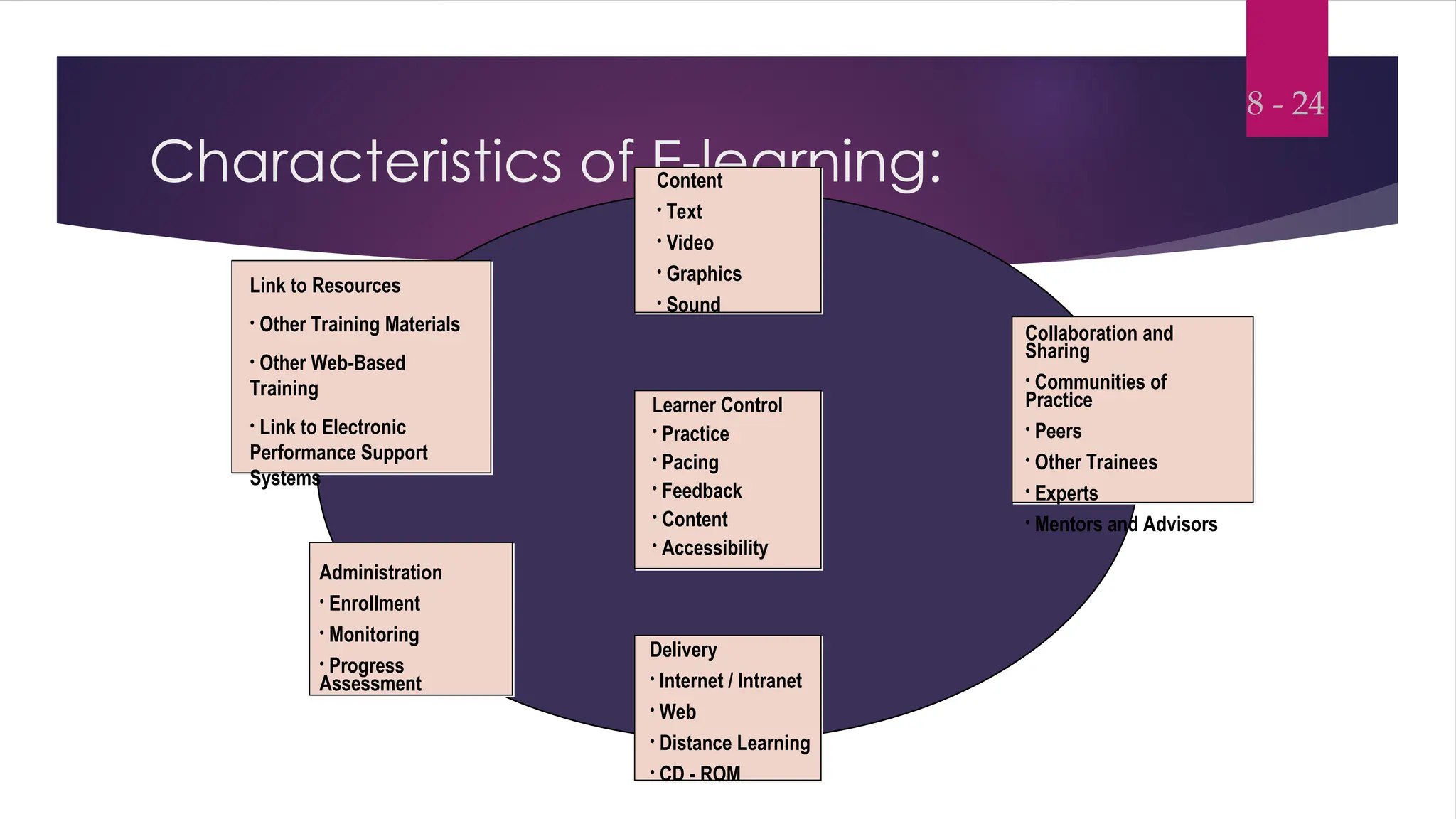
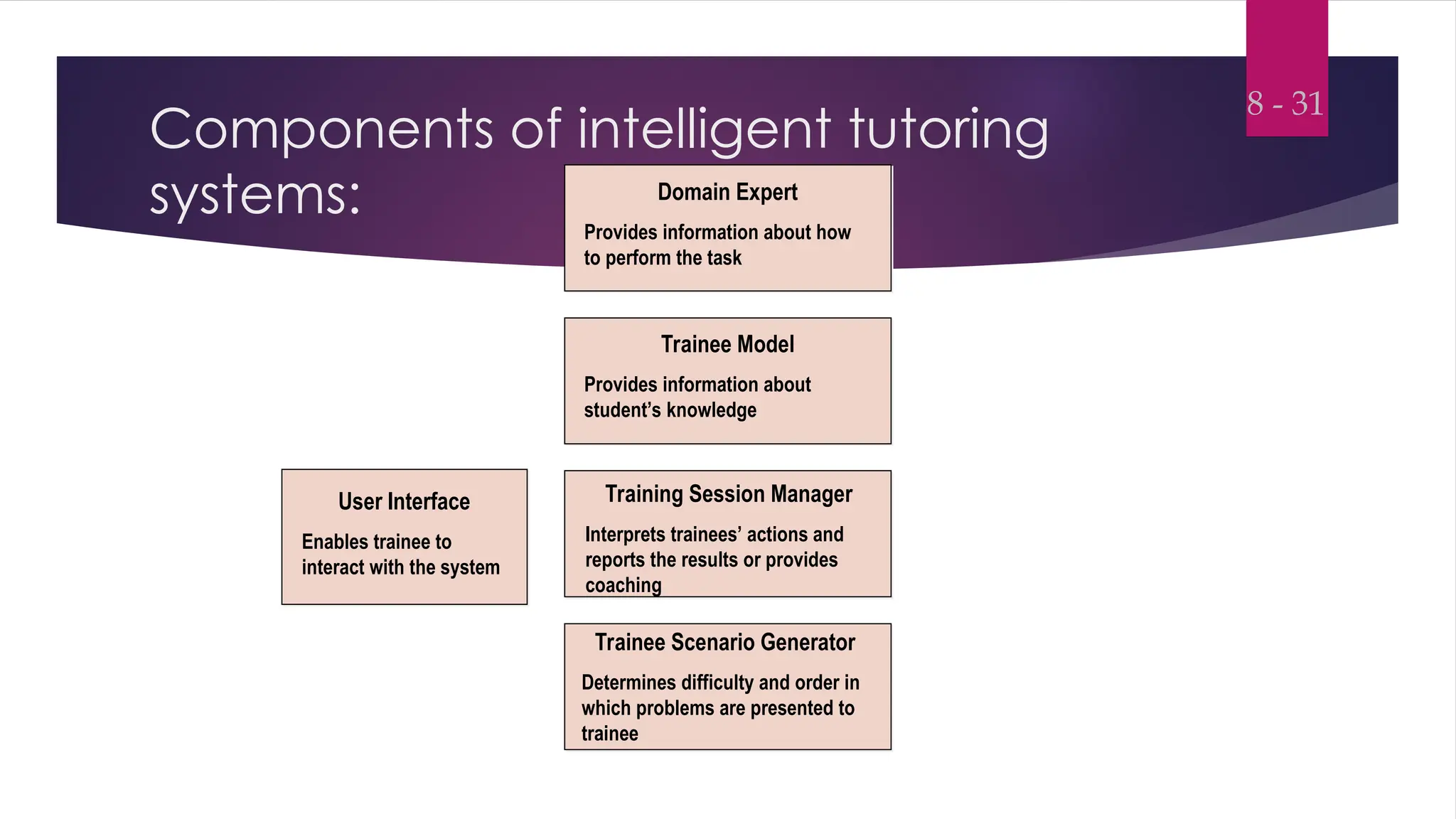
Instructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Design and Learning TheoriesInstructional Desi