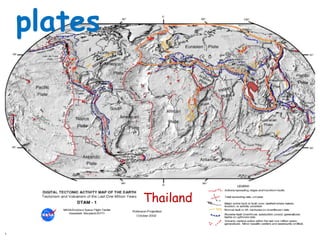
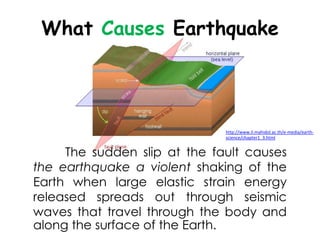
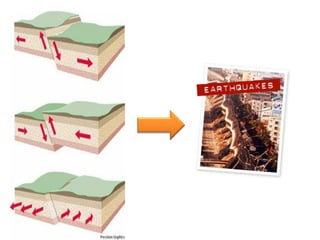
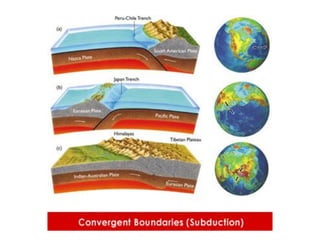
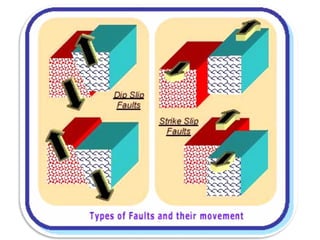
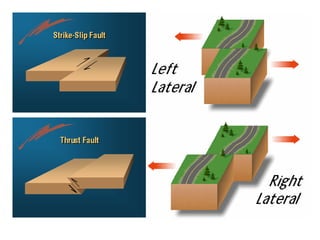
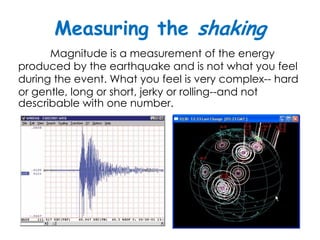
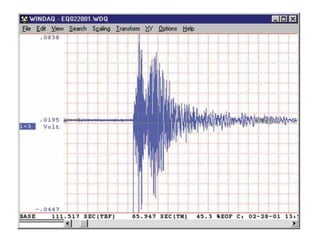
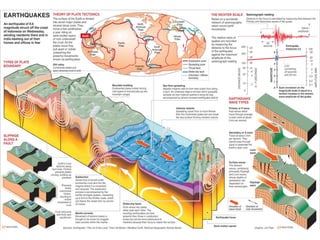
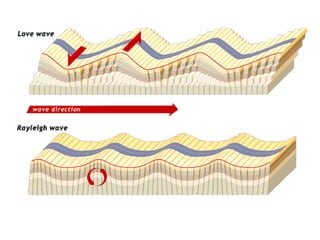
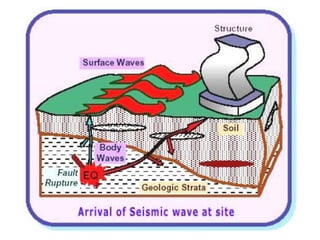
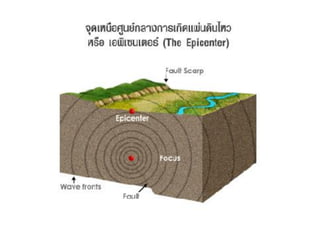
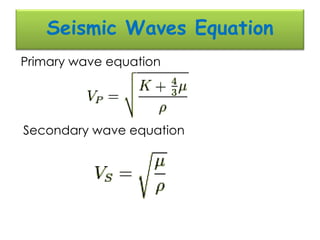
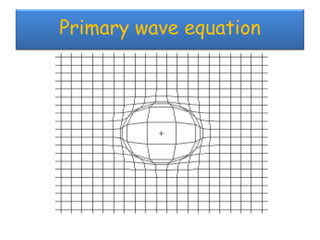
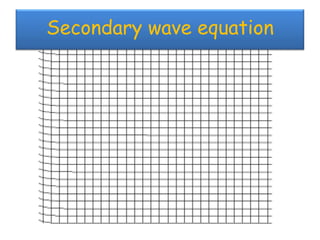
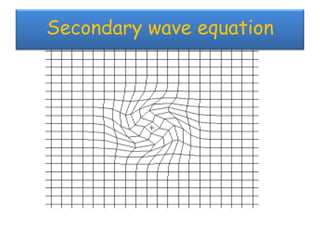
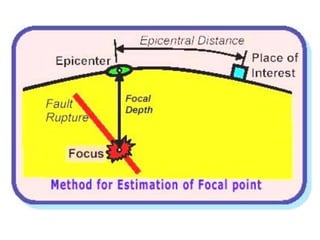
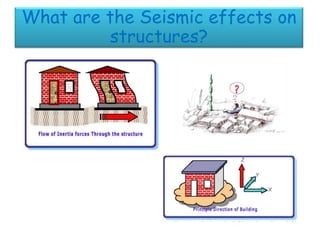
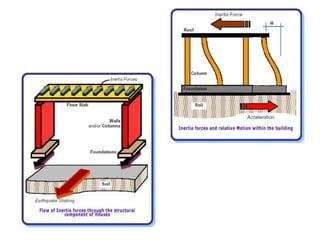
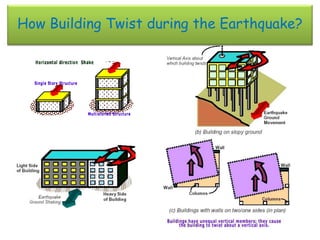
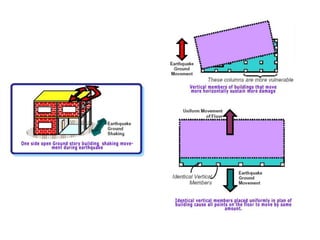
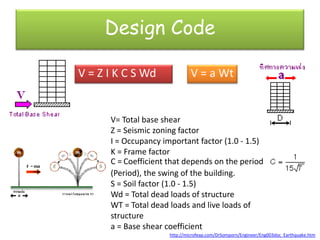
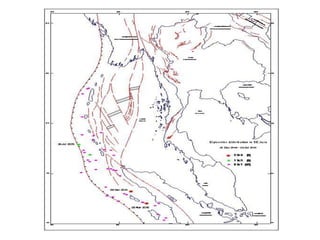
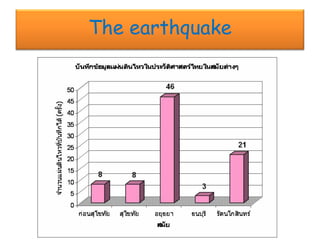
The document discusses earthquakes, including what causes them, how they are measured, their effects, and statistics on major earthquakes around the world. Specifically, it defines an earthquake as rapid shaking caused by the sudden release of energy along fault lines. It describes the movement of tectonic plates and how this results in earthquakes. Key points covered include earthquake magnitude scales, the different types of seismic waves generated, and data on some of the largest earthquakes by magnitude and their impacts.