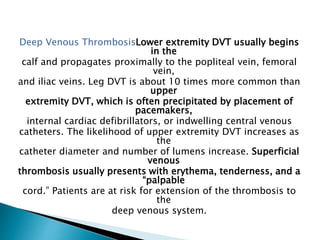
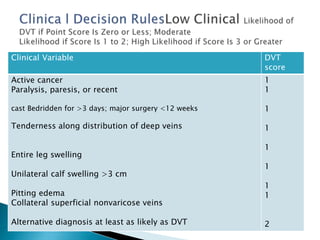
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) includes deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), which can cause death or disability. Post-thrombotic syndrome damages venous valves and causes leg swelling and pain. Inflammation and platelet activation via neutrophil extracellular traps promote thrombosis. Genetic mutations like factor V Leiden increase thrombotic risk. Symptoms are often nonspecific, while d-dimer and imaging tests aid diagnosis. Anticoagulation prevents further clots, while thrombolysis treats active clots. Outcomes depend on risk stratification of right heart strain and biomarker levels.