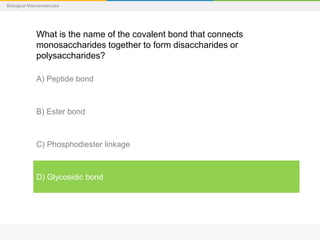
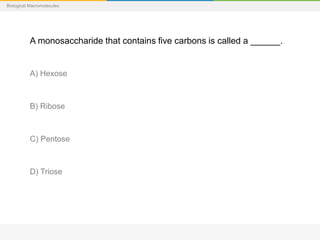
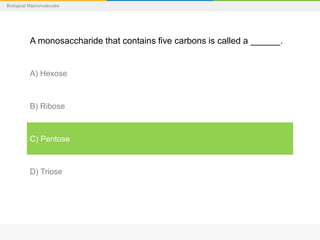
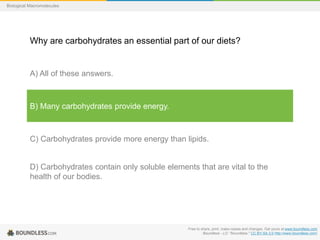
This document provides a series of questions and multiple choice answers about biological macromolecules. It begins with introductory slides on macromolecules and then provides 20 questions testing knowledge of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. For each question, the reader is instructed to consider the answer before seeing the correct response provided on the next slide.