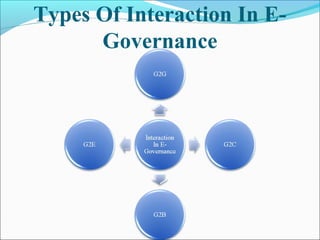
The document discusses the concepts of governance and e-governance. It defines e-governance as a two-way communication between government and citizens that uses technology to improve service delivery and ensure services reach beneficiaries. E-governance can make government more transparent and help transform citizen services. There are technological, social, cultural, political, psychological and service components to consider in e-governance. It also describes different types of interactions in e-governance including G2G, G2C, G2B, and G2E and highlights benefits like better access to information and accountability, while also noting challenges to implementing e-governance in India like lack of integration and communication between departments.