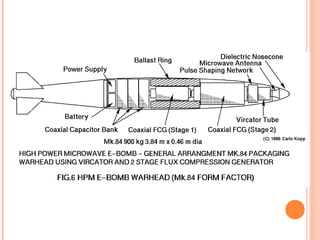
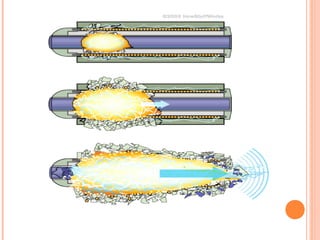
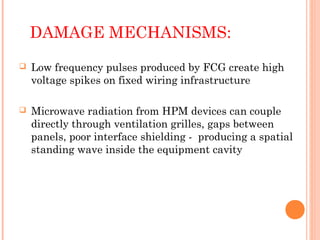
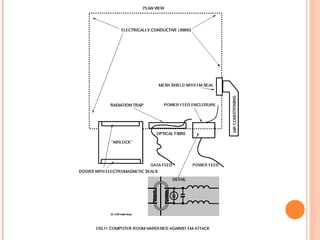
The document discusses the proposed "E-bomb" weapon, which uses electromagnetic pulses generated by explosive pumped flux compression generators and high power microwave devices to destroy electronics over a large area while minimizing harm to humans. It would function by emitting powerful electromagnetic bursts to damage equipment through coupling into wiring and antennae. The E-bomb could paralyze an opponent's communications and defense systems quickly without risking civilian casualties. While challenging to implement, it offers advantages for strategic and punitive attacks by inflicting economic and military damage from a distance.