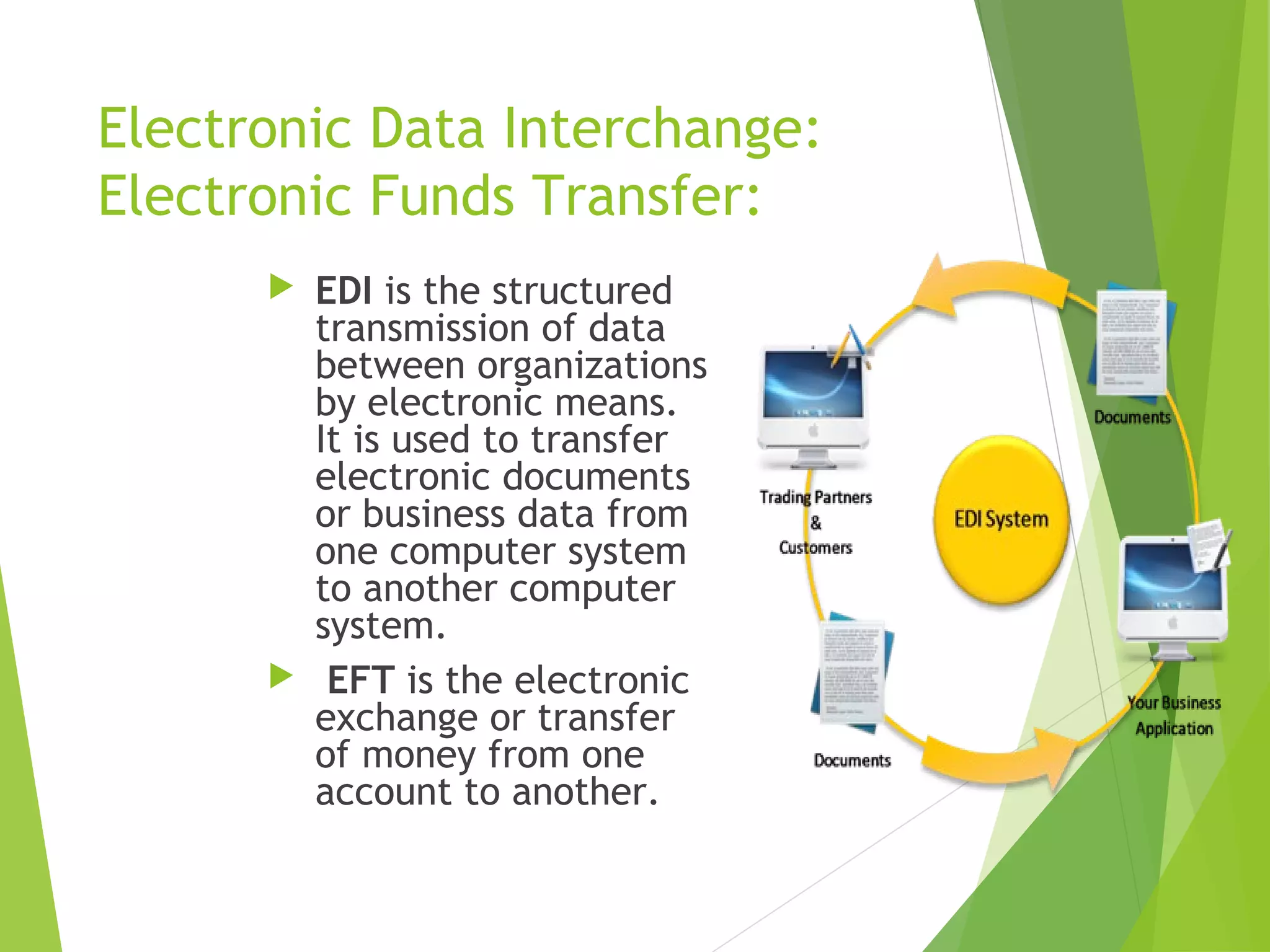
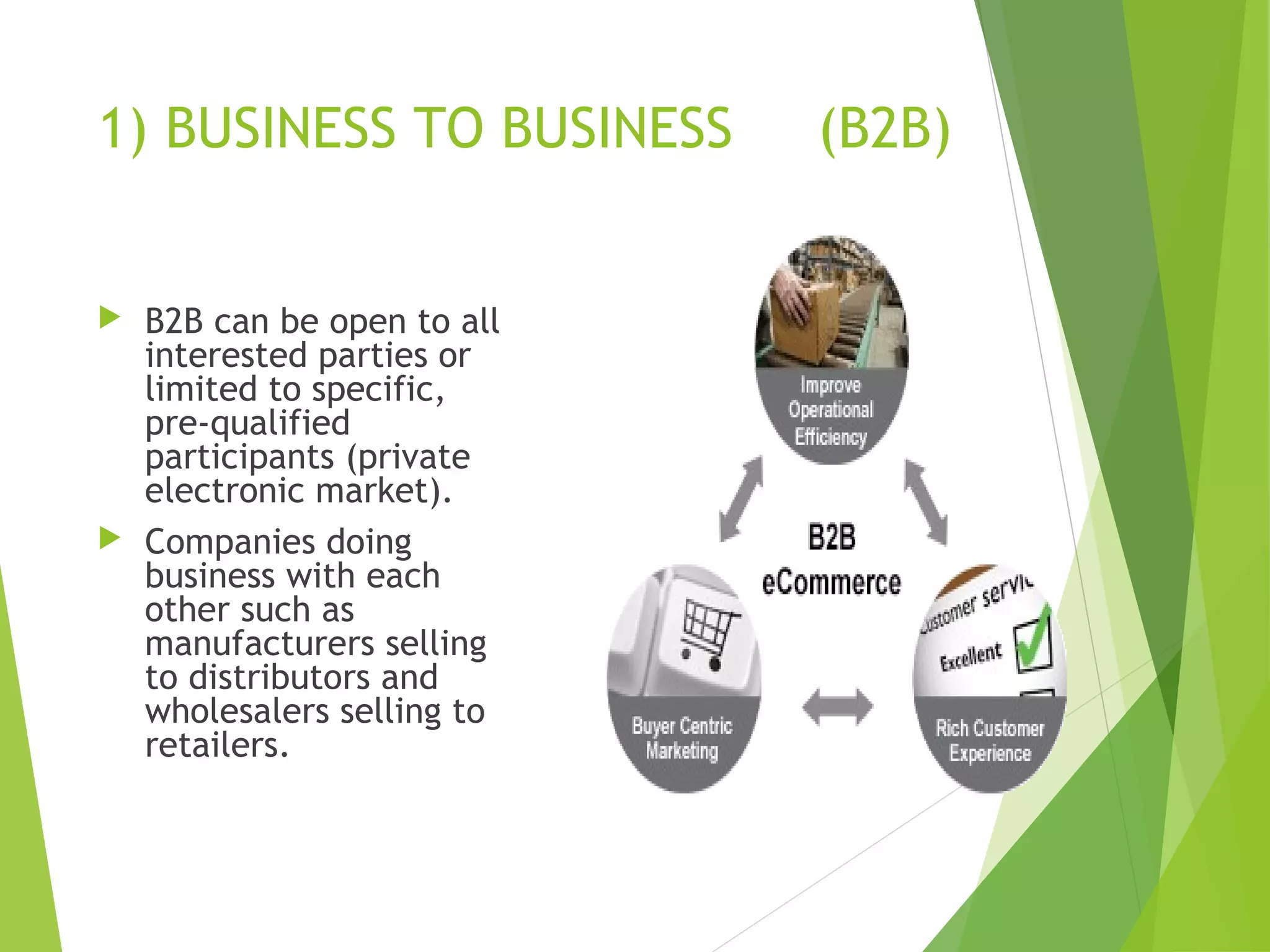
This document discusses e-commerce, including its definition as buying and selling over electronic systems like the internet. It provides a brief history of e-commerce from its origins in EDI and EFT in the 1980s to widespread use of online shopping in the 2000s. The types of e-commerce are identified as B2B, B2C, C2B, and C2C. Advantages include convenience and low costs, while disadvantages include lack of quality guarantees and security risks. Examples of e-commerce include individuals buying books online and businesses purchasing supplies electronically.