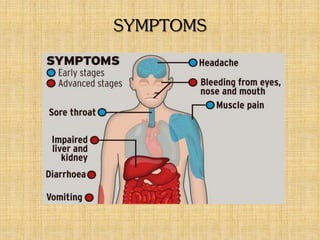
Ebola hemorrhagic fever, named after a river in the Congo, is a highly fatal disease with a mortality rate up to 90%, affecting humans and nonhuman primates. It is caused by the Ebola virus, which has five distinct sub-species and is of zoonotic origin, primarily found in Africa. Symptoms include a wide range of physical issues, progressing to severe manifestations like bleeding and shock, with death usually resulting from shock rather than blood loss.