels Airport in Belgium for onward trans-atlantic connections to Canada and the United States.
The recession forced Jet Airways to discontinue the following routes: Ahmedabad–
London, Birmingham-Brussels, Amritsar–London, Bangalore–Brussels,Mumbai–Shanghai–San
Francisco and Brussels-New York City. It also had to put an indefinite delay on its expansion plans. Jet
Airways was forced to lease out seven of its ten Boeing 777-300ERs to survive the financial crunch.
Due to the recession all flights to North America were operated on an Airbus A330-200 replacing
the Boeing 777-300ERs. It also had to sell a brand-new, yet-to-be-delivered Boeing 777-300ER in 2009
and had to defer all new aircraft deliveries by at least two years. The airline planned to restore
theMumbai-Shanghai route by the end of 2011 but never went through with it. As the economic crisis in
the Eurozone countries worsened, Jet also closed the Delhi-Milan route. Jet Airways relaunched service
to New York's JFK International Airport and San Francisco via Abu Dhabi on May 1, 2014, and
November 18, 2014, respectively, using its joint venture relationship with Etihad Airways.
Jet Airways Airbus A340-300 atLondon Heathrow Airport in 2005 with the 1993-2007 livery
Also, Jet Airways will introduce the Mumbai-Paris route using the Airbus A330 aircraft from Mid May
2014 - a mid-day departure from Mumbai to reach evening in Paris CDG and Leaving CDG Paris in
night arriving next morning in Mumbai similar to Air India's schedule on Delhi-Paris route.
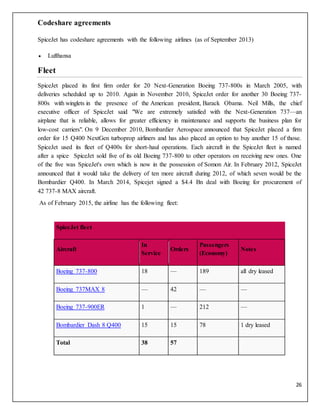
Codeshare agreements
Jet Airways has codeshare agreements with the following airlines (as of June 2013):
Air Canada [Star Alliance]
Air France [Sky Team]
All Nippon Airways [Star
Alliance]
Alitalia [Sky Team]
Brussels Airlines [Star Alliance]
Etihad Airways
Garuda Indonesia [Sky Team]
Kenya Airways [Sky Team]
KLM [Sky Team]
Korean Air [Sky Team]
Turkish Airlines [Star
South African Airways [Star
Alliance]
Qantas [One World]
United Airlines [Star Alliance]
Vietnam Airlines [Sky Team]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-43-320.jpg)
![44
Alliance]
MalaysiaAirlines [OneWorld]
Jet Airways also has a codesharing agreement with Thalys European rail serviceEffective 1 February
2014, the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration lowered India's aviation safety rating to a Category 2.
As a result of the FAA action, all U.S.-based airlines are required to suspend all codeshare cooperation
with any India-based airlines. This FAA decision is country specific for India, not airline specific.
Fleet
4 Airbus A330 in Delhi Airport
Jet Airways Boeing 777-300ER with the present livery
Jet Airways Boeing 737-800
As of November 2014, the Jet Airways fleet consists of the following aircraft with an average age of 5.4
years:
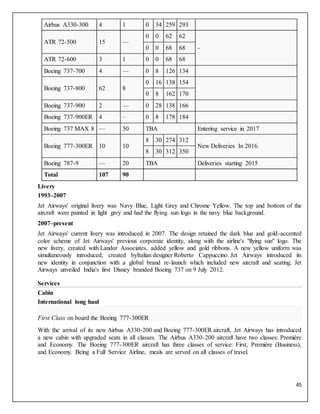
Jet Airways Fleet
Aircraft
In
Service
Orders
Passengers
Notes
F J Y Total
Airbus A330-200 3 — 0 30 196 226 3 more Dry Leased to Turkish Airlines](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-44-320.jpg)



![49
Subsidiaries (affiliates)
AirAsia India
AirAsia X
Indonesia AirAsia
Indonesia AirAsia X
Philippines AirAsia
AirAsia Zest
Thai AirAsia
Thai AirAsia X
AirAsia Japan
Fleet size 182
Destinations 121 incl. affiliate airlines
Company slogan Now Everyone Can Fly
Parent company Tune Group
Headquarters Kuala Lumpur International Airport
Sepang, Selangor, Malaysia
Key people Tony Fernandes, Co-founder and CEO of AirAsia Group
Aireen Omar, CEO[2]
Revenue RM 5.19 billion/US$1.58 billion(2013)
Net income RM 364 million/US$ 111 million(2013)
Employees +10,000 (2014)
Website www.airasia.com
An AirAsia Boeing 737-300 in special livery denoting the Malaysian flag.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-49-320.jpg)

![51
During 2007, passengers from "The Barrier-Free Environment and Accessible Transport Group"
protested against the airline over its refusal to fly passengers who were completely immobile. They
claimed that people with disabilities were discriminated against when booking tickets online; the CEO
of the airline said it did not turn away wheelchair-bound passengers.
An AirAsia A320 with the Malaysian flag on the tail and Cartoon drawings on the fuselage.
On 27 September 2008, the company announced 106 new routes to be added to its list of 60. The
number of old routes discontinued has not been disclosed.
In August 2011, AirAsia agreed to form an alliance with Malaysia Airlines by means of a share
swap.[11] The alliance was struck down by the Malaysian government, in effect voiding the agreement of
both airlines.
By early 2013, AirAsia's profits increased by 168% on a year-over-year basis compared to the same
period in 2012. For the quarter ending 31 December 2012, the airline's net profit stood at 350.65 million
ringgit (US$114.08 million). Despite a 1% rise in the average fuel price, the airline recorded profits of
1.88 billion ringgit for its full 2012 fiscal year.
In February 2013, AirAsia submitted an application to the Indian Foreign Investment Promotion Board,
through its investment arm, AirAsia Investment Limited, to seek approval for commencing its
operations in India. AirAsia asked to take a 49% stake in the Indian sister airline, which was the
maximum allowed by the Indian government at that time. AirAsia committed to invest up to US$50
million in the new airline. Operations would begin in Chennai, expanding its network throughout South
India, where AirAsia already operates flights from Malaysia and Thailand.
Corporate affairs
KLIA LCCT, which houses the AirAsia head office
The head office is the LCC Terminal at Kuala Lumpur International Airport in Sepang, Selangor.
The registered office is on level 13 of the Menara Prima Tower B in Petaling Jaya.
The airline plans to move its head office to a new facility constructed at klia2. Until the new head office
opens, the airline's head office will remain at LCCT. The new klia2 head office is scheduled to open in
the end of 2015. Aireen Omar, the AirAsia Country CEO of Malaysia, stated that the headquarters](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-51-320.jpg)


![54
Indonesia AirAsia X
Indonesia AirAsia X is a joint venture of AirAsia X. It serves Indonesia AirAsia's regularly scheduled
long haul international flights from Bali's Ngurah Rai International Airport. Indonesia AirAsia X was
scheduled to launch its first flight to Melbourne on 22 December 2014.
Philippines AirAsia
Philippines AirAsia is a joint venture between Filipino investors and AirAsia. The Filipino group
include Antonio Cojuangco, Jr., former owner of Associated Broadcasting Companywith flagship
television station TV5, Michael Romero, a real estate developer and port operator, and Marianne
Hantavirus. The joint venture was approved on 7 December 2010 by the Board of Investments, an
agency in the Philippines in charge of big ticket investments.
Philippines AirAsia is one of the Philippine air carriers banned in the European Union. On 15 August
2011, Philippines Air Asia took delivery of its first brand-new aircraft, an Airbus A320 which arrived
at Clark International Airport in Clark, Angeles City, Pampanga. On 8 November 2011, Philippines Air
Asia took delivery of its second A320. On 7 February 2012, the airline received its Air Operator
Certificate from the Civil Aviation Authority of the Philippines which gives the airline permission to fly
in Philippine airspace.
Thai AirAsia
Thai AirAsia is a joint venture between AirAsia and Thailand's Asia Aviation. Thai AirAsia launched
domestic operations on February 2004. It serves AirAsia's regularly scheduled domestic and
international flights from Bangkok and other cities in Thailand. Thai AirAsia was the only low-cost
airline operating both domestic and international flights from theSuvarnabhumi Airport. The airline
shifted all operations from Suvarnabhumi Airport to Don Mueang International Airport effective 1
October 2012. Thai AirAsia is 55% owned by Asia Aviation, 45% owned by AirAsia International. The
airline sponsors the Thai football teams Buriram United, SCG Muangthong United, Chonburi, Osotspa
Saraburi, BEC Tero Sasana, Chiangrai UTD, Esan United, Chainat, Samut Prakan CUTD, Bangkok
United, FC Phuket, Krabi, Air Force United, Nakhon Phanom, Loei City, Trang and the referee
of Football Association of Thailand.
Thai AirAsia X
Thai AirAsia X is Thailand’s first long-haul low-cost airline. It was scheduled to begin operations in
June 2014. After putting off the launch that had been planned for the first quarter, Thai AirAsia X was to
launch its maiden service from Bangkok to Incheon, South Korea on 17 June and then begin regular
flights to Japan’s Narita Airport in Tokyo and Osaka around July.[48]
Destinations
Fleet
The total AirAsia fleet (excluding AirAsia X) consists of the following aircraft (as of January 2015):](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-54-320.jpg)







![64
flight prices by selling directly to passengers and excluding the costs imposed by travel agents. Within a
year, the website was handling three-quarters of all bookings.
Ryanair launched a new base of operation in Charleroi Airport in 2001. Later that year, the airline
ordered 155 new 737-800 aircraft from Boeing at what was believed to be a substantial discount, to be
delivered over eight years from 2002 to 2010. Approximately 100 of these aircraft had been delivered by
the end of 2005, although there were slight delays in late 2005 caused by production disruptions arising
from a Boeing machinists' strike. In 2003, Ryanair ordered a further 100 new 737-800 aircraft.
Ryanair cabin with advertising on overhead lockers and safety cards on seatbacks
In April 2003, Ryanair acquired its ailing competitor Buzz from KLM. By the end of 2003, the airline
flew 127 routes, of which 60 had opened in the previous 12 months.
During 2004, Michael O'Leary warned of a "bloodbath" during the winter from which only two or three
low-cost airlines would emerge, the expectation being that these would be Ryanair and EasyJet A loss
of €3.3 million in the second quarter of 2004 was the airline's first recorded loss for 15 years but the
airline became profitable soon after. The enlargement of the European Union on 1 May 2004 opened the
way to more new routes for Ryanair.
Carrying under 700,000 annually in its early years, passenger figures grew to 21.4 million in 2003.[citation
needed] The rapid addition of new routes and new bases has enabled this growth in passenger numbers and
made Ryanair among the largest carriers on European routes. In August 2005, the airline claimed to
have carried 20% more passengers within Europe than British Airways.
Ryanair posted record half-year profits of €329 million for the six months ending 30 September 2006.[
Over the same period, passenger traffic grew by more than a fifth to 22.1 million passengers and
revenues rose by a third to €1.256 billion.
On 13 February 2006, Britain's Channel 4 broadcast a documentary as part of its Dispatches series,
"Ryanair caught napping". The documentary criticisedRyanair's training policies, security procedures
and aircraft hygiene, and highlighted poor staff morale. Ryanair denied the allegations and claimed that
promotional materials, in particular a photograph of a stewardess sleeping, had been faked by
Dispatches.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-64-320.jpg)


![67
In August 2010, Ryanair held a press conference in Plovdiv and announced its first ever Bulgarian
destination connecting Plovdiv with London Stansted. The service was planned to start in November
2010 with two flights weekly.
In late 2010, Ryan began withdrawing all their routes from their smallest base, Belfast City, and
Shannon due to rises in airport fees.
In the last three months of 2010, Ryanair made a loss of €10.3 million, compared with a loss of €10.9
million in the same period the previous year. In this time, more than 3,000 flights were cancelled.
Ryanair blamed the losses on strikes and flight cancellations due to severe weather.
In March 2011, Ryanair opened a new maintenance hangar at Glasgow Prestwick International Airport,
making it Ryanair's biggest fleet maintenance base.
In June 2011, Ryanair and COMAC signed an agreement to co-operate on the development of the C-
919, a Boeing 737 competitor.
Ryanair cut capacity by grounding 80 aircraft between November 2011 and April 2012 due to the high
cost of fuel and continuing weak economic conditions.
On 19 June 2012, Ryanair Chief Executive Michael O'Leary announced his intentions to make an all-
cash offer to buy Aer Lingus. However, the bid is likely to face a stiff challenge from the European
Commission, which blocked an earlier 2007 bid. The combined companies would control 80% of the
370,000 journeys between the UK and Ireland every month. The Irish government said it was looking to
sell its 25% stake in Aer Lingus; however, it was made clear that they would not sell their share to
Ryanair due to competition concerns. Michael O'Leary pledged that he would keep the two airlines
separate and competitive to one another.
On 25 October 2013, Ryanair unveiled what it called a series of "customer service improvements" over
the next six months. These included lower fees for reprinting boarding passes, free changes of minor
errors on bookings within 24 hours, and a second small carry on bag. Ryanair said it was making these
changes due to customer feedback.[57]
On 27 January 2014, Ryanair moved into their new €20m, 100,000 sqft Dublin Head Office in Airside
Business Park, having outgrown their previous office based within Dublin Airport.[58] The building was
officially opened on Thursday 3 April 2014 by Taoiseach Enda Kenny, Minister for Finance Michael
Noonan and the Lord Mayor of DublinOisin Quinn.
On 8 September 2014, Ryanair agreed to purchase up to 200 Boeing 737 MAX 8s (100 confirmed and
100 options) for over $22 billion.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-67-320.jpg)









![79
Airline Pilots' Association, a union not affiliated with the Air Line Pilots Association, represents the
airline's pilots.The Aircraft Maintenance Technicians are represented by the Aircraft Mechanics
Fraternal Association (AMFA). Customer Service Agents and Reservation Agents are represented by the
International Association of Machinists and Aerospace Workers Union (IAM). Flight Dispatchers,
Flight Attendants, Ramp agents and Operations agents are represented by the Transport Workers Union
(TWU).
Impact on carriers
Southwest has been a major inspiration to other low-cost carriers, and its business model has been
repeated many times around the world. The competitive strategy combines high level of employee and
aircraft productivity with low unit costs by reducing aircraft turn around time particularly at the
gate.[80] Europe's EasyJet and Ryanair are two of the best known airlines to follow Southwest's
business strategy in that continent. Other airlines with a business model based on Southwest's system
include Canada's WestJet, Malaysia's AirAsia (the first and biggest LCC in Asia), Qantas's Jetstar
(although Jetstar now operates three aircraft types), Philippines's Cebu Pacific, Thailand's Nok Air,
Mexico's Volaris and Turkey's Pegasus Airlines. Although Southwest has been a major inspiration to
many other airlines, including Ryanair, AirAsia and Jetstar, the management strategies, for example, of
Ryanair, AirAsia and Jetstar differ significantly from those of Southwest. All these different
management strategies can be seen as means of differentiation from other competitors in order to gain
competitive advantages.
Lobbying Texas rail
Southwest has fought against the development of a high-speed rail system in Texas.
In 1991 a plan was made to connect the Texas Triangle (Houston – Dallas – San Antonio) with a
privately financed high speed train system which would quickly take passengers from one city to the
next. This was the same model Southwest Airlines used 20 years earlier to break into the Texas market
where it served the same three cities.
Southwest Airlines, with the help of lobbyists, created legal barriers to prohibit the consortium from
moving forward and the entire project was eventually scuttled in 1994, when the State of Texas
withdrew the franchise.
Destinations
Southwest Airlines destination map
As of March 2015, Southwest Airlines has scheduled flights to 94 destinations in 41 states, Puerto Rico
and abroad, the newest being San José, CR (SJO) on March 7, 2015. Southwest has announced plans to
increase its city count to 96 so far in 2015. Southwest does not use the "hub and spoke" system of other
major airlines, preferring the "point-to-point" system.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-79-320.jpg)

![83
Livery
Original desert gold livery, used until 2001
Southwest's original primary livery was desert gold, red and orange, with pinstripes of white separating
each section of color. The word Southwest appeared in white on the desert gold portion of the tail. On
the original three 737-200s, from June 1971, on the left side of the plane, the word Southwest was
placed along the upper rear portion of the fuselage, with the word Airlines painted on the tail N21SW.
On the right side, the word Southwest was on the tail, but also had the word Airlines painted on the
upper rear portion of the fuselage.N20SW.
Canyon blue livery used from 2001 to 2014
Southwest introduced the canyon blue livery on January 16, 2001, the first primary livery change in
Southwest's [then] 30-year history. Spirit One was the first plane painted in the canyon blue fleet color
scheme. The second livery replaces the former primary color, desert gold, with canyon blue and changes
the Southwest text and pinstripes to gold. The orange and red stripes continued to be used. The pinstripe
along the plane was drawn in a more curved pattern instead of the straight horizontal line separating the
colors in the original. For aircraft equipped with blended winglets, the blended winglets were painted to
include the text Southwest.com. Southwest completed repainting its entire fleet with the new Canyon
Blue livery in early 2010; however, The Colleen Barrett Classic (N714CB), The Herbert D. Kelleher
One (N711HK), & The Metallic Gold One (N792SW), which are Boeing 737–700 aircraft, retain the
original desert gold livery. However, these classics do not have the black paint printed on the nose of the
plane and do not have the number one heart on it.
Heart livery used 2014-present
A new livery, named "Heart" and developed with firms GSD&M, Lippincott, VML, Razorfish, and
Camelot Communications, was unveiled on September 8, 2014. The new livery uses a darker shade of
blue. The orange stripe on the tail is changed to yellow, both the red and yellow stripes are now enlarged
in reverse pattern, and the belly of the aircraft is now in blue and features a heart, which has been a
symbol for Southwest during its 43-year history. Additionally, the pinstripes are changed to a silver-gray
and the Southwest text, now white, has been moved to the front of the fuselage. Lettering is in a font
custom designed by Monotype, Southwest Sans. The engines now feature the airline's web address,
Southwest.com.
Special liveries and decals
Some Southwest aircraft feature special liveries or are named with special decals. Southwest gives these
aircraft special names, usually ending in "One". All special liveries painted prior to Spirit One originally
wore the standard Desert Gold, red and orange colors on the vertical stabilizer and rudder. Subsequent
special liveries feature tails with the canyon blue livery. All earlier specials, with the exception of Triple
Crown One, have been repainted with the Spirit livery tail. Aircraft painted in special liveries have white
painted blended winglets with the exception of Warrior One which added the split scimitar winglet in
May 2014.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-83-320.jpg)
![84
Southwest Airlines special liveries
Name Year Description Registration Photo
2,000th 737NG & 5,000th 737 produced 2006 Southwest received both the 5,000th 737 produced
(February 13, 2006) (N230WN) and the 2,000th "Next Generation" 737 produced (July 27, 2006)
(N248WN). The 2,000th "Next Generation" 737 is marked as such in its livery, though the 5,000th 737
is not similarly marked on the outside. It does have a placard stating that it is the 5000th 737 on the
upper part of the inside entry door frame. 2,000th (N248WN), 5,000th (N230WN)
Silver One 1996 25th Anniversary aircraft. Originally polished bare metal, it was later painted
silver for easier maintenance. It was then re-painted with a silver metallic paint. This aircraft also
featured silver seats, which were replaced to conform with the rest of the fleet for simplicity. Silver One
also featured silver heart shaped drink stirrers. Most recently Silver One was repainted in the fleet
standard Canyon Blue theme due to the silver paint looking dingy and the company felt it did not fit the
company's cheerful, bright personality. The Silver One nose logo remained but the interior was replaced
with the fleet standard blue and tan. N629SW (Original, Silver Paint, Canyon Blue)
Slam Dunk One 2005 Basketball superimposed on side of aircraft and a different NBA team
logo on each overhead bin in the cabin, recognizing Southwest's partnership with the National
Basketball Association. On October 11, 2010 Southwest Airlines and the National Basketball
Association ended their partnership and the aircraft was repainted to standard canyon blue livery.
Source: Dallas Morning News Aviation Blog (N224WN). N224WN
The Spirit of Hope 2004 Dedicated to the Ronald McDonald House. Overhead bins are covered in
artwork from kids at a Ronald McDonald House in Washington State. N443WN
The Spirit of Kitty Hawk 1984 Livery and title introduced the first three Boeing 737–300 aircraft
to the Southwest Airlines fleet. N300SW is the oldest −300 in the fleet, followed by N301SW and
N302SW N300SW, N301SW, N302SW
Spirit One 2001 30th Anniversary aircraft, first aircraft in canyon blue paint scheme N793SA
Sports Illustrated 2009 A large decal of Sports Illustrated Swimsuit Edition Cover Model Bar Refaeli
adorns the fuselage of N922WN. However on June 16, 2009 this aircraft was photographed in full
canyon blue on a photo posted on airliners.net.[109] N922WN
Tinker Bell One 2008 Includes the logo of the Tinker Bell movie and a sticker featuring the
phrase "Powered by Pixie Dust". However on April 2, 2010 this aircraft was photographed in full
canyon blue, and later with the "Free Bags Fly Here" sticker just above the cargo door to promote
Southwest's Bags Fly Free campaign. N912WN
Triple Crown One 1997 Livery dedicated to the employees of Southwest, in recognition of
Southwest receiving five Triple Crown airline industry awards (best on-time record, best baggage
handling, and fewest customer complaints). The overhead bins in Triple Crown One are inscribed with
the names of all employees that worked for Southwest at the time, in honor of their part in winning the
award. N647SW Southwest Triple Crown.jpg
Warrior One 2012 Named in salute of the Southwest Employees' Warrior Spirit, and was the first
Boeing 737–800 to enter Southwest service. It will keep the Southwest Spirit livery. N8301J](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-84-320.jpg)



![88
10.EasyJet
.
EasyJet Airline Company Limited
IATA
U2
ICAO
EZY
Callsign
EASY
Founded 1995
AOC # 2091
Operating bases List of bases[show]
Fleet size 204
Destinations 134
Company slogan "europe by EasyJet"
"business by EasyJet"
"This is Generation easyJet"
Parent company EasyJet plc
Headquarters London Luton Airport
Luton, United Kingdom
Key people John Barton (Chairman)
Carolyn McCall (CEO)
Sir Stelios Haji-Ioannou(Founder)
Revenue £4,527 million (2014)
Operating income £581 million (2014)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-88-320.jpg)
![89
Net income £450 million (2014)
Total assets £4,412 million (2014)
Total equity £2,172 million (2014)
Employees 8,945 (2013)
Website www.easyjet.com
EasyJet (styled as easyJet; LSE: EZJ) is a British airline carrier based at London Luton Airport. It is
the largest airline of theUnited Kingdom, by number of passengers carried, operating domestic and
international scheduled services on over 700 routes in 32 countries. EasyJet plc is listed on the London
Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index. EasyGroupHoldings Ltd (the investment
vehicle of EasyJet founder Sir Stelios Haji-Ioannou and his family) is the largest shareholder with a
34.62% stake (as of July 2014). As of 30 September 2014, it employed more than 8,900 people, based
throughout Europe but mainly in the UK.
EasyJet has seen rapid expansion since its establishment in 1995, having grown through a combination
of acquisitions and base openings fuelled by consumer demand for low-cost air travel. The airline, along
with associate company EasyJet Switzerland, operates more than 200 aircraft, mostly Airbus A319. It
has 24 bases across Europe, the largest beingGatwick. In 2014, EasyJet carried more than 65 million
passengersand is the second-largest low-cost carrier in Europe, behind Ryanair. EasyJet was featured in
the television series Airline broadcast on ITV which followed the airline's operations at London Luton
and later at other bases.
History
Origins
The airline was established in 1995 as part of the EasyGroup conglomerate. It was launched by Greek
Cypriot businessman Sir Stelios Haji-Ioannou with two wet leased Boeing 737-200 aircraft, initially
operating two routes: London Luton to Glasgow and Edinburgh. In April 1996, the first wholly owned
aircraft was delivered to EasyJet, enabling its first international route, to Amsterdam. Until October
1997, the aircraft were operated by GB Airways and subsequently by Air Foyle as EasyJet had not yet
received its Air Operator's Certificate.
EasyJet was floated on the London Stock Exchange on 5 November 2000. In October 2004 the FL
Group, owner of the airlines Icelandair and Sterling, purchased an 8.4% stake in EasyJet.[16] Over the
course of 2005, FL increased its share in the company periodically to 16.9%, fuelling speculation that it
would mount a takeover bid for the UK carrier. However, in April 2006 the threat of takeover receded as
FL sold its stake for €325 million, securing a profit of €140m on its investment. In November 2005,
Ray Webster stood down after 10 years as EasyJet's chief executive officer (CEO) and was replaced by
former RAC plc CEO, Andrew Harrison.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-89-320.jpg)
![90
Expansion and acquisitions
EasyJet has expanded greatly since its establishment, driven by high demand from both the United
Kingdom and continental Europe. As part of this, EasyJet has also purchased several rival airlines,
including GB Airways.
Go Fly Boeing 737-300 in 2004
In March 1998, EasyJet purchased a 40% stake in Swiss charter airline TEA Basle for three
million Swiss Francs. The airline was renamedEasyJet Switzerland and commenced franchise services
on 1 April 1999, having relocated its headquarters to Geneva International Airport. This was EasyJet's
first new base outside the United Kingdom. In 2002, EasyJet purchased rival airline, London Stansted-
based Go for £374 million. EasyJet inherited three new bases from Go, at Bristol Airport, East Midlands
Airport and London Stansted Airport. The acquisition of Go almost doubled the number of Boeing 737-
300 aircraft in the EasyJet fleet.
In 2002, EasyJet opened its base at Gatwick Airport, and between 2003 and 2007 opened bases in
Germany, France, Italy and Spain, establishing a sizeable presence in continental Europe. In 2007,
EasyJet claimed to be operating more flights per day than any other European airline.On 25 October
2007 EasyJet purchased the entire share capital of GB Airways from the Bland Group. The deal was
worth £103.5 million and used by the airline to expand operations at Gatwick, and also to establish a
base at Manchester Airport.
In June 2011, EasyJet opened of its 11th UK base at London Southend Airport, offering flights
to Alicante, Amsterdam, Barcelona, Belfast International, Faro, Malaga, Jersey,Palma de
Majorca and Ibiza.
In March 2013, EasyJet and its CFO Chris Kennedy celebrated the airline's promotion to the FTSE
100 and launched its 100th route from Gatwick Airport, offering flights directly from London to
Moscow.In Spring 2014, EasyJet opened its 23rd European base, in Hamburg, with 3 A319 aircraft, and
15 additional routes added to the 6 currently served from the airport. Additionally, it opened its smallest
base in Naples. Current plans indicate that only two aircraft will be based there and just 20 routes
served.
Corporate affairs
Business strategy
EasyJet, like Ryanair, borrows a business model popularized by Southwest Airlines. Both airlines have
adapted this model for the European market through further cost-cutting measures such as not selling
connecting flights or providing complimentary snacks on board. The key points of this business model
are high aircraft utilization, quick turnaround times, charging for extras (such as priority boarding, hold
baggage and food) and keeping operating costs low.[30] One main difference EasyJet and Ryanair have
from Southwest is they both fly a young fleet of aircraft. Southwest has an average fleet age of 11.9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-90-320.jpg)
![91
years whereas Ryanair's and EasyJet's average fleet ages are just a little over five years each.Initially,
EasyJet's employment strategy was to maintain control with minimal union involvement. In recent years,
the airline has adopted a more committed approach with a strategy in place to accommodate
unions.While the two airlines share a common business charter and concept, EasyJet's strategy differs
from Ryanair's in several areas. The most noticeable is that EasyJet flies mainly to the primary airports
in the cities that it serves, for the convenience of passengers, while Ryanair often chooses secondary
airports to further reduce costs. For example, in servicing Paris, EasyJet flies to Charles de Gaulle
Airport and Orly Airport, the primary airports, while Ryanair flies to the smaller Beauvais-Tillé Airport,
53 miles and a 75-minute bus journey from Paris. To service Rome, all EasyJet services are out
of Leonardo da Vinci–Fiumicino Airport, while the majority of Ryanair's services to Rome
use Ciampino–G. B. Pastine International Airport. EasyJet also focuses on attracting business
passengers by offering convenient services such as the "Flexi fare" which allows free of charge changes
to the flight within a window, speedy boarding and a checked in bag.
Originally, much like Southwest, EasyJet did not allocate seats – passengers took any available seats,
with the option to pay for "Speedy Boarding" and be first onto the aircraft. However, since 2012, all
passengers are allocated numbered seats before boarding commences, as it was found that this does not
slow down boarding times and could earn more revenue than Speedy Boarding. Passengers can pay an
additional fee for certain seats such as the front few rows and overwing seats (which have extra
legroom).
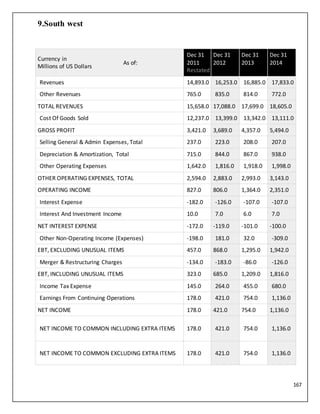
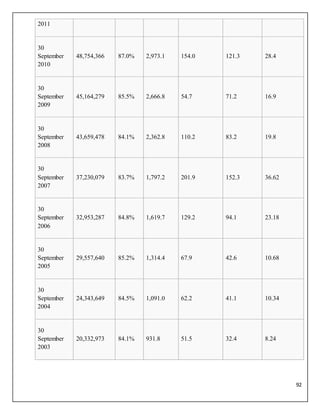
Financial performance
EasyJet financial performance
Year ended
Passengers
flown[nb 1]
Load
factor
Turnover
(£m)
Profit/loss
before tax
(£m)
Net
profit/loss
(£m)
Basic EPS (p)
30
September
2014
64,769,065 90.6% 4,527 581 450 114.5
30
September
2013
60,757,809 89.3% 4,258 478 398 101.3
30
September
2012
58,399,840 88.7% 3,854 317 255 62.5
30
September
54,509,271 87.3% 3,452 248 225 52.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-91-320.jpg)
![93
30
September
2002
11,350,350 84.8% 551.8 71.6 49.0 14.61
30
September
2001
7,115,147 83.03% 356.9 40.1 37.9 15.2
30
September
2000
5,600,000 263.7 22.1 22.1 11.9
Head office
Hangar 89 at London Luton Airport, EasyJet head office
EasyJet's head office is Hangar 89 (H89), a building located on the grounds of London Luton
Airport in Luton, Bedfordshire; the hangar, a former Britannia Airways/TUI facility, is located 150
metres (490 ft) from EasyLand, the previous headquarters of EasyJet. Hangar 89, built in 1974, has
30,000 square feet (2,800 m2) of office space and can house three aircraft the size of an Airbus A319 at
one time. When EasyJet received H89, it had a 1970s-style office setup. EasyJet modernised the
building and painted it orange.
Marketing
EasyJet's early marketing strategy was based on "making flying as affordable as a pair of jeans" and
urged travellers to "cut out the travel agent". Its early advertising consisted of little more than the
airline's telephone booking number painted in bright orange on the side of its aircraft.
The Airline TV series created by LWT and filmed between 1999 and 2007 made EasyJet a household
name in the United Kingdom. The series, while not always portraying EasyJet in a positive light, did
much to promote the airline during this time.[35] EasyJet has used a number of slogans since its
establishment including "The Web's Favourite Airline" (a reflection on the airline's cheeky and cheerful
image), "Come on, lets fly" and "To Fly, To Save" (a cheeky take on British Airways' slogan "To Fly,
To Serve"). This was then followed by "(something) by EasyJet" with "Europe by EasyJet" and
"business by EasyJet" being the most widely used.
It currently uses the slogan "This is Generation easyJet".](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-93-320.jpg)

![95
EasyJet has 19 European 'bases'. Despite EasyJet being a British airline and having a significant
presence there, it has a significant presence in France, Germany, Italy, Spain and many other European
countries. The United Kingdom is its biggest market, containing the airlines largest base and nine others
as well as a total of six other non-base airports. Its three largest British bases in order of size are
London's Gatwick and Luton airports followed by Bristol. Stansted was once the second largest base but
has seen significant reduction in recent years with flights being moved to Gatwick and the newest UK
base, Southend which is in the same catchment area as Stansted.
EasyJet's largest competitor is Ryanair, which unlike EasyJet has a focus on smaller or secondary
airports and in recent years, has started targeting holiday makers. EasyJet focuses heavily on business
passengers but operates a greater variety of holiday destinations than Ryanair. However, EasyJet has a
very low presence at holiday destinations like Greece with limited frequencies and only a small number
of airports to fly from. Ryanair's is much higher, especially at the Canary Islands and some Greek
Islands, in particular Kos and Rhodes. Ryanair often refers to EasyJet as a high fares airline but EasyJet
often criticises Ryanair for its choice of airports.
Codeshare agreements
EasyJet entered a commercial agreement with Transaero Airlines to set up a codeshare
agreement[47][48] whereby Transaero acquire the right to sell a certain number of seats on EasyJet LGW-
DME route. The agreement was signed by Olga Pleshakova, CEO Transaero Airlines, and Chris
Kennedy, Chief Financial Officer for EasyJet. According to the agreement, Transaero Airlines will
distribute a proportion of seats on EasyJet flights on the Moscow (Domodedovo) – London (Gatwick)
route. This agreement applies to the flights since 27 October 2013 that are operated under the following
codes: from London UN7401/U28401 and UN7403/U28403 as well as from Moscow UN7402/U28402
and UN7404/U28404. This is the first codeshare agreement for EasyJet. Low cost airlines usually do not
rely on codeshare agreements, as they operate a point-point route network.
Fleet
Overview
EasyJet Airbus A319](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-95-320.jpg)












![111
NCAER, theNational Council of Applied Economic Research in New Delhi,India's first independent
economic policy institute established in 1956. In 1968, he founded Tata Consultancy Services as Tata
Computer Centre. In 1979, Tata Steel instituted a new practice: a worker being deemed to be "at work"
from the moment he leaves home for work till he returns home from work. This made the company
financially liable to the worker for any mishap on the way to and from work. In 1987, he founded Titan
Industries. Jamshedpur was also selected as a UN Global Compact City because of the quality of life,
conditions of sanitation, roads and welfare that were offered by Tata Steel.
Awards and honors
JRD Tata received a number of awards. He was conferred the honorary rank of Group Captain by
the Indian Air Force in 1948, was promoted to the Air Commodore rank (equivalent to Brigadier in
army), and was further promoted on 1 April 1974 to the Air Vice Marshal rank. Several international
awards for aviation were given to him – The Tony Jannus Award in March 1979, the Gold Air Medal of
the Federation Aeronautique International in 1995, the Edward Warner Award of the International Civil
Aviation Organization, Canada in 1986 and the Daniel Guggenheim Award in 1988.[12] He received
the Padma Vibhushan in 1955 . The French Legion of Honor was bestowed on him in 1983. In 1992,
because of his selfless humanitarian endeavors, JRD Tata was awarded India's highest civilian honor,
the Bharat Ratna. In the same year, JRD Tata was also bestowed with the United Nations Population
Award for his crusading endeavors towards initiating and successfully implementing the family planning
movement in India,much before it became an official government policy. In his memory Government of
Maharashtra termed its first double decker bridge as Bharatratne JRD Tata Over-bridge at Kasarwadi
Phata, Pune.
Death
JRD Tata died in Geneva, Switzerland on 29 November 1993 at the age of 89 of a kidney Infection. On
his death, the Indian Parliament was adjourned in his memory – an honor not usually given to persons
who are not members of parliament. He is buried at the Pere Lachaise Cemetery in Paris.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-111-320.jpg)






![120
Fernandes' biggest achievement was to open up countries within the region to new budget carriers,
which previously did not have open-skies agreements. As a result of Fernandes' lobbying in mid-2003,
Dr Mahathir brought up the idea with leaders from neighboring countries. Those nations subsequently
granted landing rights to AirAsia and other discount carriers.
In Thailand and Indonesia, AirAsia holds a minority stake in the respective local companies. Thai
AirAsia, a joint venture with Shin Corporation, Thailand’s largest telecommunication conglomerate,
took to the skies in Feb 2004 and has to date carried over 1 million passengers in its first year of
operations. PT Awair, re-launched as a low fare airline on 8 December 2004 and subsequently
renamed Indonesia AirAsia, presently serves 5 domestic destinations in Indonesia.
Other ventures
In 2007, Fernandes started a hotel chain, Tune Hotels, based on the no frills concept. It has properties in
Britain, Australia and the Far East.
As of 2013, Fernandes is also involved in a reality TV series: The Apprentice Asia is an Asian reality
game show in which a group of aspiring young businessmen and women compete for the chance to work
with Fernandes, who also serves as the host of the show.
In March 2012, Tony Fernandes served on the International Advisory Board of Global March to
Jerusalem, which aims to "mobilize the international community in solidarity with Palestinians and to
protect Jerusalem." A Joint Statement was issued, signed by the various members of the Board,
including Fernandes.
Caterham Group
Fernandes is the founder of the Caterham F1 Formula One team, which began racing in 2010 as Lotus
Racing and raced in 2011 as Team Lotus. On 2 July 2014, Caterham F1 was sold to a Swiss and Middle
Eastern consortium.
On 16 December 2009, Fernandes accepted a "challenge" from Richard Branson, a fellow airline boss
and the owner of Lotus' fellow F1 newcomers Virgin Racing. The losing team's boss would work on the
winner's airline for a day dressed as a stewardess. Fernandes joked "The sexier the better. Our
passengers will be delighted to be served by a Knight of the Realm, but knowing Richard, the real
challenge will be to prevent him from asking our guests 'coffee, tea or me?' That would be scary." In
addition, the team produced a poster depicting Branson in an Air Asia uniform. However, the date of the
flight was delayed several times: first because of Branson breaking his leg, then because of the royal
wedding, finally because of a fire at the Necker Island. On 19 December 2012, Fernandes announced
that Branson would honor his bet in May 2013. Branson ultimately honoured the bet on 13 May 2013.
Caterham Racing, also created by Fernandes, competes in the GP2 Series.
On 27 April 2011, Fernandes announced that his company had purchased Caterham Cars.
EQ8 is a natural energy drink and the first FMCG product from Fernandes and his business partner
Kamarudin Meranun. EQ8 is also the Official Drink of Caterham F1.
Football
Fernandes is a fan of English club West Ham United and was involved in talks regarding a potential
takeover of the club back in May 2011, at which stage it looked as if he was going to acquire a 51 per
cent stake in the club. Former West Ham chairman Andrew Bernhardt even flew to Kuala Lumpur to try
and finalize the deal, but the two parties failed to agree on the price.[25] It was just one month later when
Fernandez made another offer to buy 51 per cent of the club, although co-owners David Sullivan and
David Gold rejected his bid. Sullivan told the London Evening Standard: "He wanted 51% of the club
for two bob." Sullivan's comments started a war of words on Twitter. "It was a good offer with good](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-120-320.jpg)


![123
Ryanair
Michael O'Leary (businessman)
Michael O'Leary
Born Michael Kevin O'Leary[1]
20 March 1961 (age 53)
Mullingar, County Westmeath, Ireland
Residence Delvin, County Westmeath
Nationality Irish
Education Clongowes Wood College
Alma mater Trinity College, Dublin
Occupation Businessman
Known for Chief executive officer of Ryanair
Spouse(s) Anita Farrell
Children 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-123-320.jpg)

![125
been that emissions 'per passenger' had been cut by half. O'Leary has been reported to have
impersonated a journalist in an attempt to find information passed on to a newspaper following a safety
incident on a Ryanair flight. On occasion he has apologised for personal attacks under threat of legal
action. He has been criticized by a judge for lying, who said he was lucky not to be found guilty of
contempt of court.In a press conference discussing Ryanair's planned intercontinental
service RyanAtlantic, O'Leary jokingly described the airline's planned business class travel experience
as featuring "whores and rum". In 2002 he said that his company is against any long-haul transatlantic
services, stating that:
The low-cost model only really works for short-haul flights If we started flying farther afield, we'd have
to do something stupid like introducing what I call a 'rich class' to make it pay.
However more than a decade later, in 2013 he said, while at the Paris Air Show, that he wanted to sell
cheap flights from the U.S. to Europe for as low as 10 euros ($13) or $10, if conditions were right. He
said that he needed a fleet of at least 30 twin-aisle aircraft and access to ports (e.g. major U.S. and
European cities, in the airline industry there are so called slots or sometimes gates, often regulated by
law, and without obtaining them it is impossible to have regular service to airports). Despite his claims
in 2002, there were so called budget airliners in the past – for example Laker Airways flights from
London to New York in the late 1970s or long-hauls at budget-fares on other continents like AirAsiaX
in Malaysia and the Australian Jetstar Group.
Reacting to the decision to close European airspace in April 2010 over worries about the ash plume
from an erupting Icelandic volcano he said "there was no ash cloud. It was mythical. It's become evident
the airspace closure was completely unnecessary." Scientists later concluded that serious structural
damage to aircraft could have occurred if passenger planes had continued to fly.[34]
In May 2014 O'Leary was highly critical of a 24-hour strike by Aer Lingus cabin crew, staged on 30
May 2014. Aer Lingus, whose biggest shareholder is O'Leary's company Ryanair, had to cancel 200
flights and disrupt travel plans for 200,000 people. O'Leary accused Aer Lingus of "mismanagement" of
its employee relations, called for the sacking of a board member, and said the striking employees should
be punished by having their discount travel incentives withdrawn for a year.§Registration of private car
as taxi
Main article: O'Leary Cabs
Michael O'Leary's personalMercedes-Benz S500, operated byO'Leary Cabs and complete with "for hire"
roof bar
In 2004 he purchased a taxi plate for his Mercedes-Benz S-Class, to enable it to be classified as a taxi so
that he could legally make use of Dublin's bus lanes to speed up his car journeys around the city. A press
report suggested that since he was stopped driving his own taxi, he has employed a driver with full PSV
license. In 2005 the Irish transport minister expressed concern at this abuse by O'Leary and others.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-125-320.jpg)



![129
Colleen Barrett
Receiving the Tony Jannus Award in 2007
President Emerita of Southwest Airlines
In office
2001–2008
Personal details
Born
September 14, 1944
Bellows Falls, Vermont
Spouse(s) Divorced
Colleen Barrett (born 14 September 1944, Bellows Falls, Vermont) is the President Emerita and
Corporate Secretary of Southwest Airlines. She joined Southwest in 1978, having previously worked for
several years as founder Herb Kelleher's executive assistant at his law firm.[1] She has served as](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-129-320.jpg)
![130
Secretary of the Corporation, as Vice President Administration from 1986 through 1990, and Executive
Vice President from 1990 through 2001. Barrett has been consistently named and recognized as one of
the most powerful American businesswomen. In October, 2007, she received the Tony Jannus Award for
distinguished achievement in commercial air transportation.
Barrett stepped down as President and Corporate Secretary of Southwest, effective July 16, 2008, but
will remain an employee of the corporation through July 2013.
Education
Becker Junior College, 1964 - Worcester, Massachusetts
Herbert "Herb" David Kelleher (born March 12, 1931) is the co-founder, Chairman Emeritus, and
former CEO of Southwest Airlines (based in the United States).
Early life and career
Kelleher was born in Camden, New Jersey on March 12, 1931 and raised in Audubon, New Jersey,
where he graduated from Haddon Heights High School. He has a bachelor's degree from Wesleyan
University where he was an Olin Scholar and where his major was English and his minor Philosophy,
and a Juris Doctor from New York University where he was a Root-Tilden Scholar.[2] At Wesleyan he
was a member of Delta Kappa Epsilon fraternity. He is married to the former Joan Negley and they have
four children.
Career
The Kellehers moved to Texas intending to start a law firm or a business. Kelleher and one of his law
clients, Texas businessman Rollin King, created the concept that later became Southwest Airlines on a
cocktail napkin in a San Antonio, Texas restaurant. From its birth in 1971 — after overcoming a year's
worth of legal challenges from competitors who tried to keep it grounded — Southwest succeeded by a
strategy of offering low fares to its passengers, eliminating unnecessary services, and avoiding the "hub-
and-spoke" scheduling system used by other airlines in favor of building traffic in such secondary
airports as Albany, Chicago-Midway (instead of Chicago-O'Hare) and Orange County.
During his tenure as CEO of Southwest, Kelleher's colorful personality created a corporate culture
which made Southwest employees well known for taking themselves lightly—often singing in-flight
announcements to the tune of popular theme songs—but their jobs seriously. How different the company
culture is can be seen in an arm-wrestling event in March 1992. Shortly after Southwest started using the
"Just Plane Smart" motto, Stevens Aviation, who had been using "Plane Smart" for their motto,
threatened a trademark lawsuit, which was resolved between Herb Kelleher and Stevens Aviation CEO
Kurt Herwald in an arm-wrestling match, now known as "Malice in Dallas". Southwest has never had an
in-flight fatality. Southwest is consistently named among the top five Most Admired Corporations in
America in Fortune magazine's annual poll. Fortune has also called him perhaps the best CEO in
America. Kelleher was inducted into the Junior Achievement U.S. Business Hall of Fame in 2004.
On July 19, 2007, Southwest Airlines announced that Kelleher would step down from the role of
Chairman and resign from the board of directors in May 2008, though he would remain a full-time
employee for another five years.[5] Kelleher ultimately stepped down as chairman on May 21, 2008.
Immediately following, Southwest Airlines named current CEO, Gary C. Kelly the new Chairman of the
Board of Directors.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-130-320.jpg)







![138
male passenger. The crew was able to subdue the hijacker, who was handed over to Italian police
officers after landing. Flight AI 105 was a scheduled service from Bombay-Santacruz Airport
(BOM), India to New York-JFK (JFK), USA with en route stops at Beirut, Rome and Paris.
On 1 January 1978 Air India Flight 855 a Boeing 747-237B (name Emperor Ashoka and registered
VT-EBD) crashed into the Arabian Sea after takeoff from Sahar International Airport
(now Chhatrapati Shivaji International Airport) in Mumbai, killing all on board (213 persons; 190
passengers, 23 crew).
1980s
On 21 June 1982 Air India Flight 403 a Boeing 707-420 (named Gouri Shankar and registered VT-
DJJ) carrying 99 passengers and 12 crew from Sultan Abdul Aziz Shah Airport, Malaysia
via Madras (now Chennai) crashed at Sahar International Airport after a heavy landing during a
rainstorm. The fuselage exploded after starting a late go-around. Two crew members and 15
passengers were killed.
On 23 June 1985 Air India Flight 182 a Boeing 747-237B (named Emperor Kanishka and registered
VT-EFO) was blown up in mid-air, mid-flight by a suitcase-bomb planted by Babbar Khalsa
Terrorists allegedly as revenge for the Indian Government's operation on the Golden Temple on June
1984. The flight was on the first leg on its Montreal-London-Delhi-Bombay flight when it exploded
off the coast of Cork, Ireland. The plane crashed into the Atlantic Ocean. All 307 passengers and 22
crew on board died.[115] After this incident Air India suspended all services to Montreal.
1990s
On 7 May 1990 Air India Flight 132 a Boeing 747-237B (named Emperor Vikramaditya and
registered VT-EBO) flying on the London-Delhi-Bombay route and carrying 215 people (195
passengers and 20 crew) touched down at Delhi's Indira Gandhi International Airport after a flight
from London's Heathrow Airport. On application of reverse thrust, a failure of the no. 1 engine
pylon to wing attachment caused this engine to tilt nose down. Hot exhaustion gases caused a fire on
the left wing. There were no fatalities but the aircraft was damaged beyond repair and written off.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-138-320.jpg)
![139
5.Issues of jet airways
Incidents and accidents
1 July 2007, Jet Airways Flight 3307, an ATR 72-212A (registered VT-JCE) which was flying
on the Bhopal - Indore route was involved in an incident which was caused by a storm. There
were no fatalities amongst the 45 passengers and four crew onboard; the aircraft suffered
damage beyond repair.
Controversies
Issues with US authorities
It took Jet Airways more than two years to get the necessary clearances from US authorities to fly to
the United States. The US State Department gave the go-ahead on 15 November 2006. Jet was
initially expected to begin service to Newark via Brussels in June 2005 but a problem arose in
March 2005, when the airline submitted an application to the US Department of Transportation.
Nancy Heckerman, CEO of US company Jet Airways Inc. based in Bethesda, Maryland, opposed
the application in letters to the Transportation Department alleging trademark infringement. Though
the litigation is still unresolved, the Department of Transportation concluded it was not a reason to
prevent Jet from flying to the U.S.
Jet Airways was originally set up as a subsidiary of Tailwinds, an Isle of Man-based holding
company designed as a tax shelter, whose sole shareholder was Naresh Goyal, the airline's non-
resident Indian (NRI) founder and chairman. Initially, both Gulf Air and Kuwait Airways had
acquired minority stakes in the airline. However, the Government of India subsequently decreed that
foreign airlines would not be allowed to own any shares in any Indian airline (though other foreign
entities and individuals could still acquire or own minority stakes in Indian carriers.
As a result of this ruling, Gulf Air and Kuwait Airways sold their stakes to Naresh Goyal, who then
became the airline's sole shareholder. Jet Airways floated a minority stake of around 20% on
the Bombay Stock Exchange in 2005 to enable it to reduce the debt that had been accumulated since
its inception as well as to fund its fleet expansion programmer, including the acquisition of a fleet of
new Airbus A330 and Boeing 777 long-haul wide-bodied jets to operate new long-range services,
primarily to Europe and North America. This resulted in a reduction of Tailwind's stake in the
airline to just below 80%. According to the company's articles of association, the bulk of Naresh
Goyal's shares in Tailwinds are held on behalf of several other individuals who all seem to be
resident citizens of India. While Indian government officials have been satisfied that these
arrangements do not compromise Jet Airways' status as an Indian-owned airline that is effectively
controlled by Indian citizens, they were viewed as "problematic" by the American authorities.
British contractor controversy
Another controversy arose when Asmin Tariq, a contractor who was working for the airline as a
security agent at Heathrow Airport (and was subsequently made a member of staff when the airline
decided to bring its London-based security operation in-house), became implicated in the foiled
terror plot of 10 August 2006 to blow up over several weeks up to ten transatlantic airliners
belonging to three different US airlines in mid-air on their way from London to New York, Newark
and Los Angeles. Asmin Tariq had been arrested along with the other 20+ suspects and is now] in
British police custody. In addition, he has been suspended from duty by Jet Airways. When asked
how such a person could have been employed by the airline in a position demanding extreme
confidence and trust, Jet Airways defended its conduct by saying that the person was a UK passport
holder who had passed the stringent security requirements of BAA, Heathrow's owner and operator.
They also said that under UK employment legislation, the company was obliged to offer any](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/air-150327222557-conversion-gate01/85/Aviation-Industry-analysis-139-320.jpg)