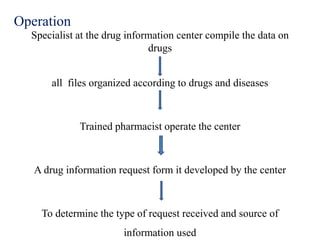
This document discusses the need for and organization of drug information centers. It notes that the number and complexity of drugs has increased, making it difficult for medical professionals to stay up to date. Drug information centers aim to provide objective, documented data about drugs to support rational drug use and improve patient care. They gather, organize and distribute drug information to health professionals and consumers. The document outlines the functions, sources of information, staffing, funding, and operations of drug information centers.