The document provides information on elemental cost analysis, including:
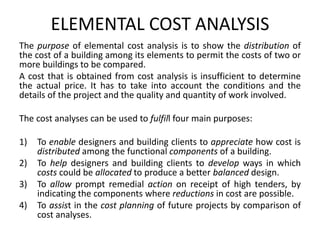
1) It explains the purposes of elemental cost analysis and the principles of preparing an analysis.
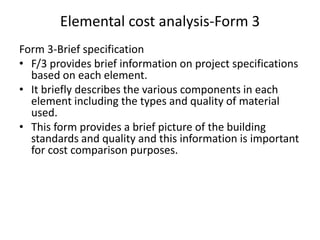
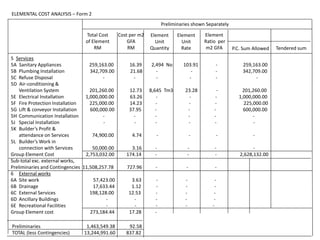
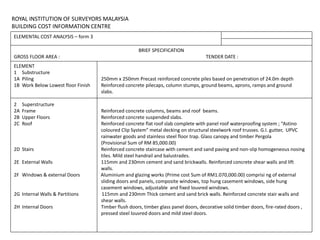
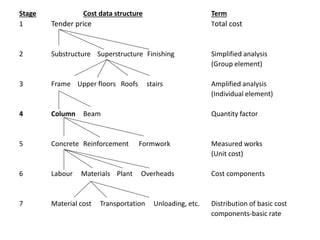
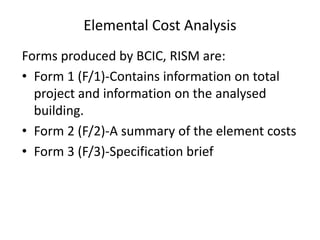
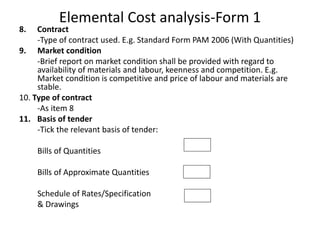
2) It describes the forms used in an analysis, including Form 1 which contains project and building information.
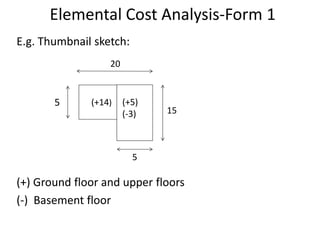
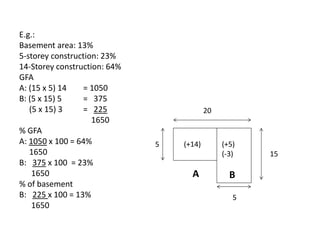
3) It details the specific information required in Form 1, such as building description, areas, storey heights, and ratios. Providing accurate cost data in the defined structure allows for comparison across projects.





























![Elemental cost analysis-Form 2
Element unit quantity (EUQ)
9. Internal walls & partitions– Area of internal walls & partitions (less
openings) (m2)
10. Internal doors- Area of internal doors measured over frames (m2)
11. Internal wall finishes- Total area of wall finishes (m2). If not self
finished, fairface works, etc. total area shall be less than [sum of
item 7 + (2 x item 9)] above.
12. Internal floor finishes-Total are of floor finishes. Check whether all
floors have finishes. If so the area shall be less than GFA.
13. Internal ceiling finishes-area of ceiling finishes. Area shall be less
that GFA
14. External finishes-No EUQ
15. Fittings and finishing-No EUQ
16. Sanitary appliances-No of draw-off points. (no)
17. Plumbing Installation-No EUQ
18. Refuse disposal-No EQU](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecaworkshop-170630114719/85/ECA-Workshop-Brief-39-320.jpg)