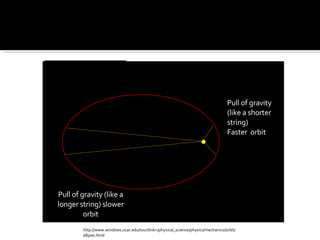
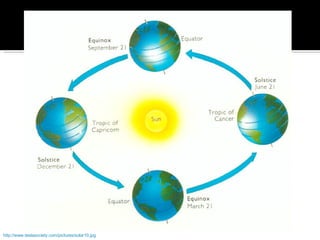
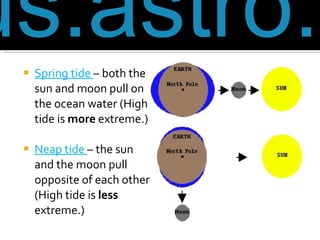
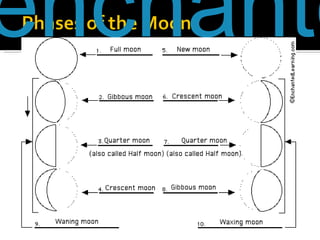
The document discusses planetary motion, eclipses, tides, and phases of the moon. It explains that planets orbit stars in ellipses rather than perfect circles, and that closer planets move faster due to gravity. It describes solar and lunar eclipses, noting that solar eclipses occur when the moon passes between Earth and the sun, while lunar eclipses occur when Earth passes between the sun and moon. It also discusses how the moon's gravity causes ocean tides, with high tide occurring when the moon is overhead or opposite the tide location. Finally, it outlines the phases of the moon as it revolves around Earth.