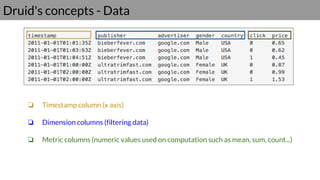
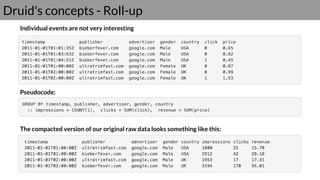
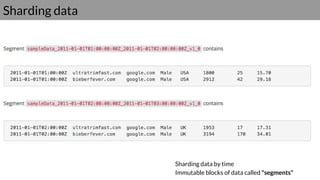
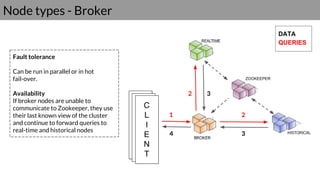
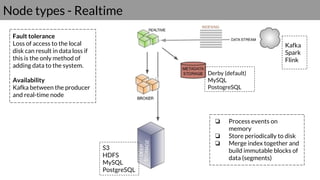
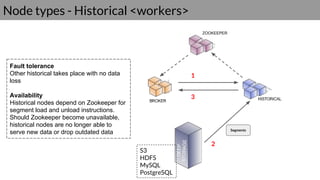
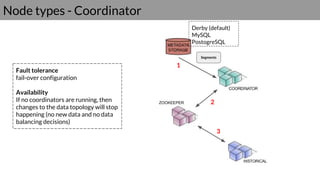
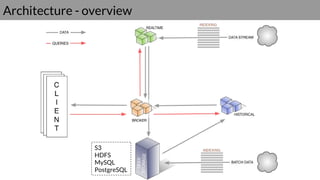
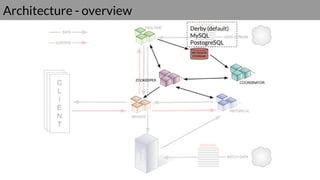
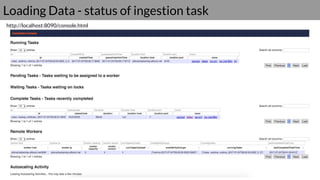
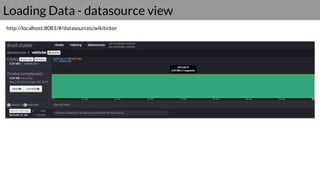
Druid is a real-time data access system designed for high availability and fast querying of large sets of data. It employs various node types and relies on external systems for metadata and storage management. The architecture supports both real-time and batch data ingestion and can efficiently handle sharding and querying processes.