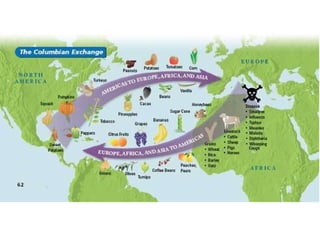
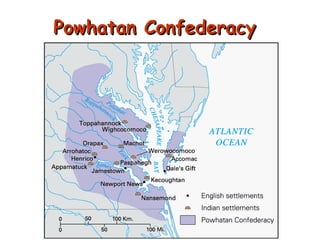
1. The document discusses the motives and methods of European colonization in North America between the 16th and 17th centuries, including the desire for wealth, spreading Christianity, and finding a Northwest Passage to Asia. 2. It examines the establishment of key colonies like Jamestown and Plymouth, which struggled at first but grew prosperous through the introduction of cash crops like tobacco. 3. It also covers the interactions between European colonists and Native Americans like the Powhatan and Pequot tribes, which often led to conflict over land and resources.
















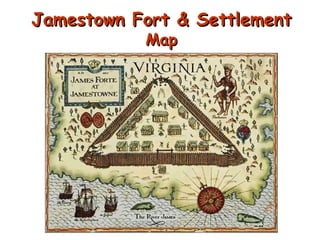
![May 24, 1607 about 100 colonists [all men] land at Jamestown, along banks of James River Easily defended, but swarming with disease- causing mosquitoes. They are ill prepared to the many adjustments to life in the New Colony. Founding of Jamestown](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/colonization-1-1284593341-phpapp01/85/Drugan-Notes-Colonization-19-320.jpg)




















![Indentured Servitude Headright System: Each Virginian got 50 acres for each person whose passage they paid. Indenture Contract: 5-7 years. Promised “freedom dues” [land, £] Forbidden to marry. 1610-1614: only 1 in 10 outlived their indentured contracts!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/colonization-1-1284593341-phpapp01/85/Drugan-Notes-Colonization-43-320.jpg)








![Puritanism Calvinism The English followers of John Calvin were known as Puritans Predestination. Good works could not save those predestined for hell . No one could be certain of their spiritual status. Puritans : Want to totally reform [purify] the Church of England. Grew impatient with the slow process of Protestant Reformation back in England.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/colonization-1-1284593341-phpapp01/85/Drugan-Notes-Colonization-54-320.jpg)



![1620 a group of 102 people [half Separatists] Negotiated with the Virginia Company to settle in its jurisdiction. Plymouth Bay way outside the domain of the Virginia Company . Became squatters without legal right to land & specific authority to establish a govt. The Mayflower](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/colonization-1-1284593341-phpapp01/85/Drugan-Notes-Colonization-58-320.jpg)



![The Massachusetts Bay Colony 1630 1,000 people set off in 11 well-stocked ships Established a colony with Boston as its hub. “ Great Migration” of the 1630s Turmoil in England [leading to the English Civil War] sent about 70,000 Puritans to America . Not all Puritans 20,000 came to MA. The Great Migration was one of the largest migrations in history .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/colonization-1-1284593341-phpapp01/85/Drugan-Notes-Colonization-62-320.jpg)





![Intelligent, strong-willed, well-spoken woman. Threatened patriarchal control. Anti-nomialism [direct revelation] Believed faith and God’s grace could save you as opposed to the observance of moral law and performance of good deeds. Holy life was no sure sign of salvation. Anne Hutchinson](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/colonization-1-1284593341-phpapp01/85/Drugan-Notes-Colonization-68-320.jpg)

![Indians especially weak in New England epidemics wiped out ¾ of the native population. Wampanoags [near Plymouth] befriended the settlers . Cooperation between the two helped by Squanto . 1621 Chief Massasoit signed treaty with the settlers. Autumn, 1621 both groups celebrated the First Thanksgiving. Puritans vs. Native Americans](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/colonization-1-1284593341-phpapp01/85/Drugan-Notes-Colonization-70-320.jpg)




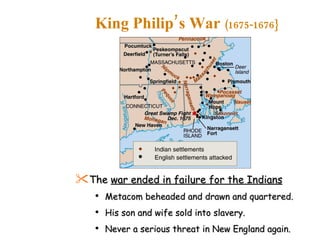
![Only hope for Native Americans to resist white settlers was to UNITE. Metacom [King Philip to white settlers] Tried to unite Indians and staged coordinated attacks on white settlements throughout New England. Frontier settlements forced to retreat to Boston. King Philip’s War (1675-1676}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/colonization-1-1284593341-phpapp01/85/Drugan-Notes-Colonization-75-320.jpg)




![New Netherlands New Netherlands founded in the Hudson River area (1623-1624) Established by Dutch West India Company for quick-profit fur trade. Aristocratic patroonships [feudal estates granted to promoters who would settle 50 people on them]. Charles II granted New Netherland’s land to his brother, the Duke of York. Renamed “New York”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/colonization-1-1284593341-phpapp01/85/Drugan-Notes-Colonization-81-320.jpg)

