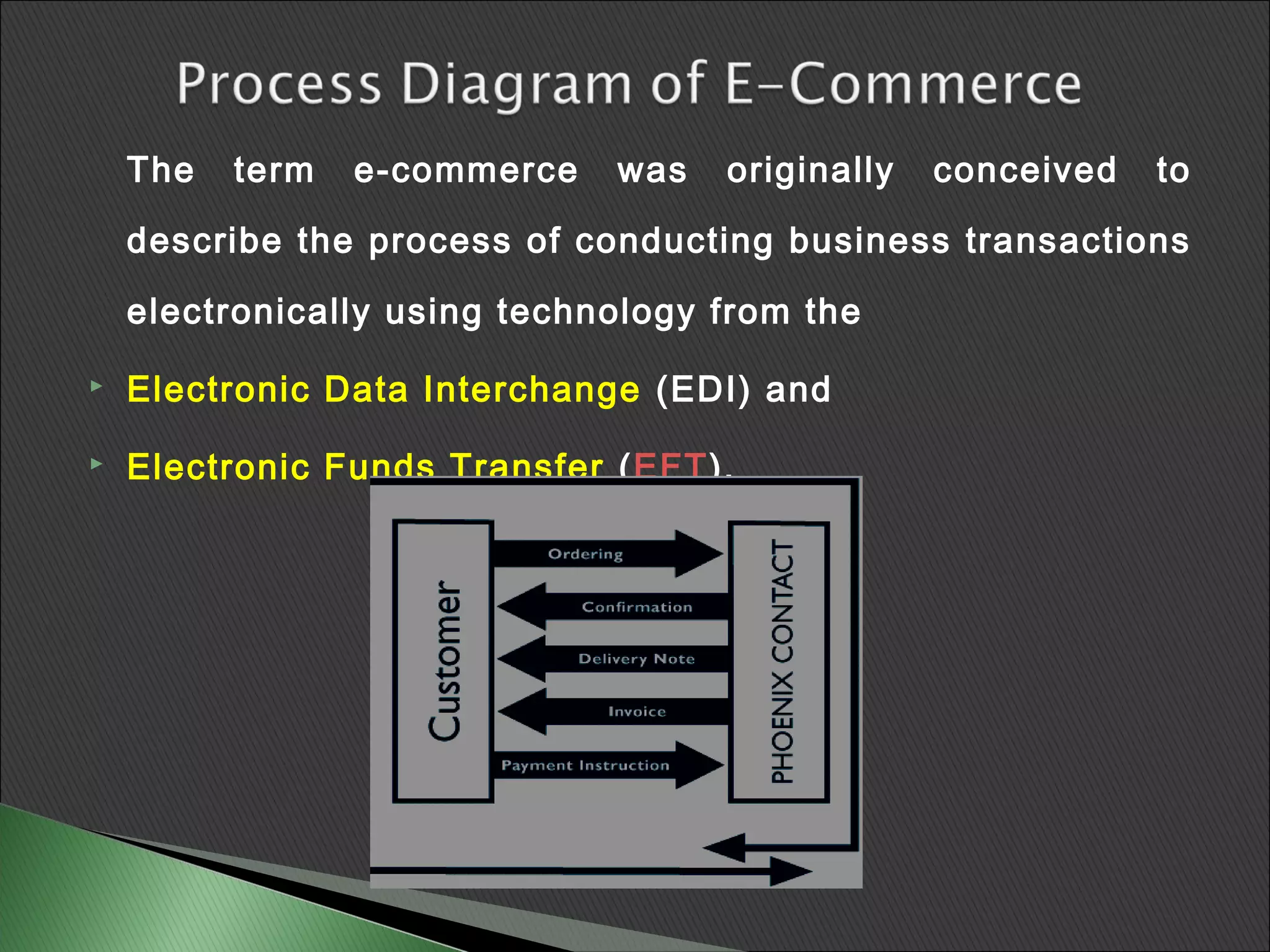
This document provides an introduction to e-commerce, including its components and types. It defines e-commerce as the exchange of commodities and products through online services and the internet. The key components of e-commerce are online shopping, which provides customer information to make purchases, and online purchasing technology. E-business is described as a superset of e-commerce that also includes internal business processes. Finally, the different types of e-commerce are outlined as B2B, B2C, C2B, C2C and mobile commerce.