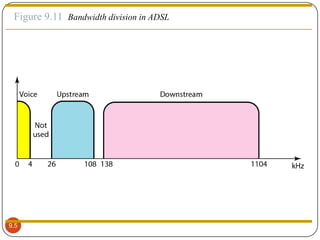
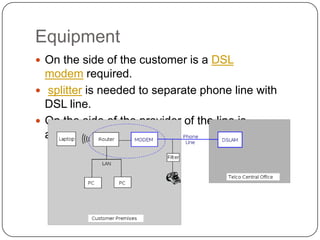
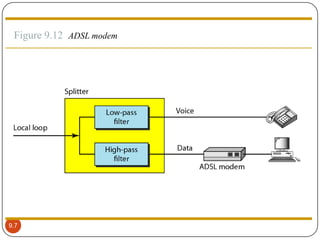
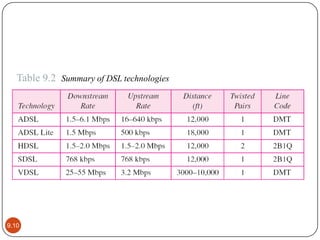
DSL is a technology that provides high-speed internet access over traditional phone lines. There are two main types: asymmetric DSL (ADSL), which provides more bandwidth for downloading, and symmetric DSL (SDSL), which provides equal bandwidth for both uploads and downloads. A DSL modem is required for the customer to connect to their internet provider, who uses equipment called a DSLAM. DSL allows voice and internet access to work simultaneously over the same phone line. It is widely used globally and supports applications like online gaming, video streaming, and telecommuting.