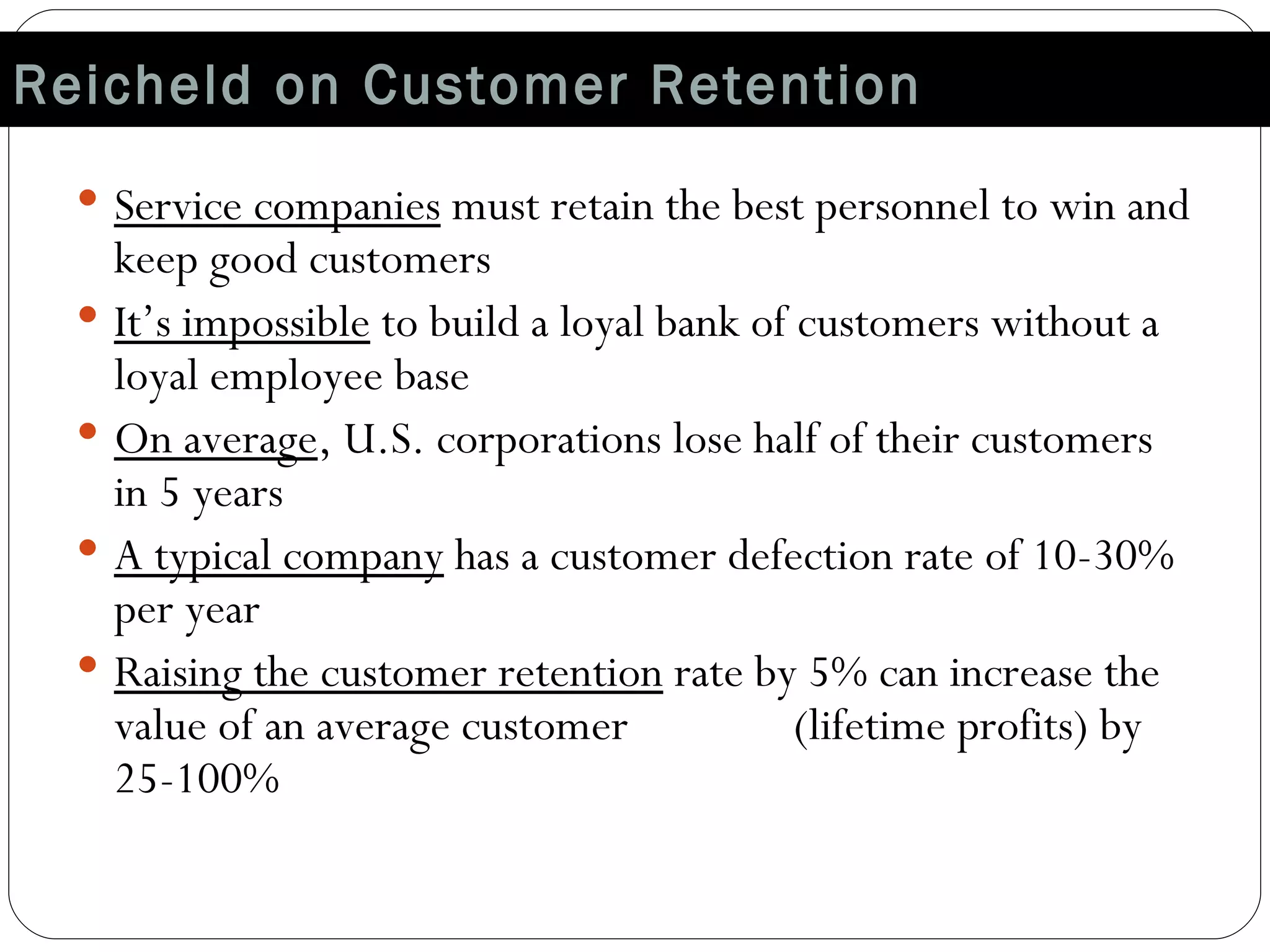
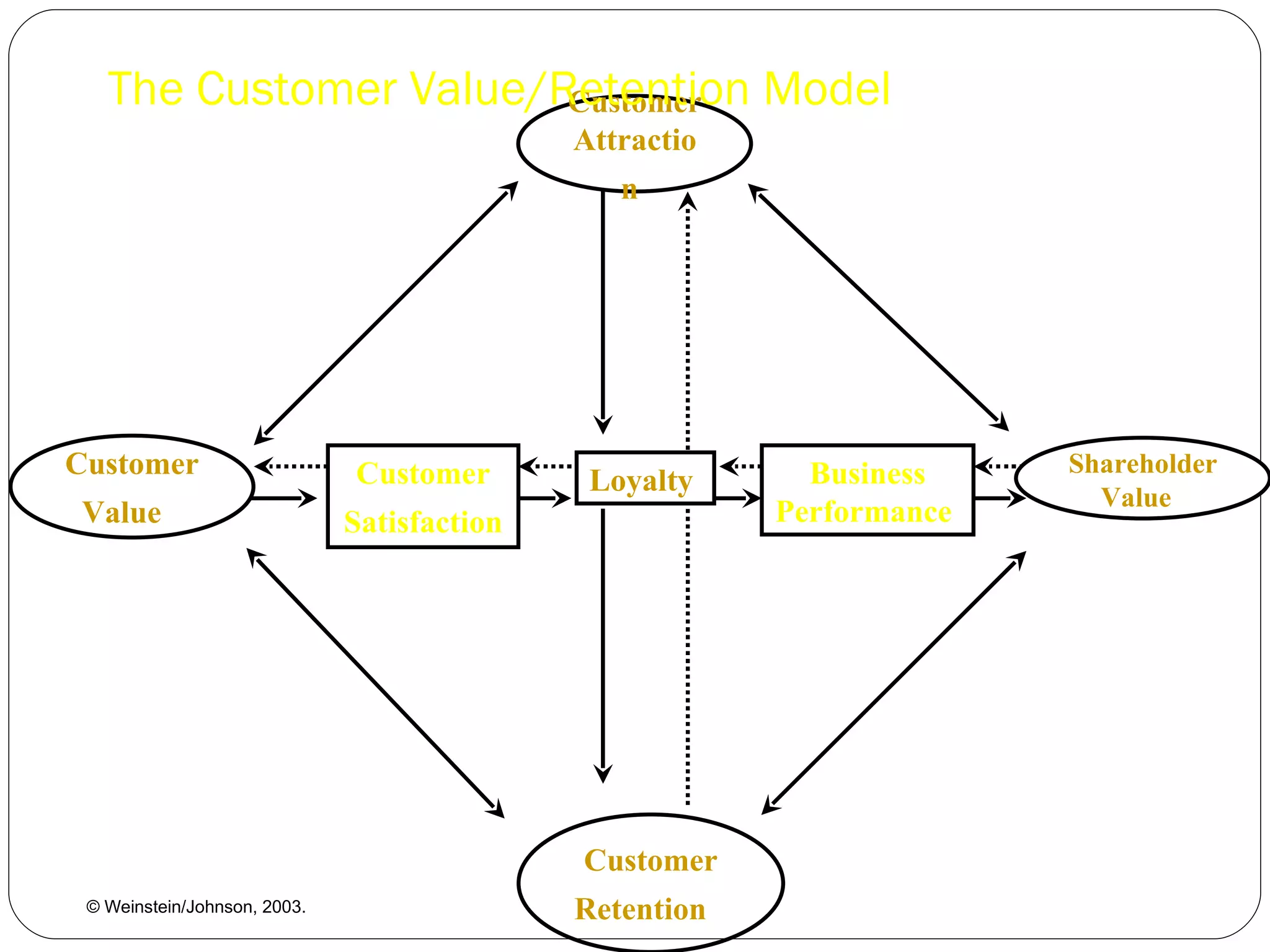
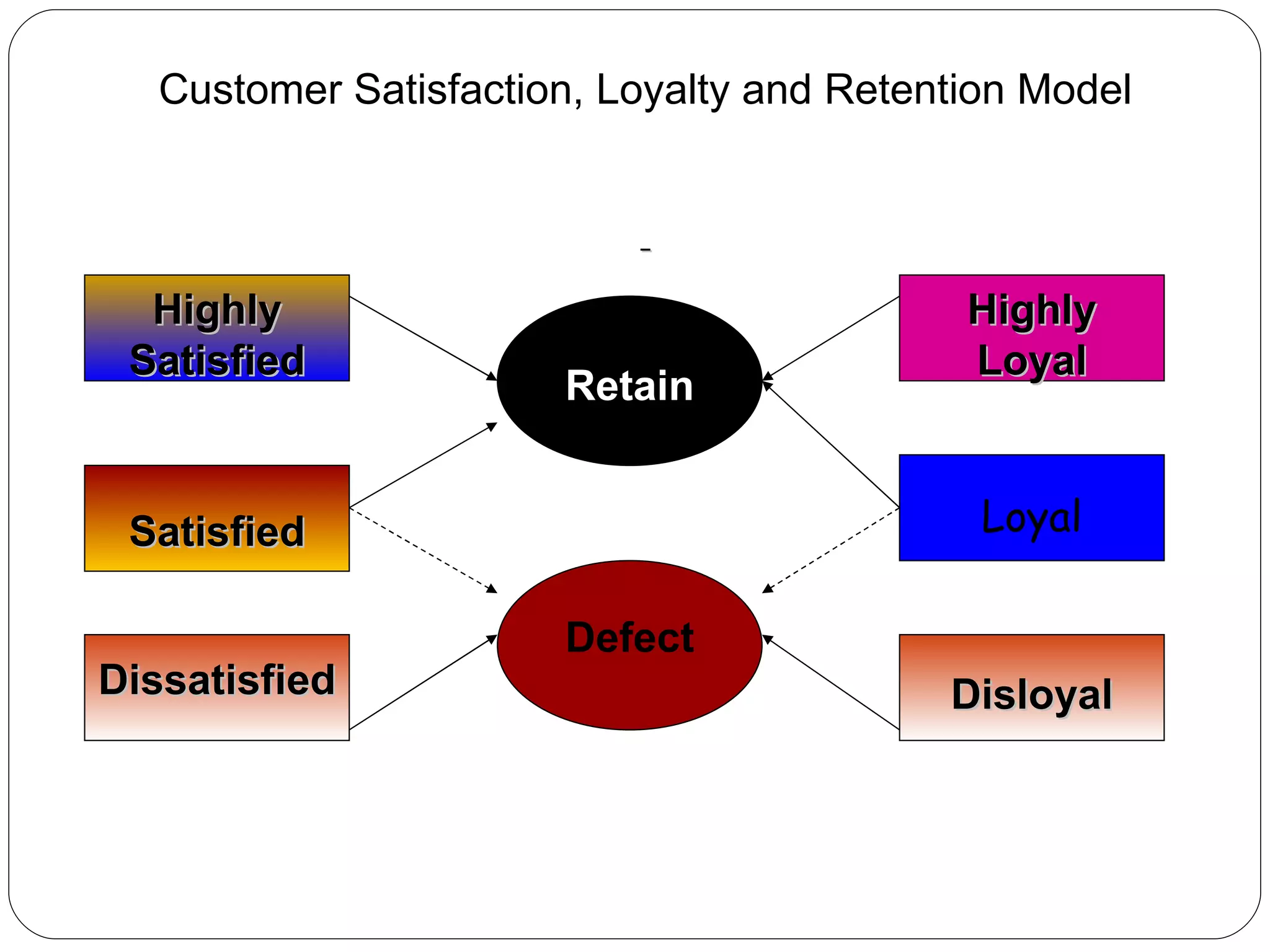
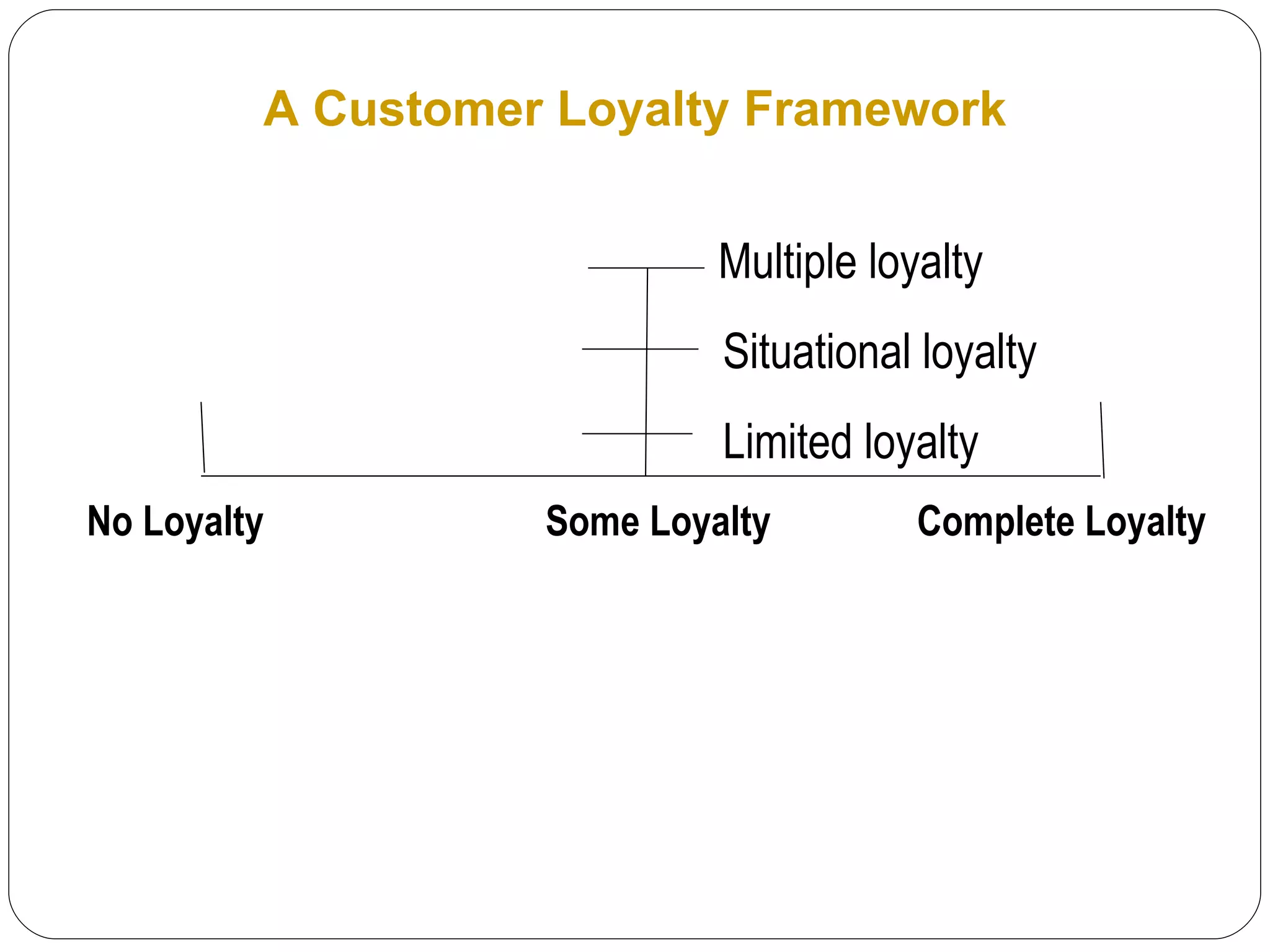
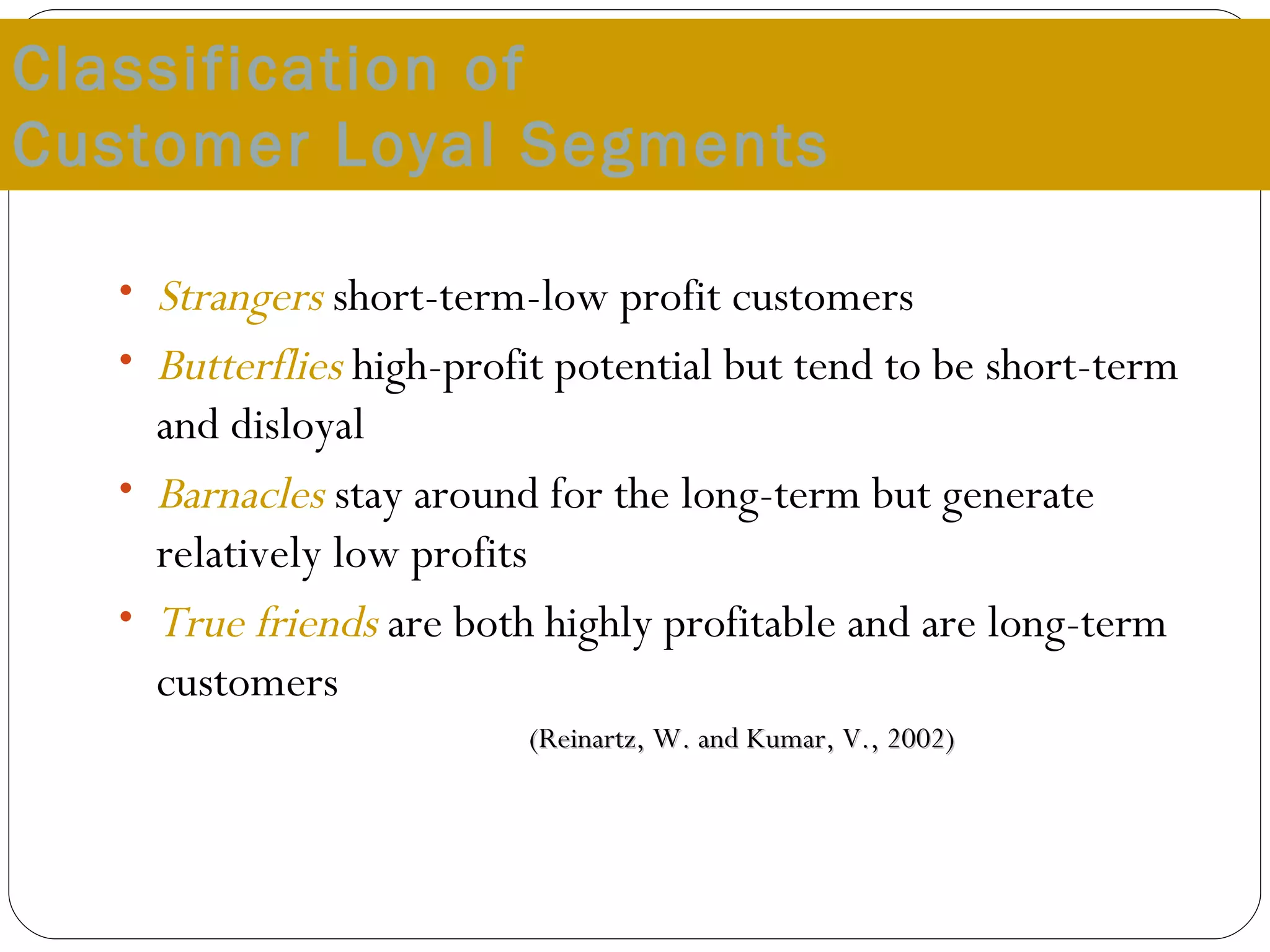
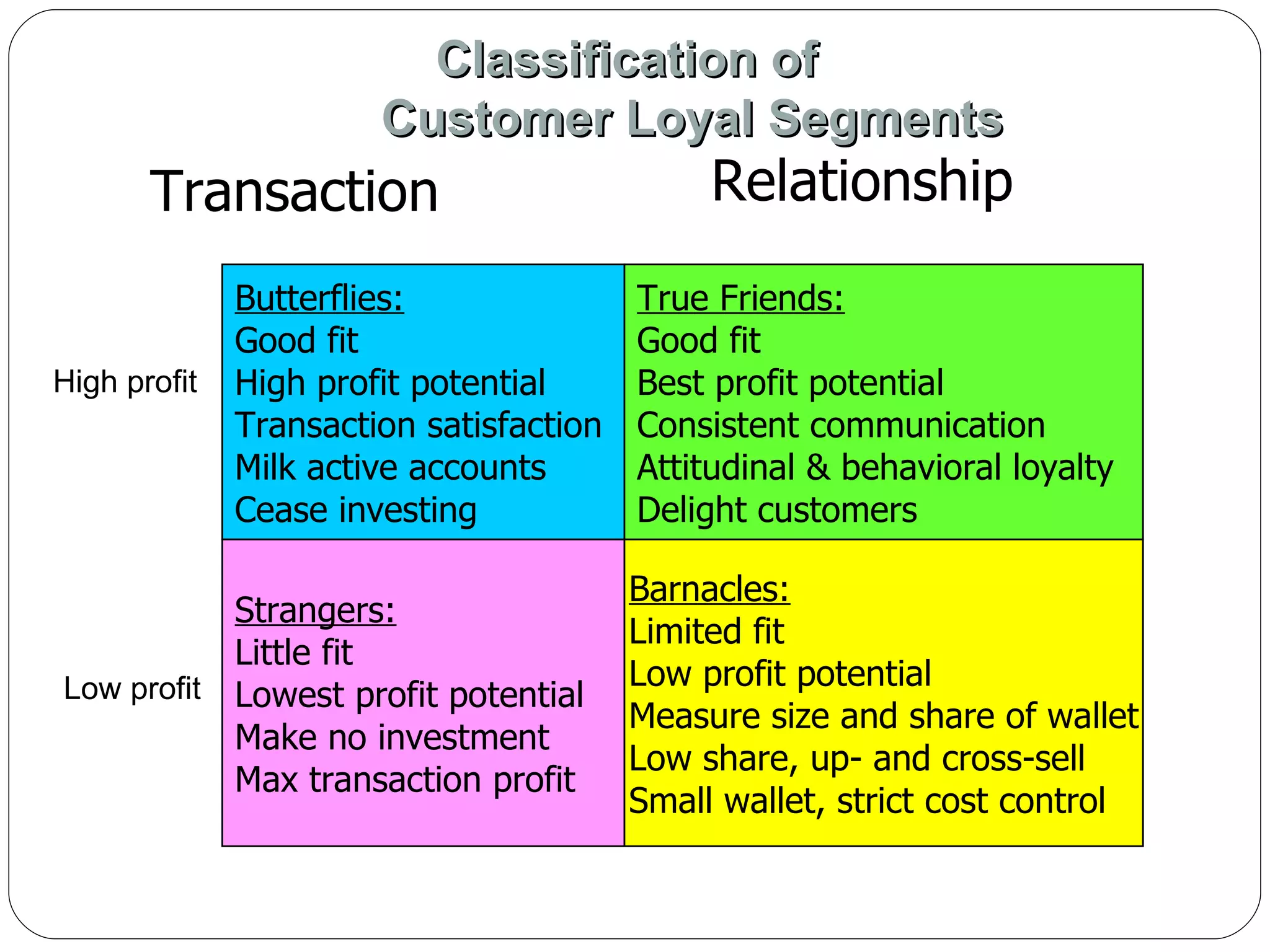
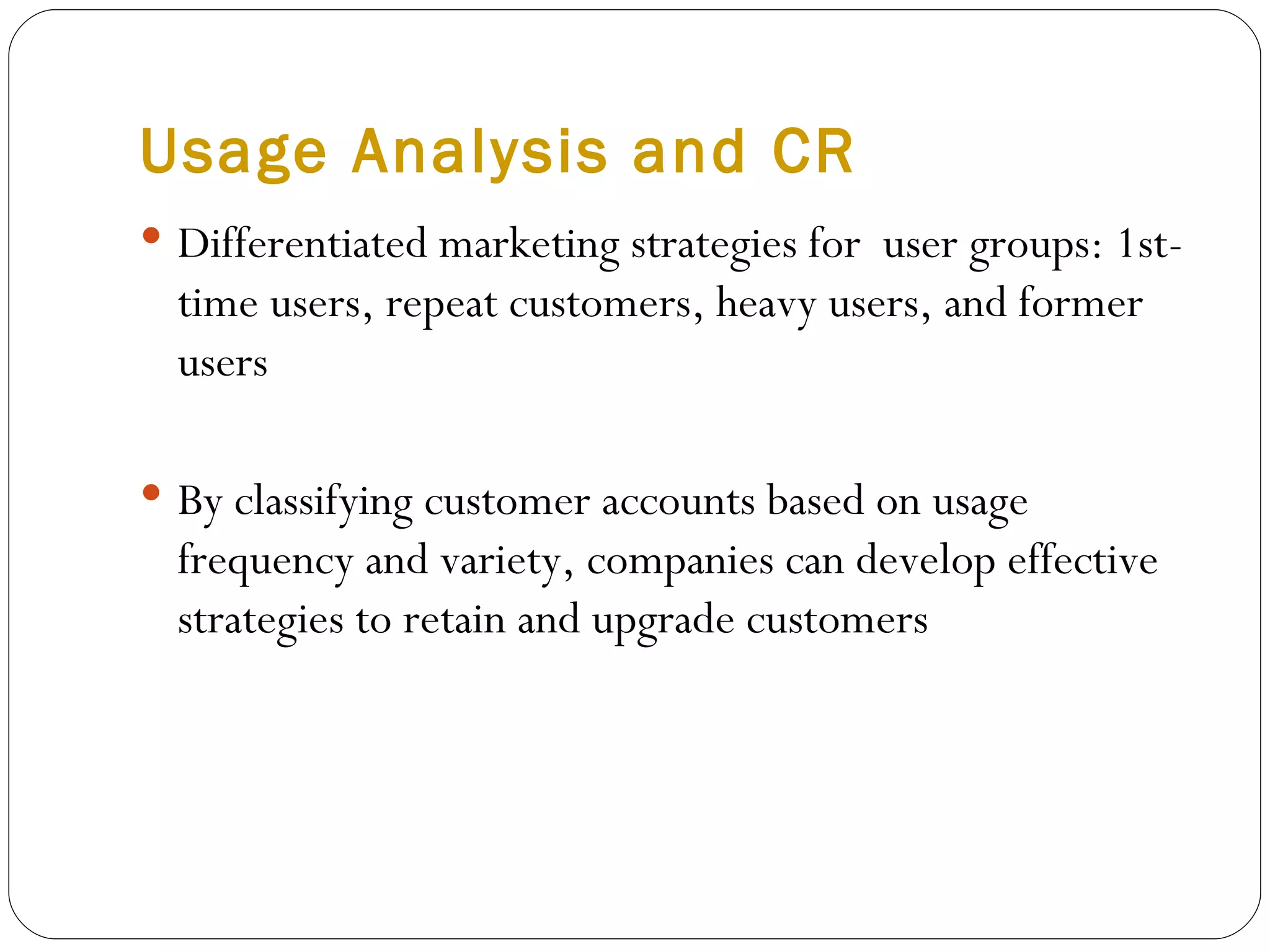
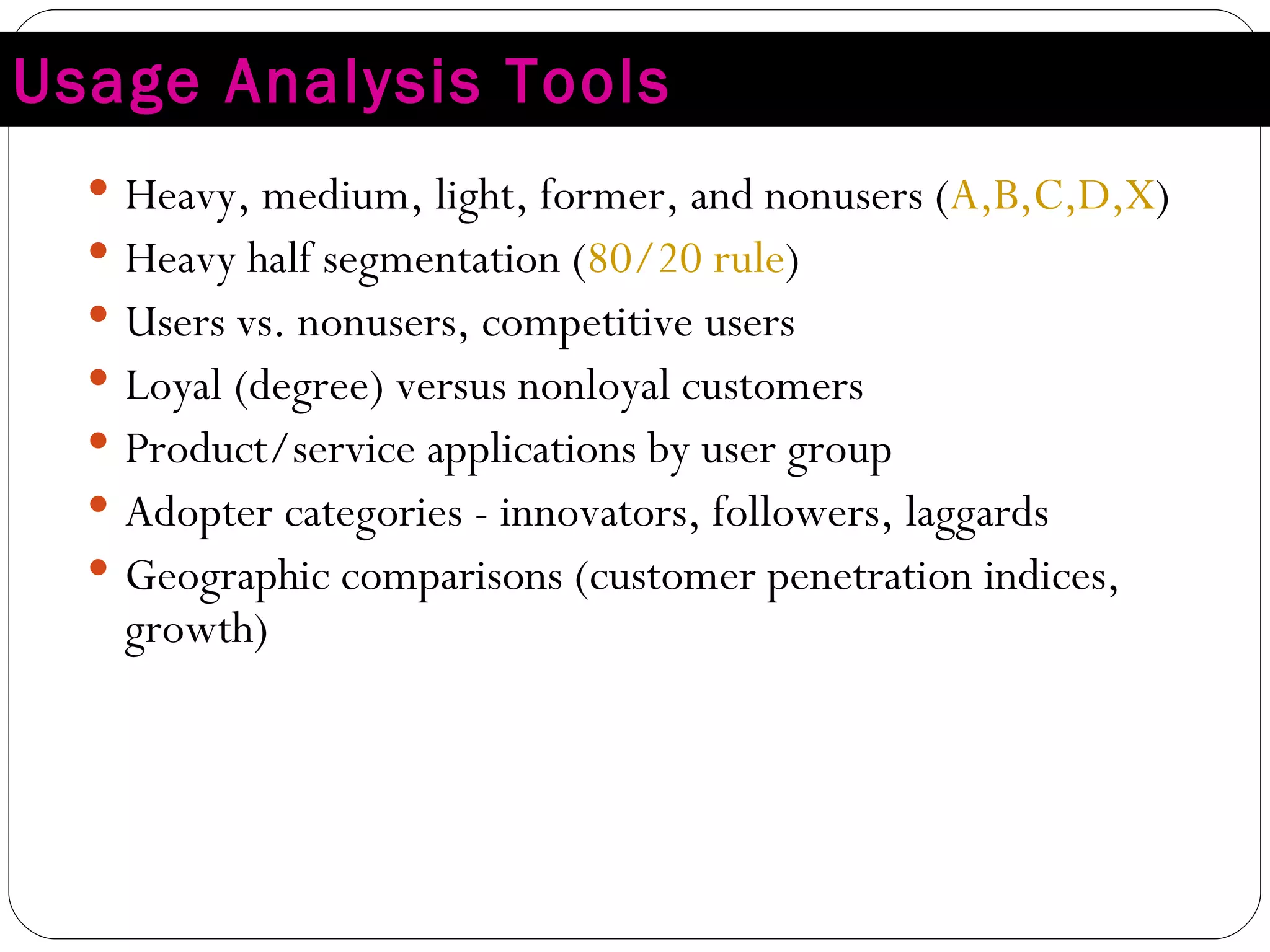
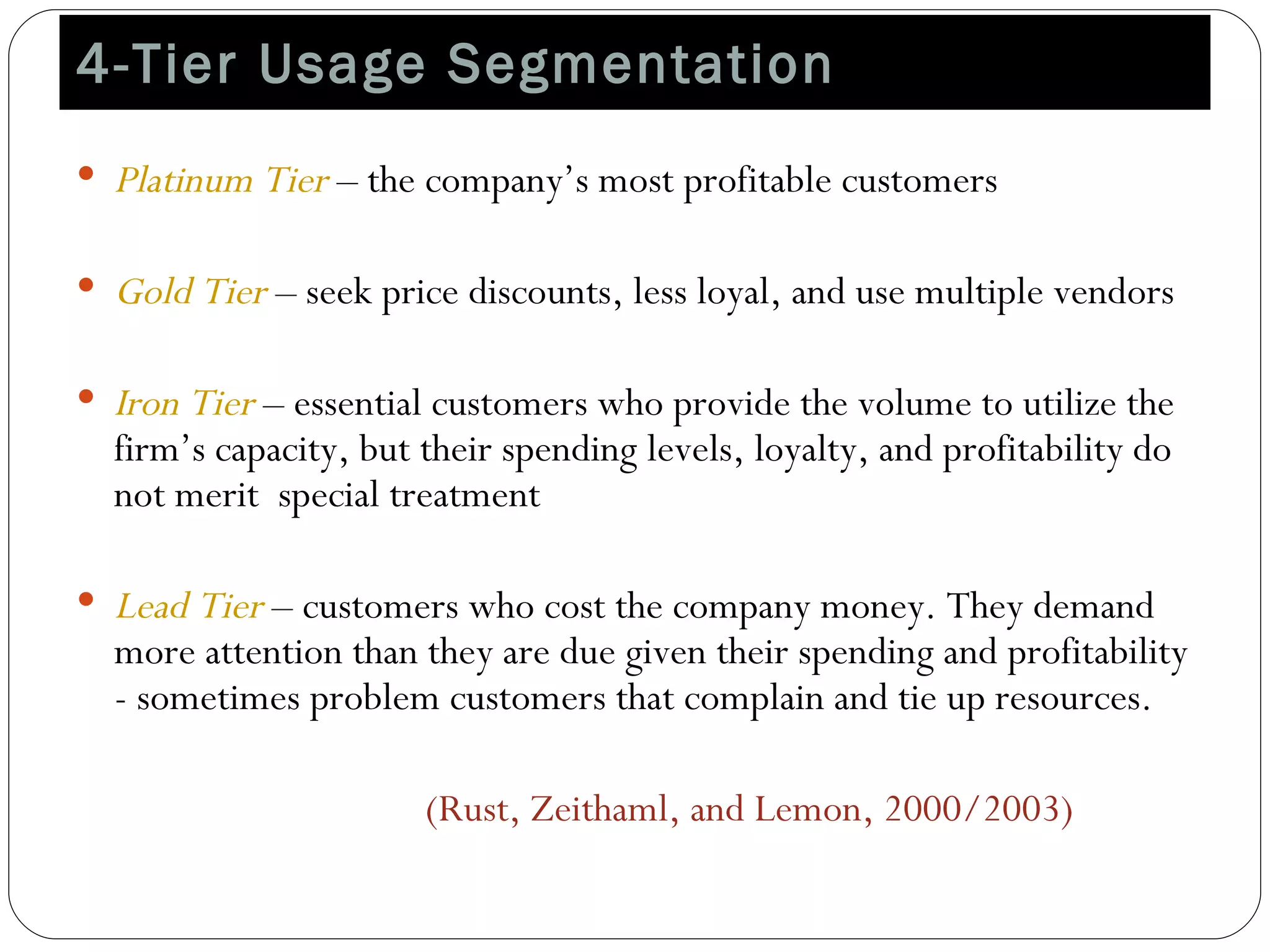
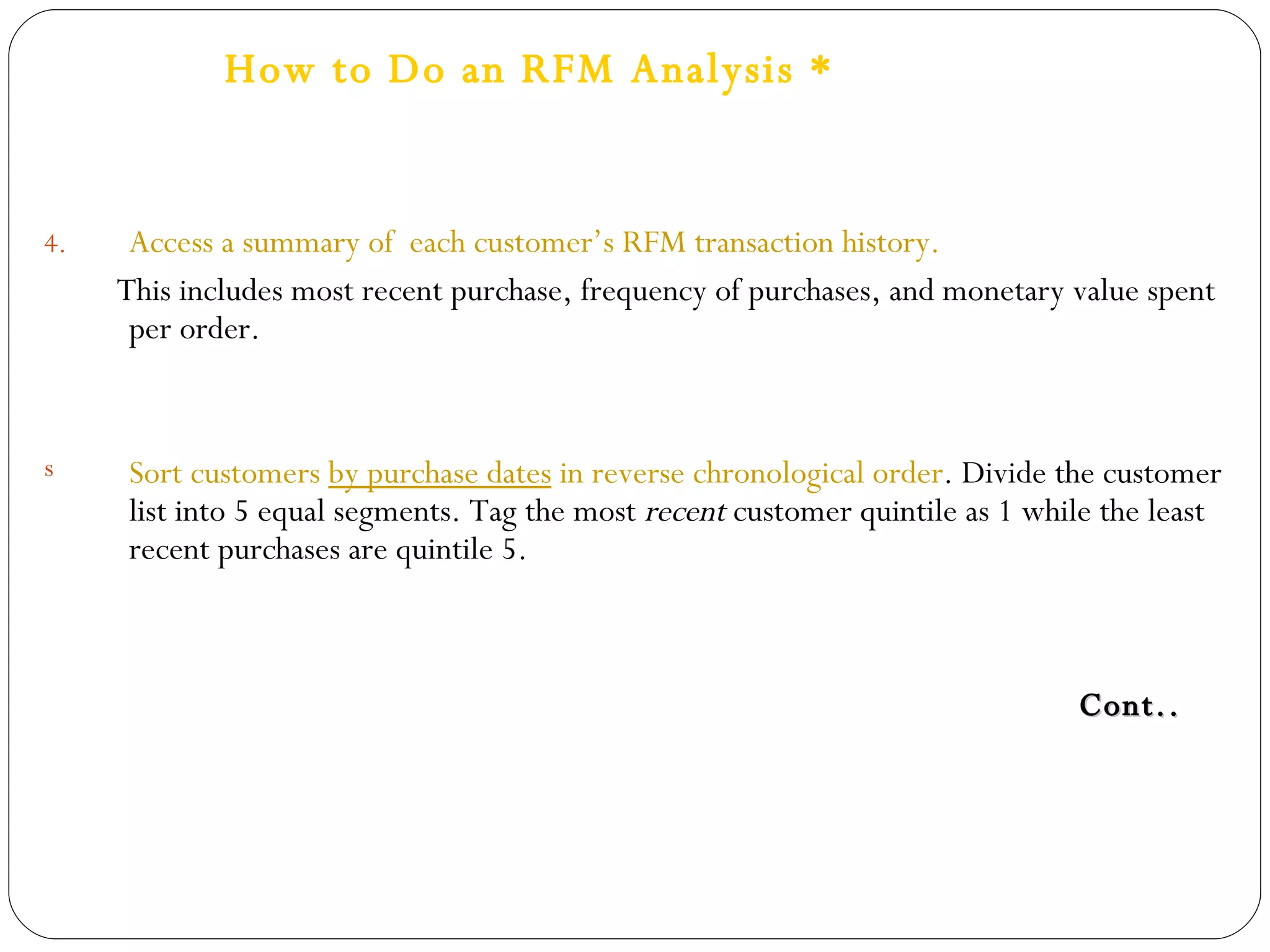
The document discusses various strategies for improving customer retention rates. It outlines factors that influence customer retention such as service quality, satisfaction, and loyalty. It then describes several models for understanding the customer retention process and analyzing customer value and segmentation. Finally, it provides examples of tactics for enhancing retention rates such as customer relationship management, targeted programs, and measuring retention through metrics like lifetime value and RFM analysis.
![By- Avinash Kumar [email_address] Retention strategy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/retentionstrategy-090919231621-phpapp01/75/Customer-Retention-Strategy-1-2048.jpg)