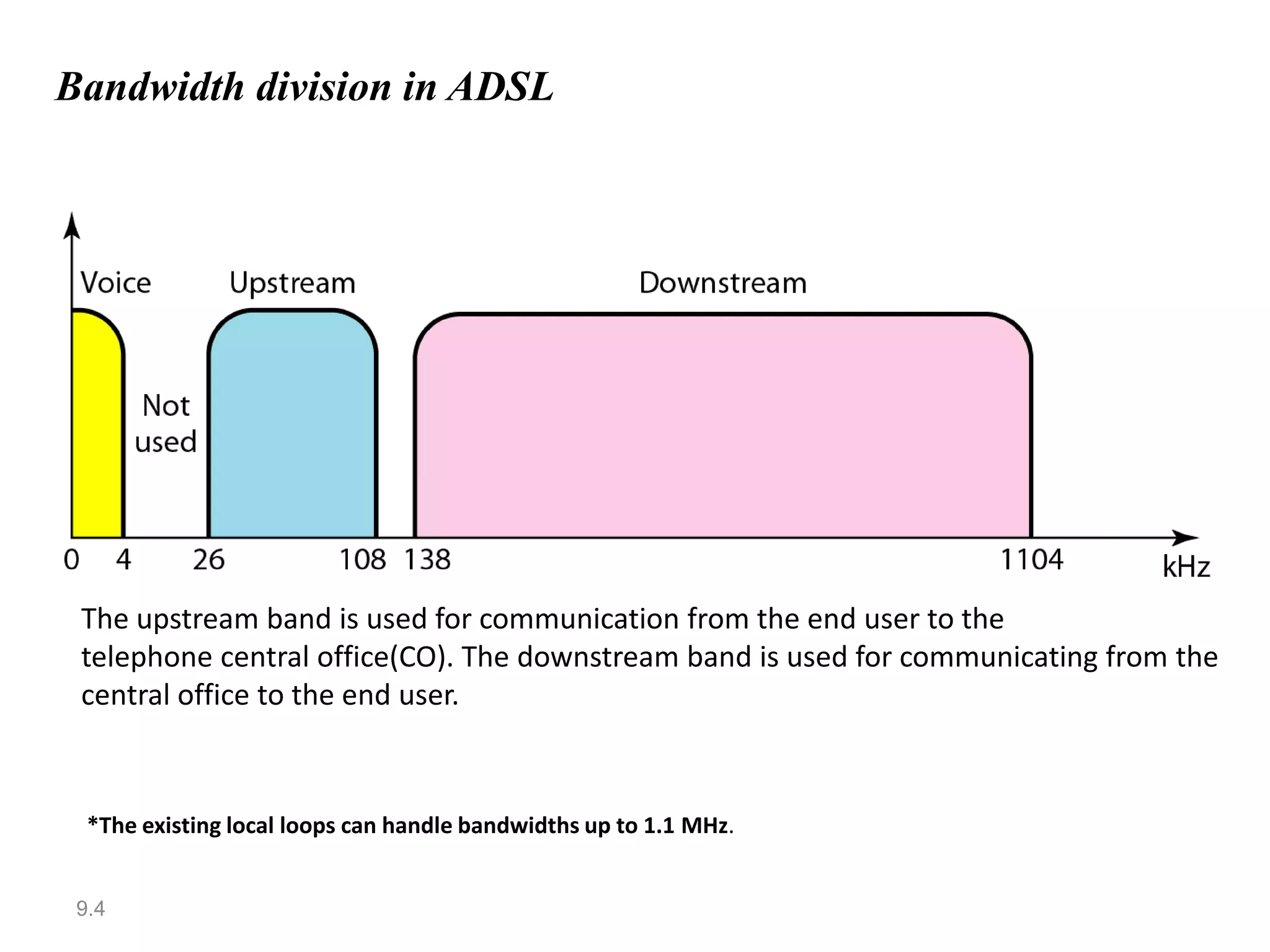
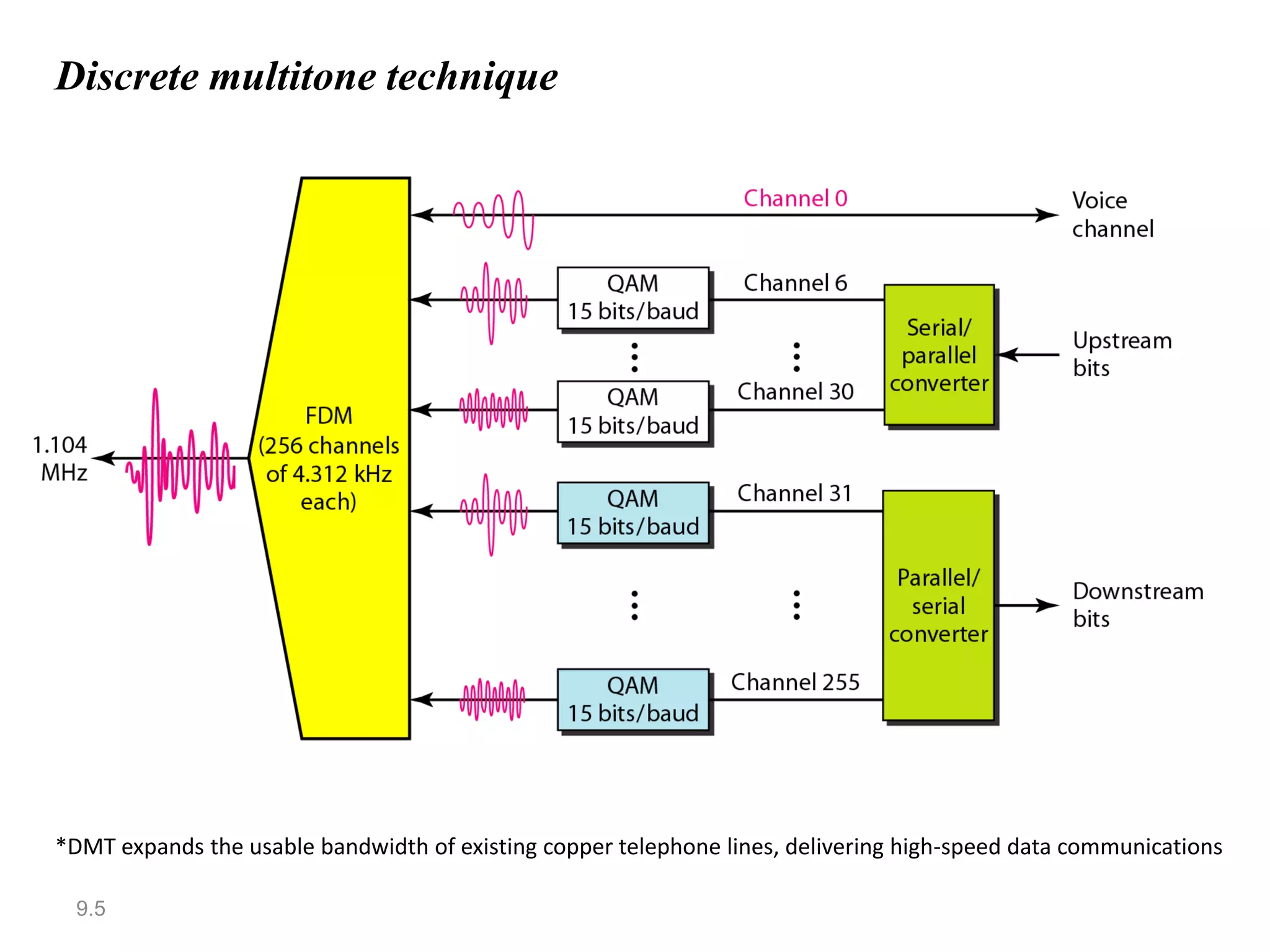
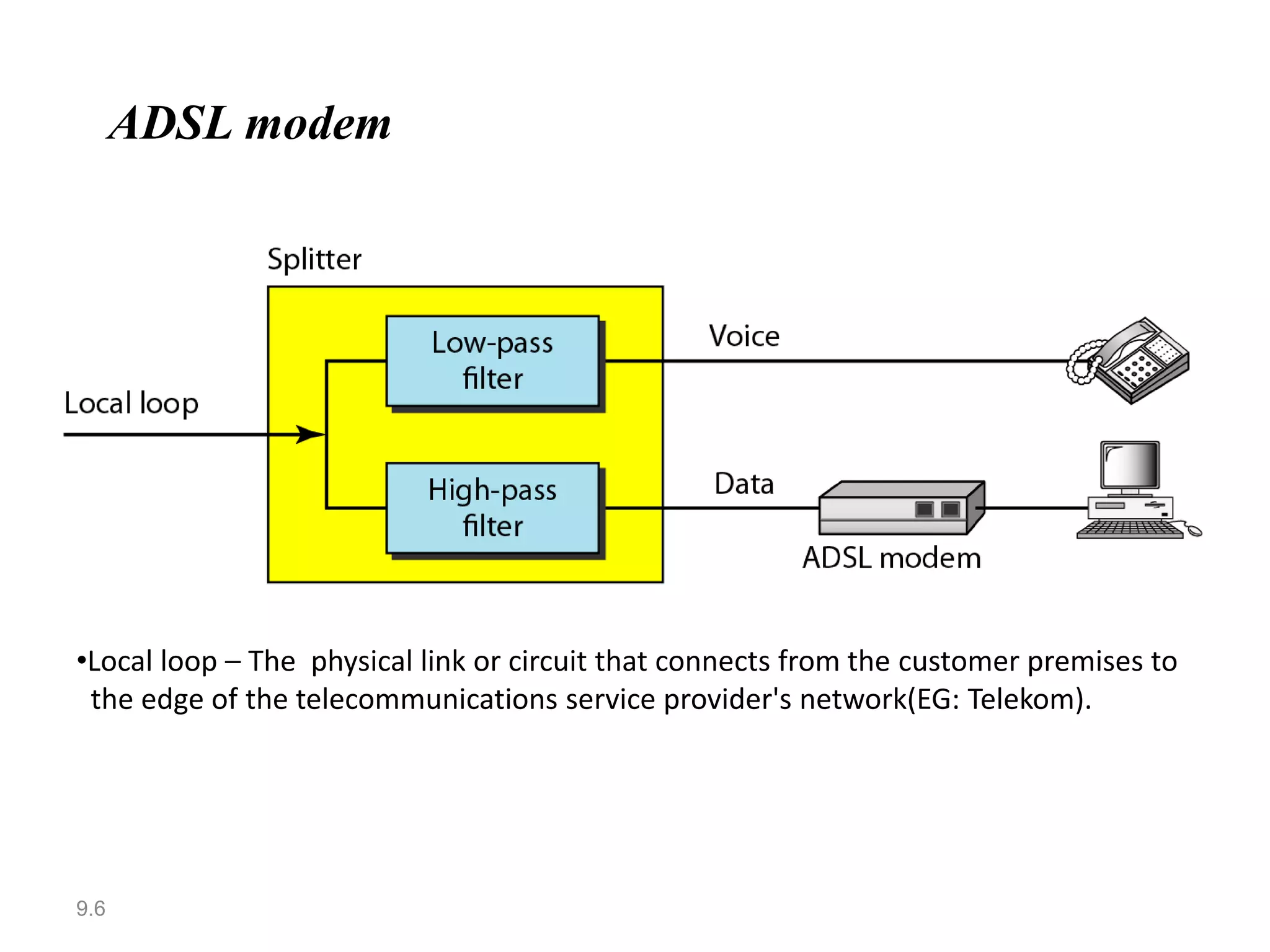
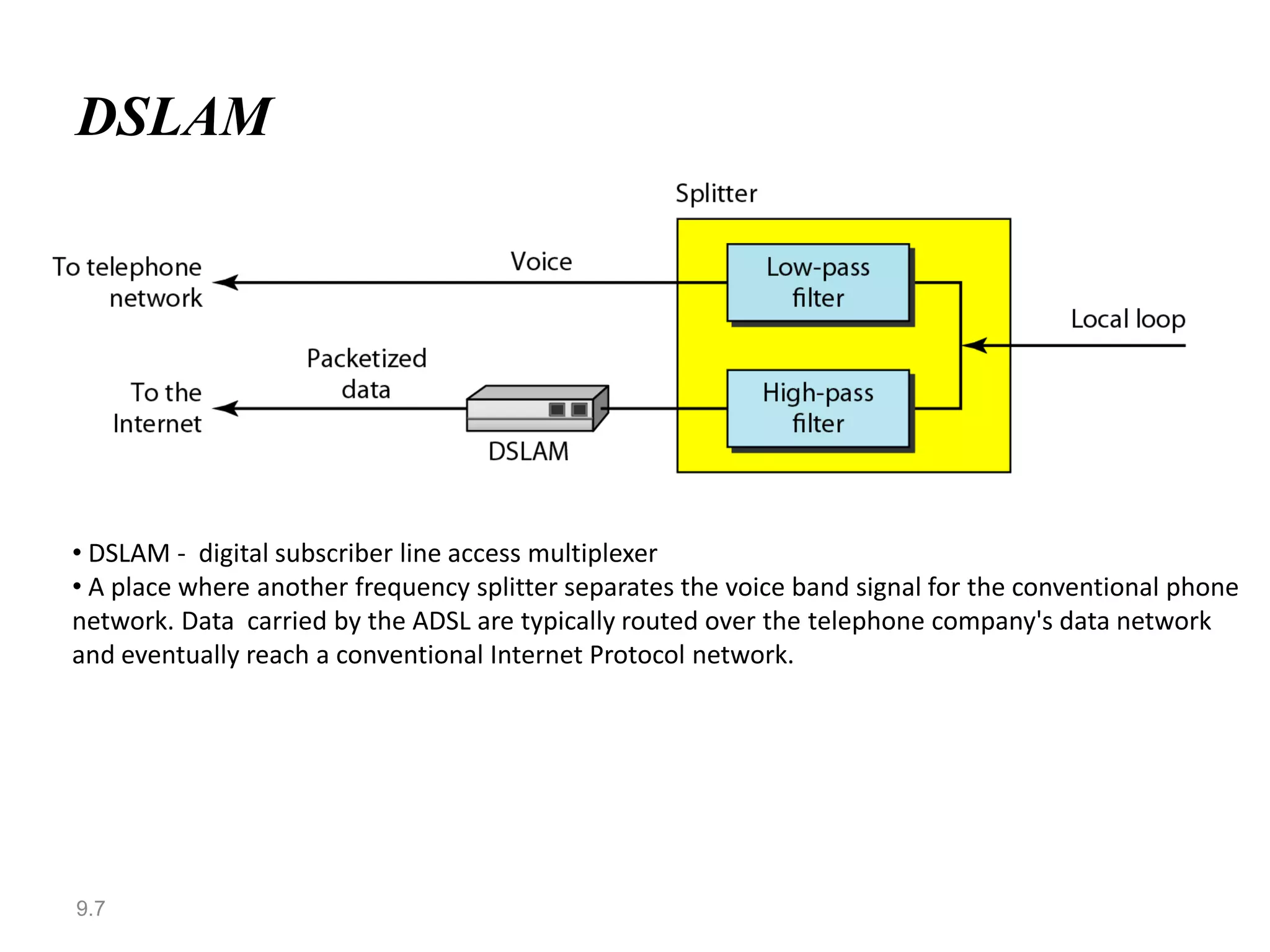
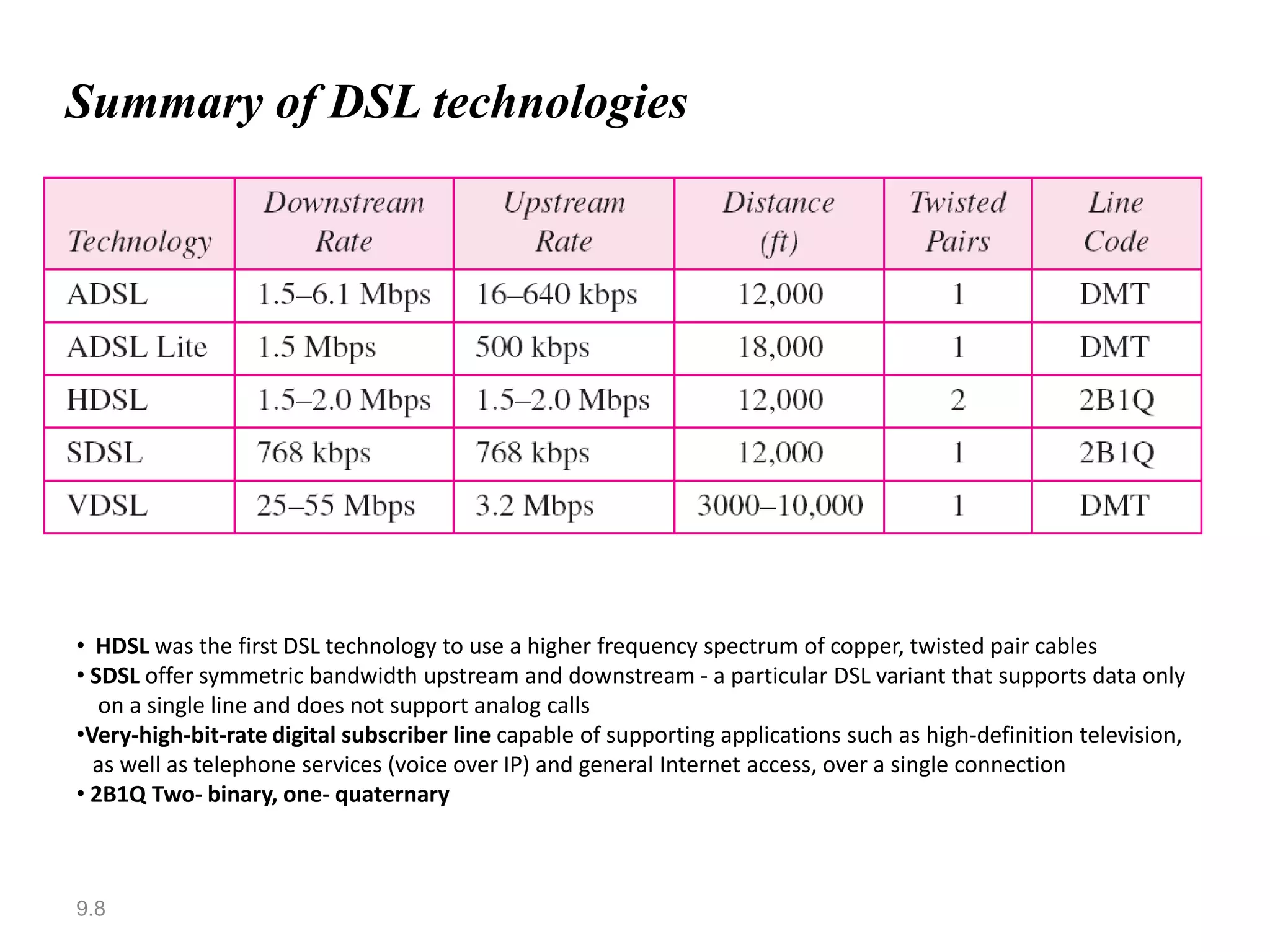
Digital subscriber line (DSL) provides higher-speed Internet access over existing telephone lines. It uses frequencies that do not interfere with voice calls to transmit data faster than a conventional modem. The most popular type of DSL is asymmetric DSL (ADSL), which allocates more bandwidth to downstream data transmission from the telephone central office to the user than to upstream transmission. ADSL uses the discrete multitone technique to maximize data rates over existing copper telephone lines.