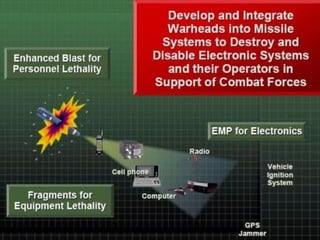
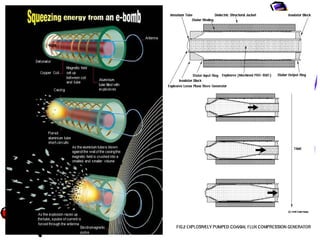
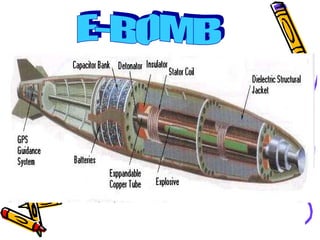
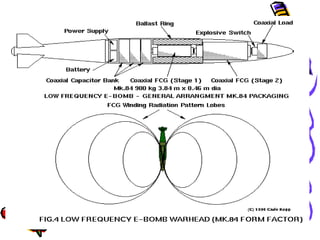
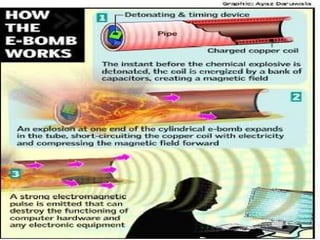
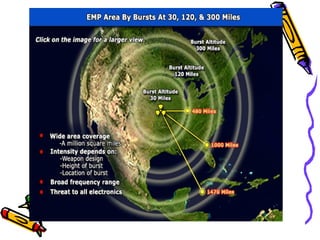
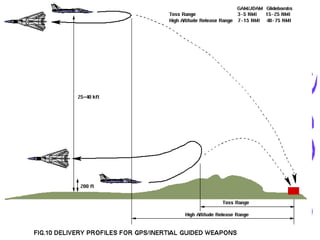
An electromagnetic bomb or E-bomb is designed to disable electronics with an electromagnetic pulse. Key technologies that can be applied to E-bomb designs include explosively pumped flux compression generators, explosive or propellant driven MHD generators, and various high-power microwave devices. Explosively pumped flux compression generators are the most mature technology, using explosives to rapidly compress magnetic fields to produce high currents. E-bombs can effectively couple with and damage electronics through wiring and cables. Low frequency E-bombs couple well into typical infrastructure wiring. Targets can include communications sites and mobile air defense equipment. Hardening systems against EMPs is an important defense. E-bombs have limitations based on delivery accuracy and range against the target damage