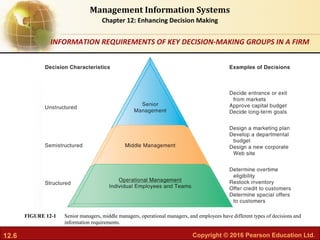
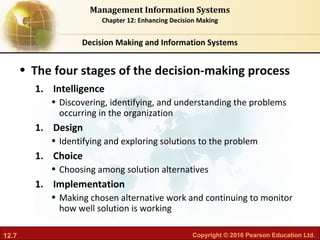
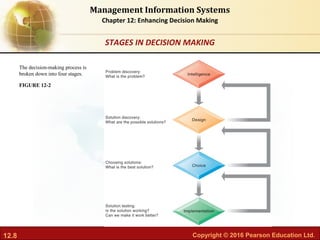
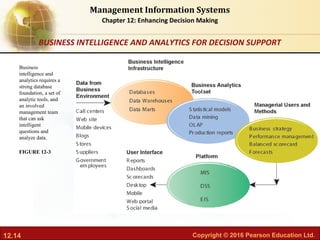
This document discusses business intelligence and analytics and how they support decision making. It defines business intelligence as the infrastructure for collecting and analyzing business data, including databases, data warehouses, and analytics tools. Business analytics are the tools and techniques used to analyze data, such as OLAP, statistics, and data mining. The document outlines the decision making process and different types of decisions made by senior managers, middle managers, and operational staff. It also discusses how business intelligence systems provide reports, dashboards, queries and other features to support different user groups in making decisions.