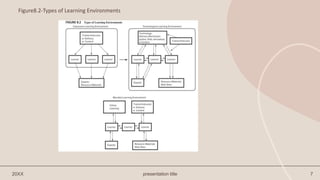
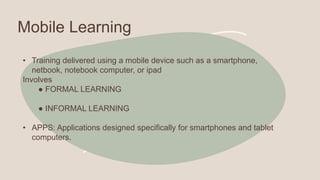
This document discusses technology-based training methods and how new technologies are influencing employee training. It evaluates different technology-based training methods like e-learning, mobile learning, simulations, and distance learning. It explains how these methods can reduce costs, increase learning effectiveness, and help training contribute to business goals compared to traditional training methods. The document also compares the strengths and weaknesses of different technology-based training methods.