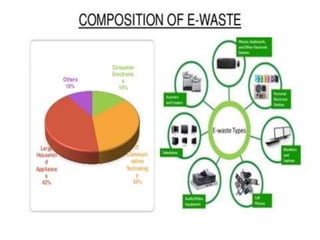
E-waste, which includes discarded electronic devices, is a rapidly growing global problem, producing around 50 million tons annually, with only 15-20% being recycled. Environmental hazards include toxic substances like mercury and lead, which pose serious health risks and environmental damage. Effective management strategies involve waste minimization techniques, inventory control, and sustainable product design to mitigate the impact of e-waste.