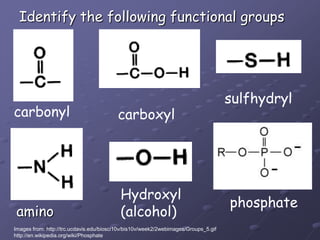
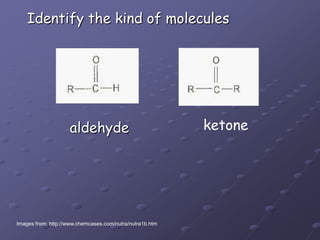
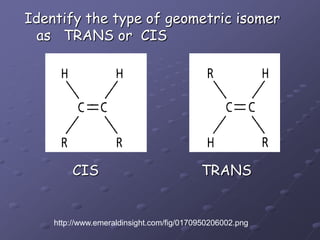
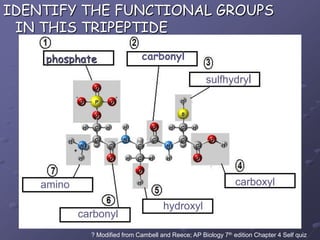
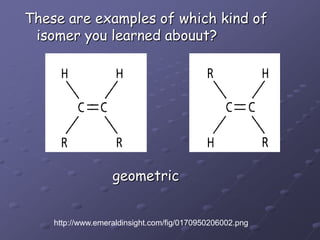
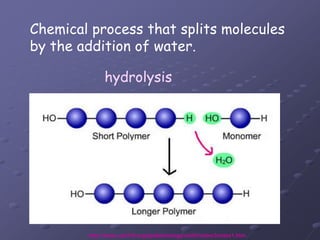
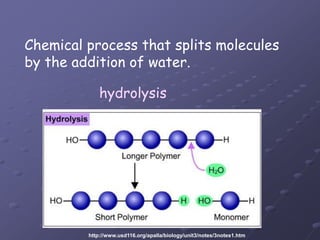
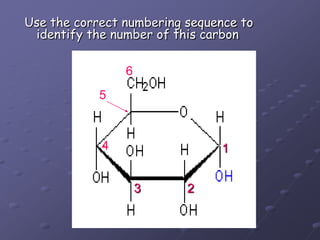
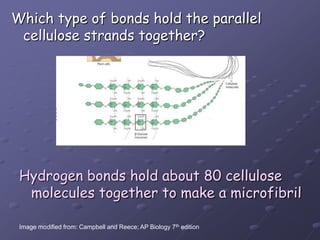
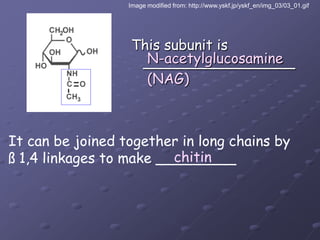
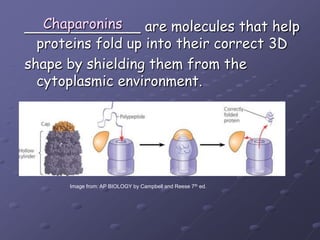
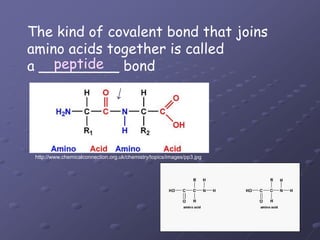
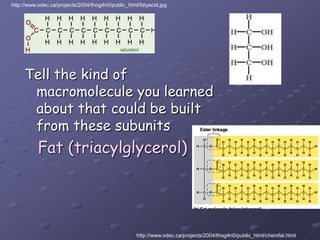
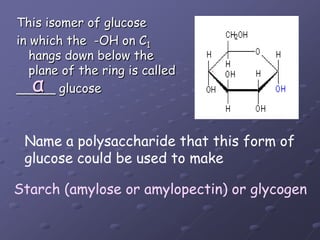
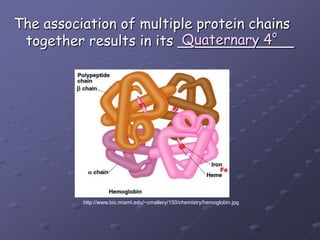
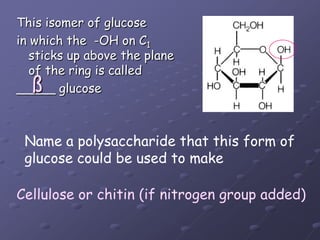
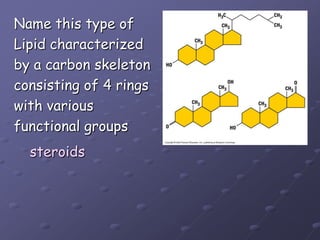
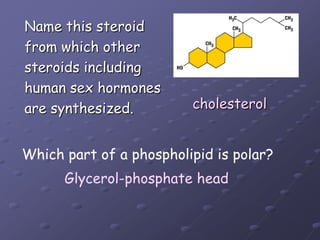
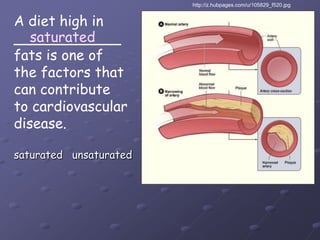
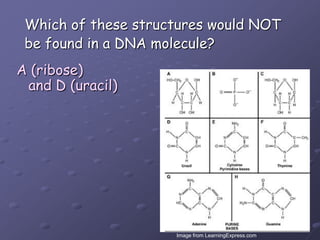
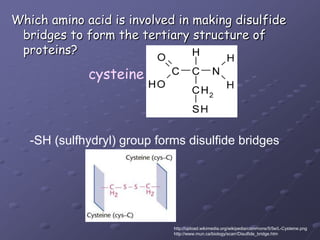
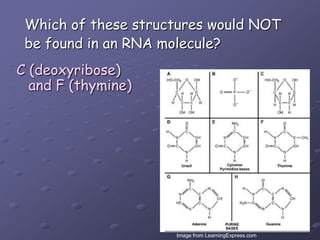
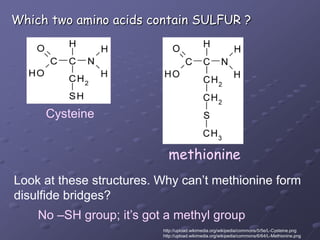
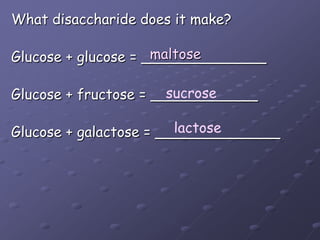Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids are the four main classes of biological macromolecules. The document identifies functional groups, types of isomers, carbohydrate monomers and polymers. It also discusses lipid structure including fatty acids, triglycerides and phospholipids. Finally, it covers protein structure from primary to quaternary levels organized by bonding interactions between amino acid subunits.