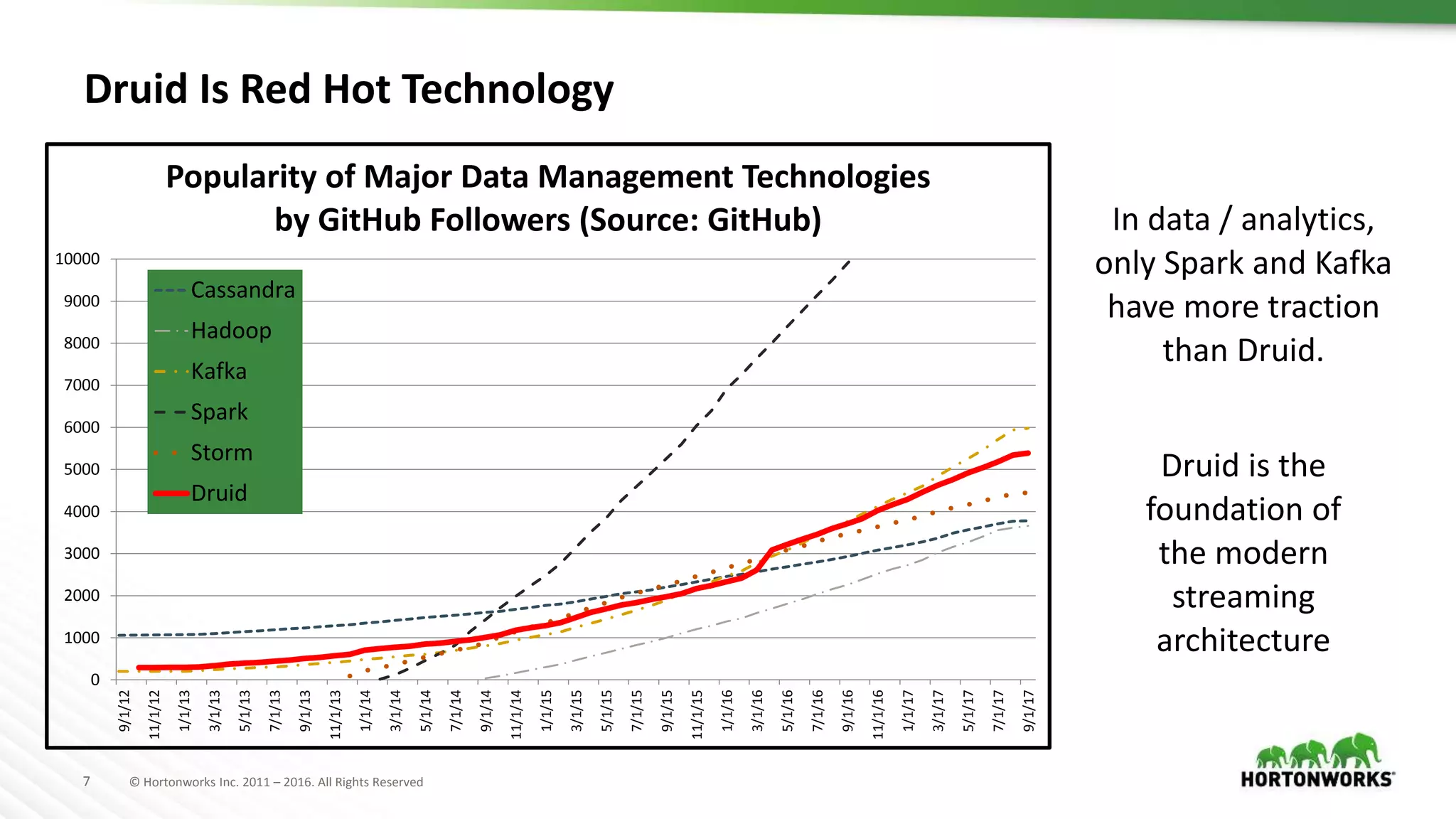
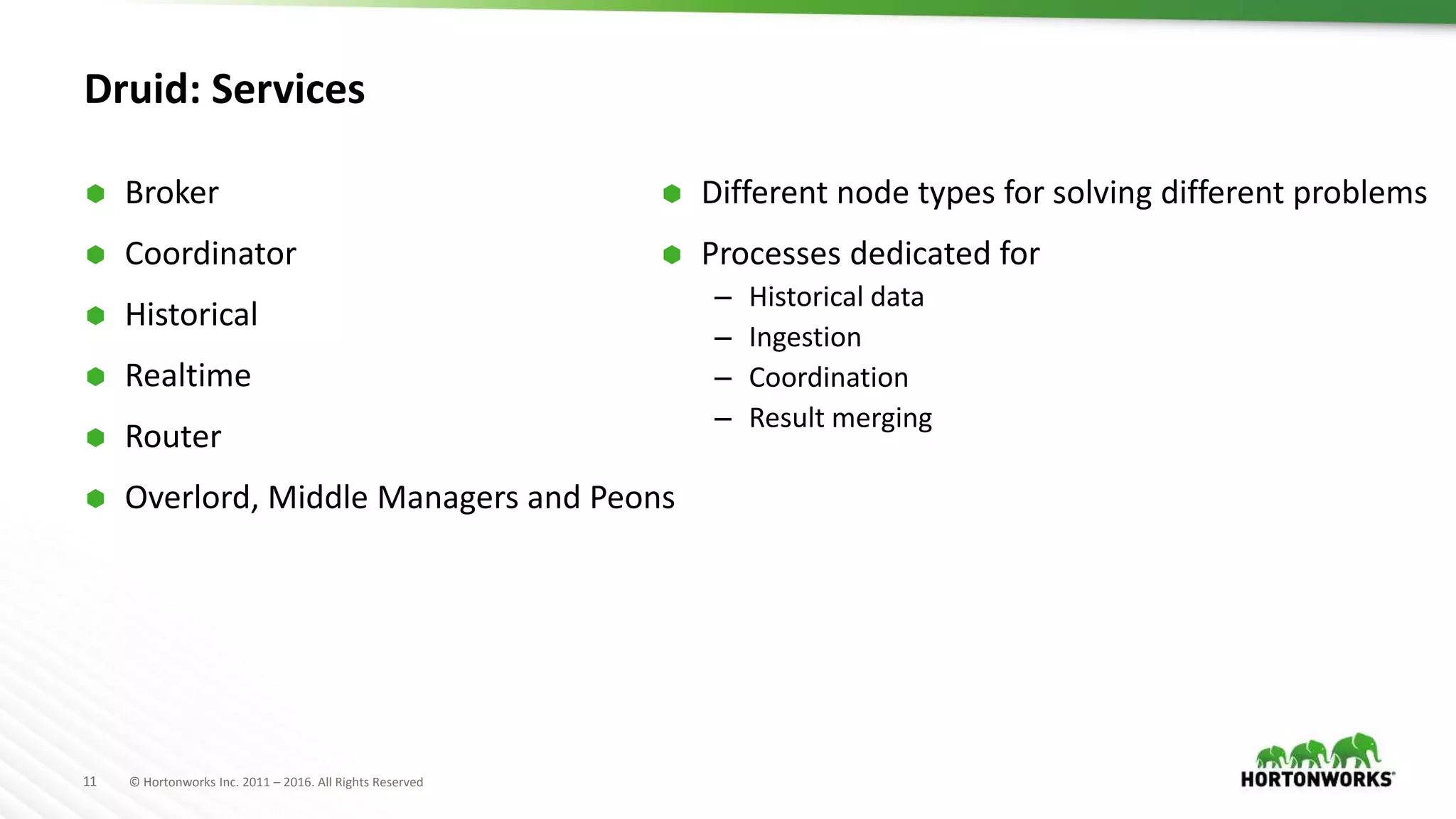
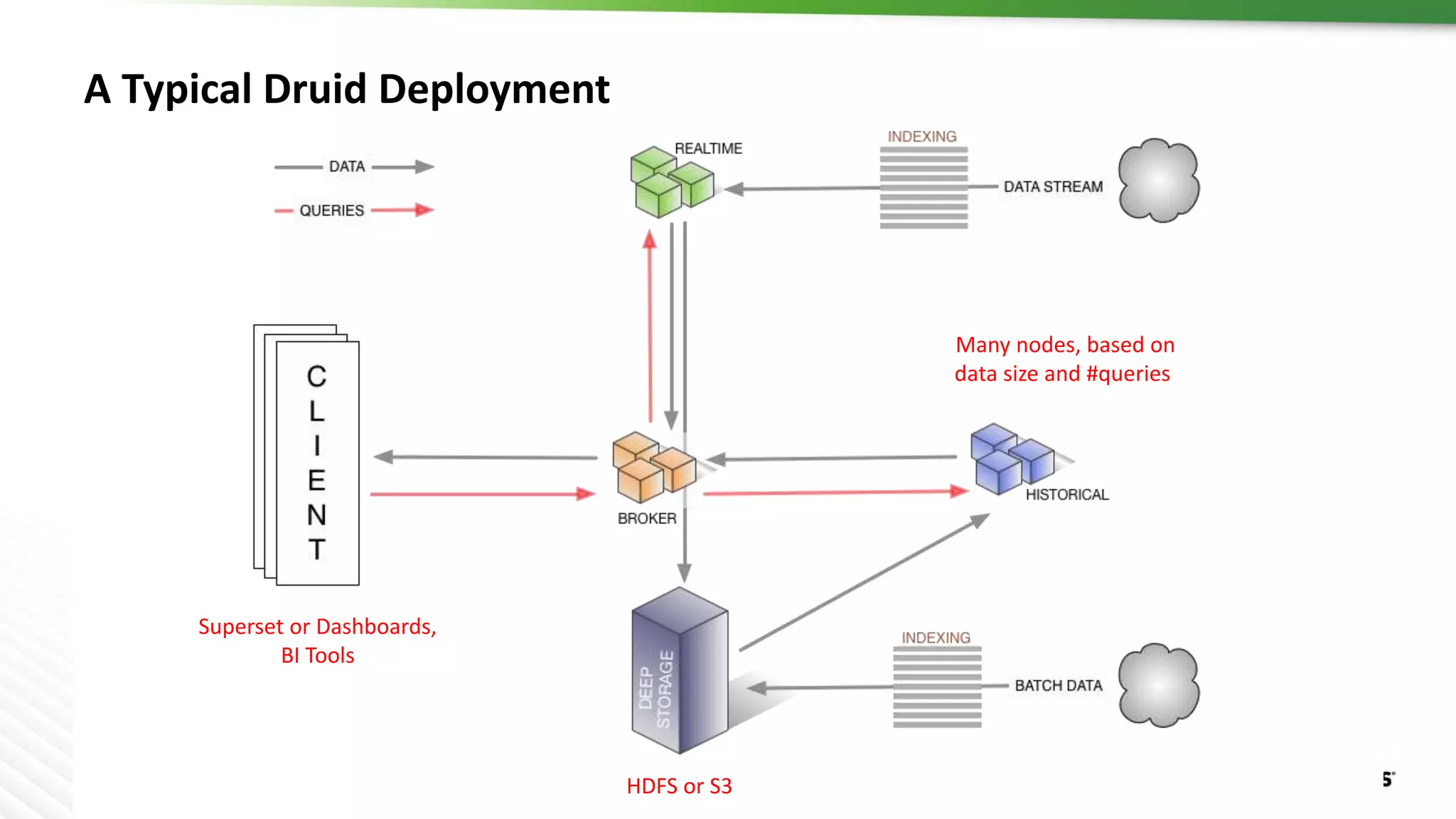
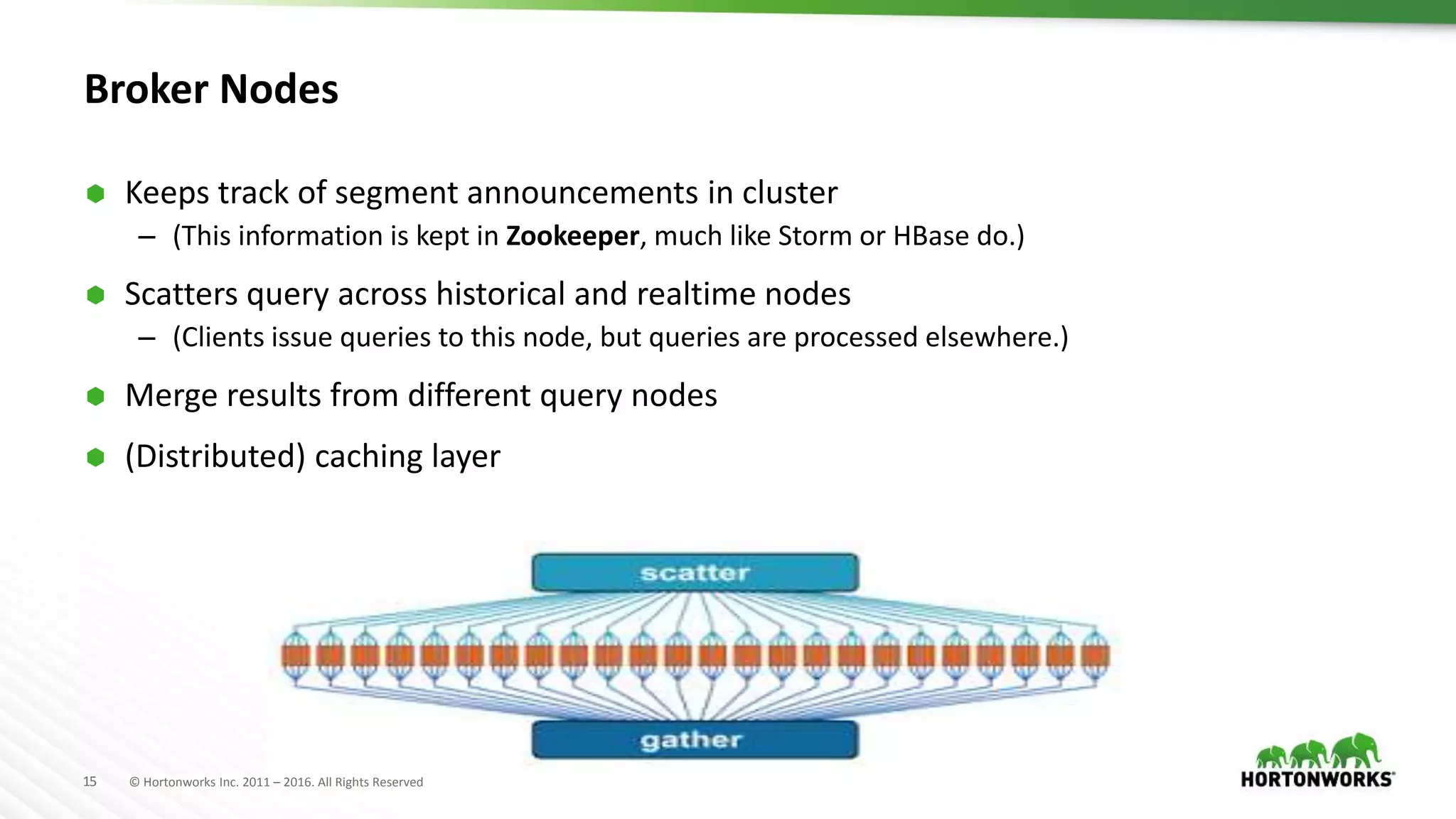
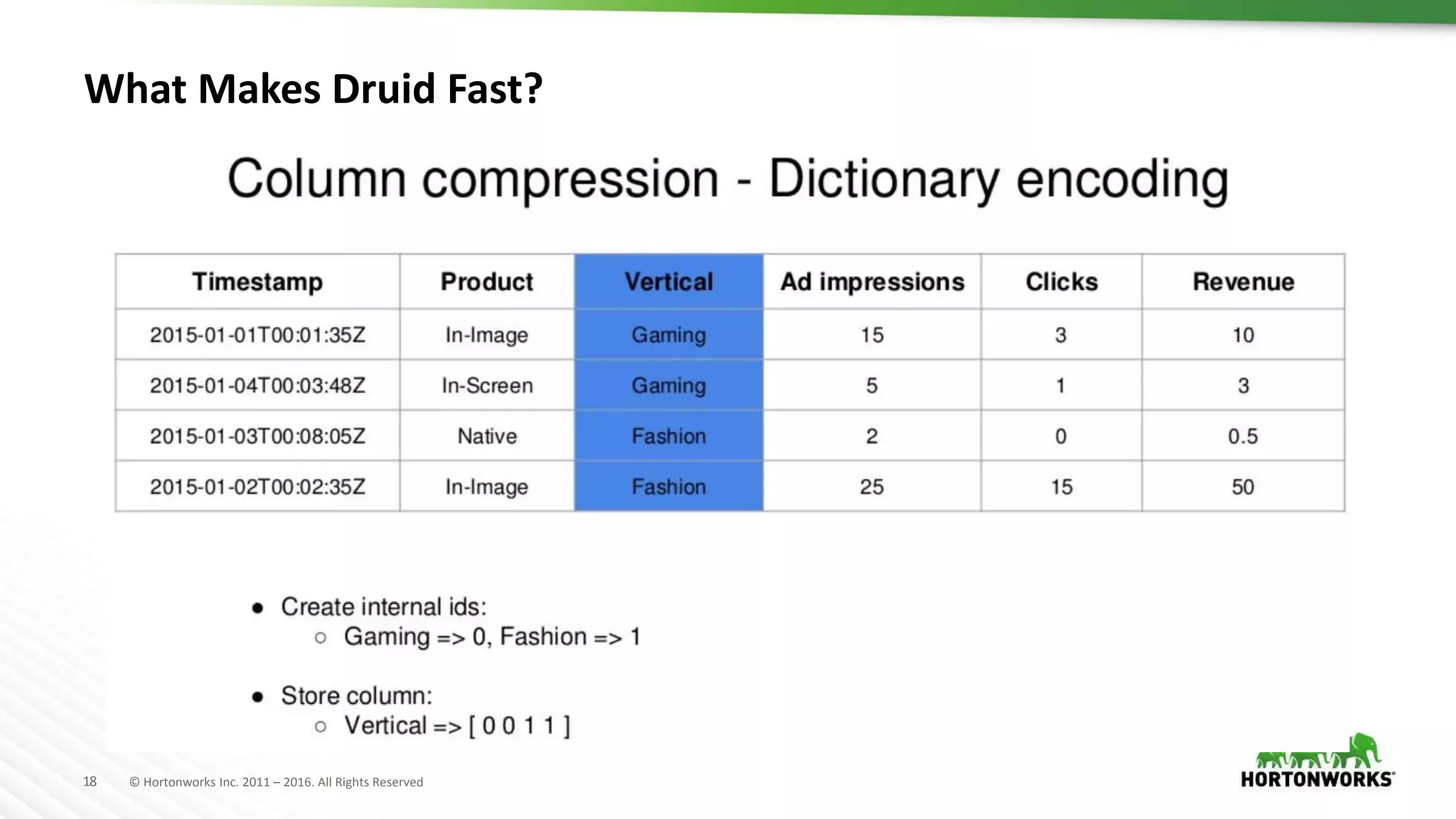
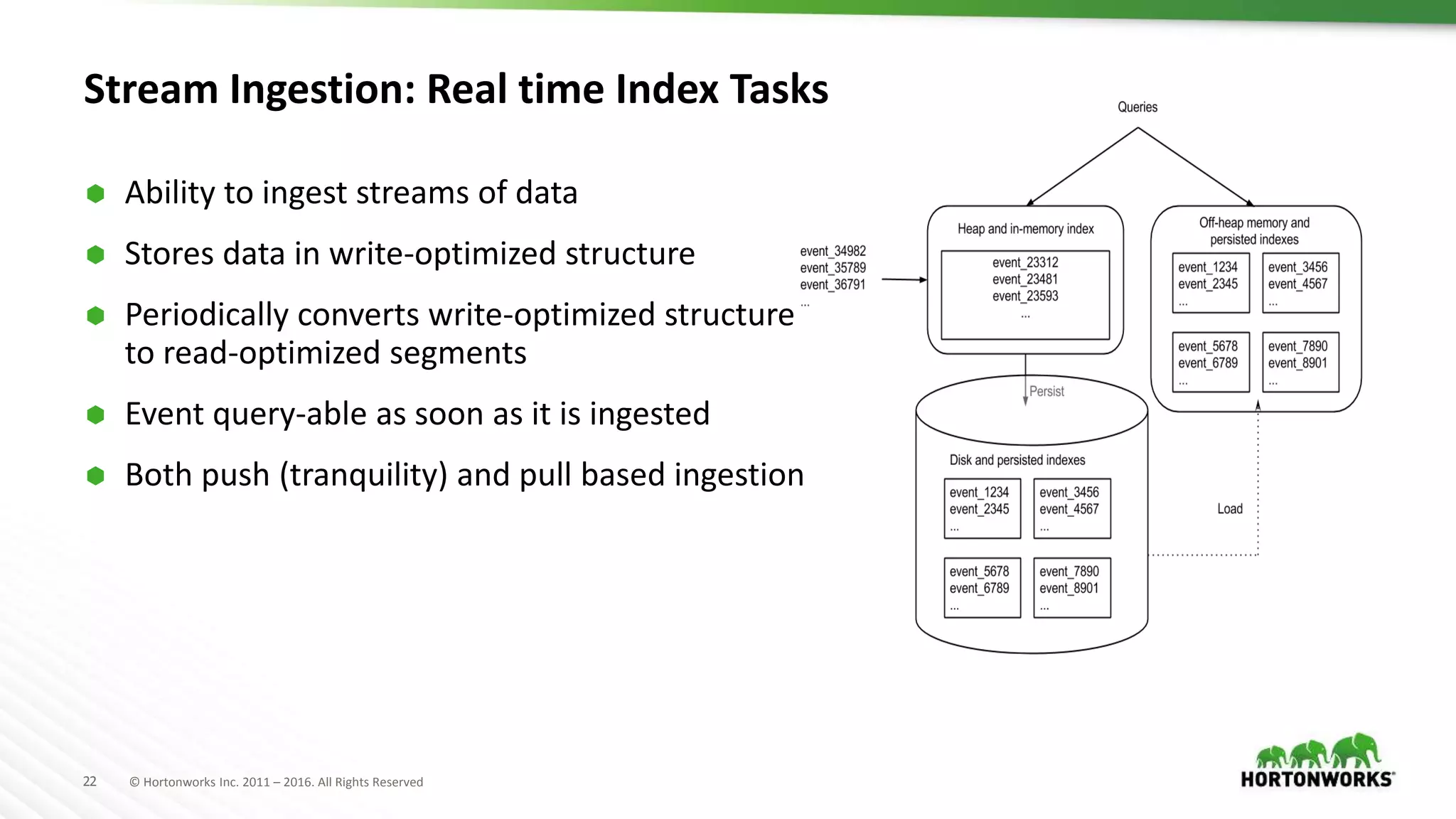
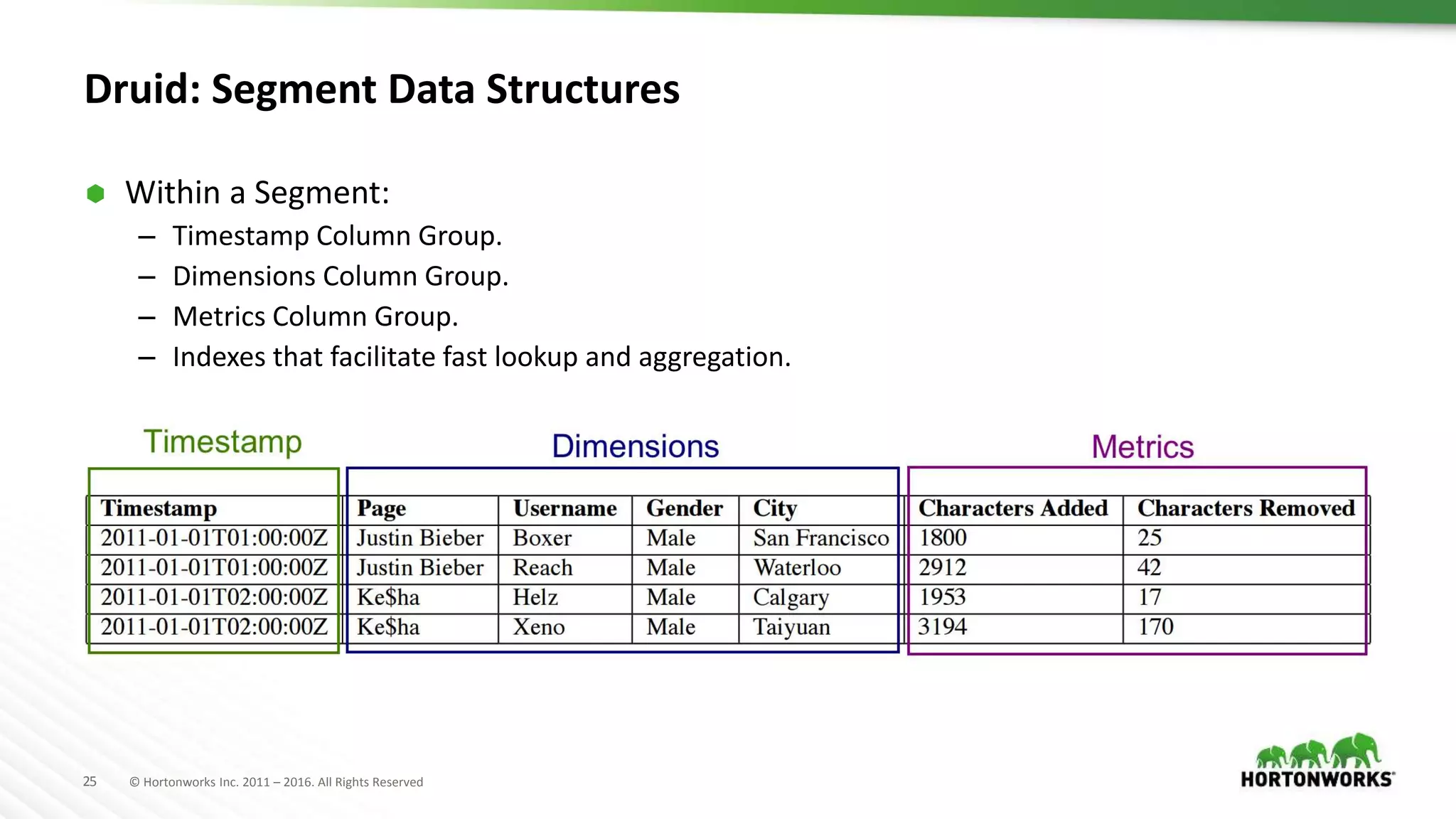
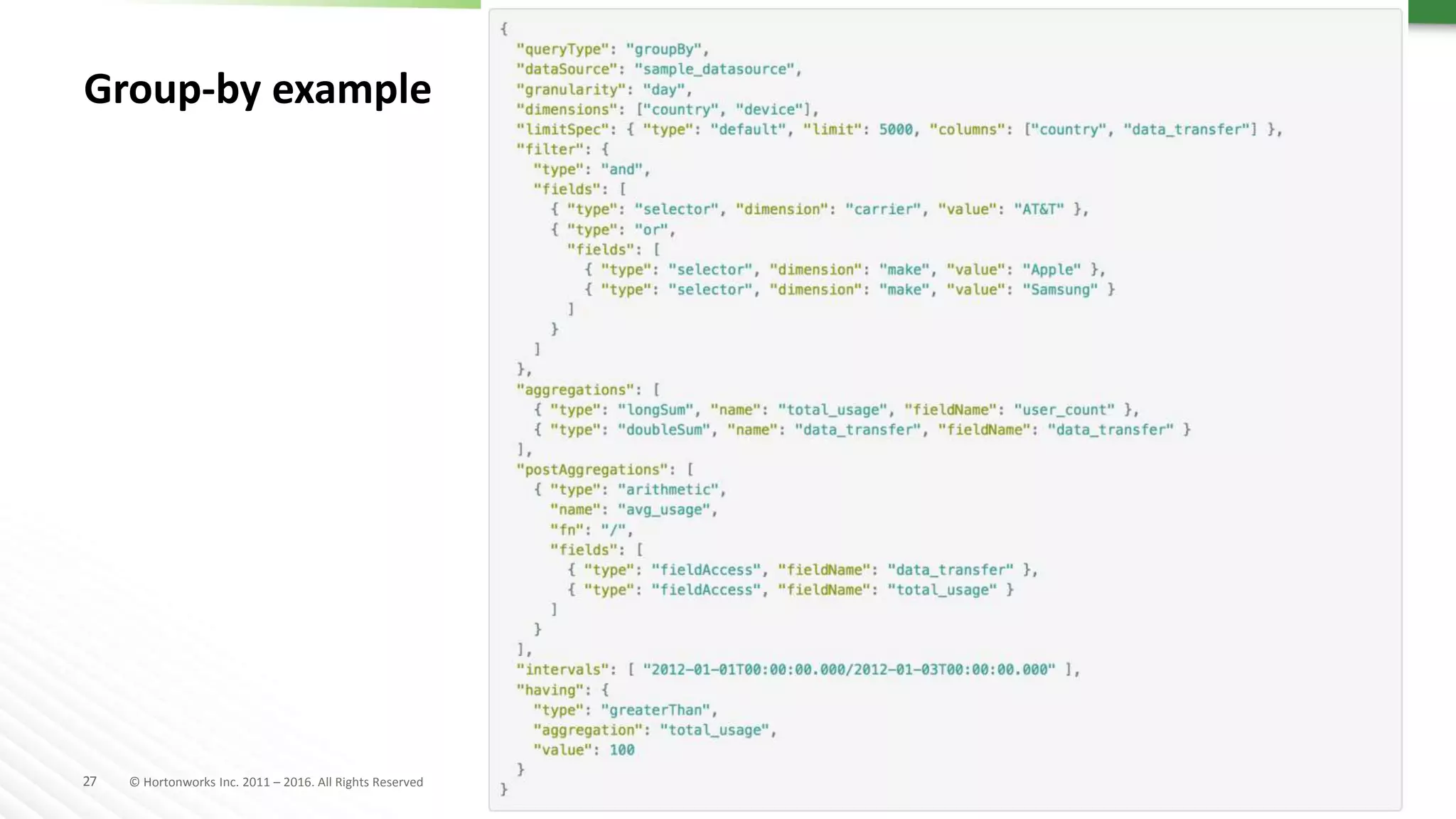
Druid is a distributed, real-time, column-oriented datastore designed for quick ingestion and indexing of large data volumes, enabling real-time analysis. Features include streaming ingestion, low query latency, and scalability for thousands of users, with companies leveraging it for modern streaming architectures. Druid integrates with Hive for enhanced data queries and supports various data ingestion strategies, making it suitable for diverse analytical tasks.