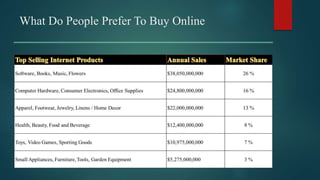
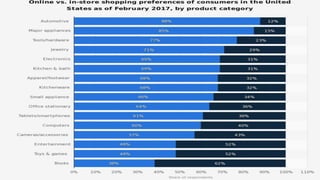
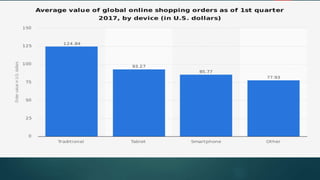
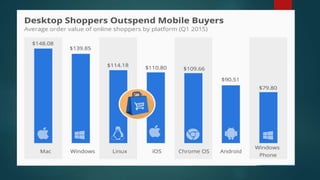
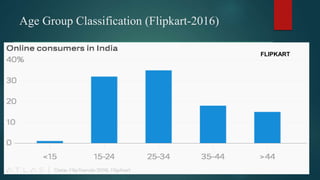
Online consumer behavior refers to how consumers interact with and make purchasing decisions on e-commerce platforms. There are several stages in the online consumer behavior process, from initial need recognition to post-purchase evaluation. Consumers are drawn to online shopping for its convenience and ability to easily compare prices and products. However, some have privacy, returns, and inability to see products in person concerns. E-commerce companies aim to understand what drives online purchases and builds consumer trust through security, usability, guarantees and reviews. Younger consumers are increasingly using mobile devices to shop online.