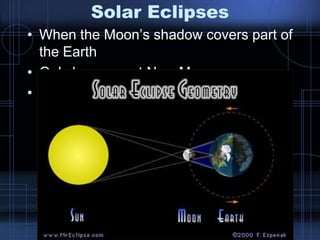
The phases of the moon are caused by the changing positions of the sun, Earth, and moon relative to one another. A new moon occurs when the moon is between the Earth and sun so its night side faces Earth. A full moon happens when the moon is on the opposite side of Earth from the sun, so its full day side faces Earth. Eclipses occur when the sun, Earth, and moon align so that one passes in front of the other, casting a shadow. Lunar eclipses happen during a full moon when Earth blocks the sun's light from reaching the moon. Solar eclipses occur during a new moon when the moon passes between the sun and Earth, casting its shadow on Earth. The moon