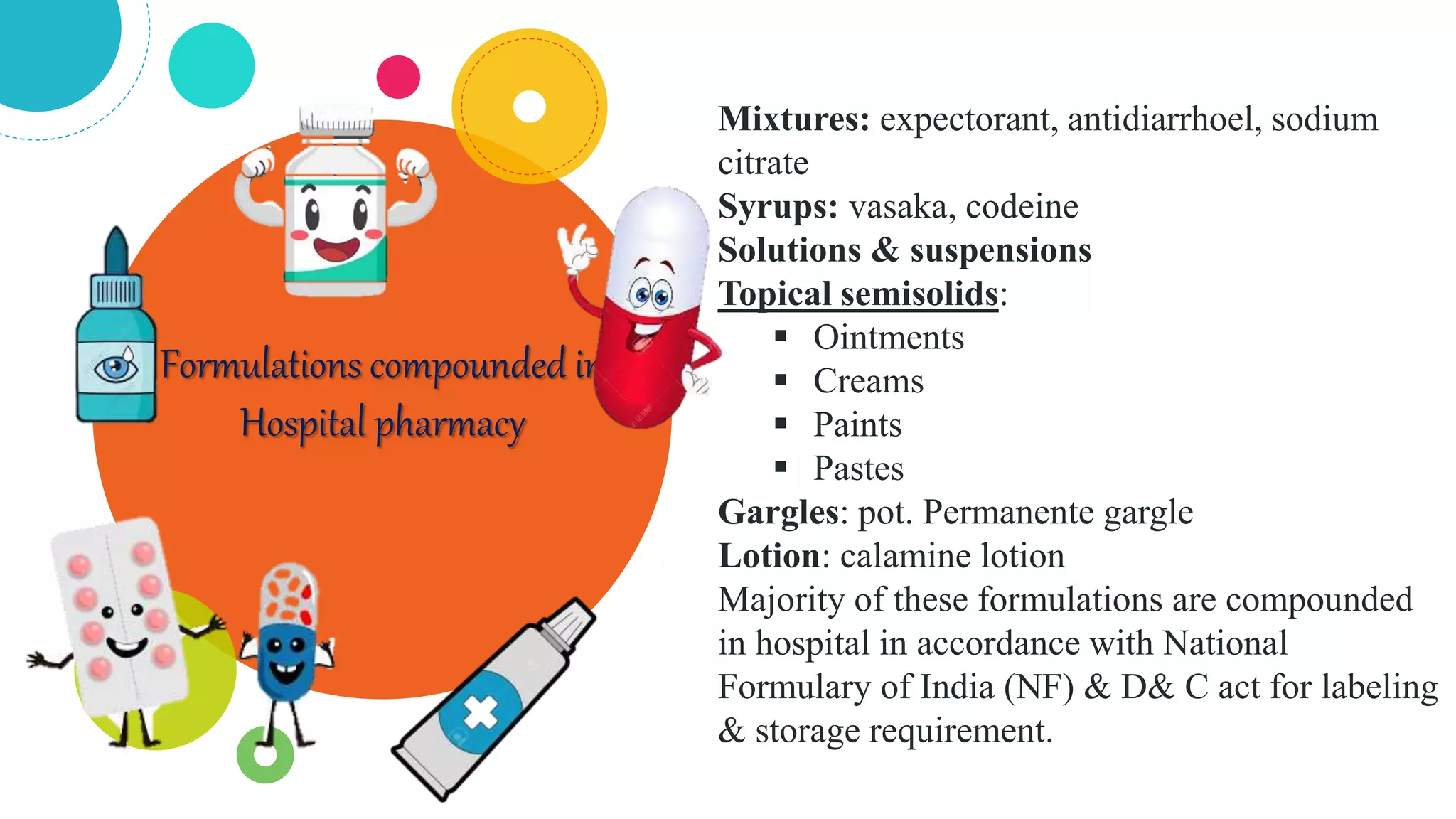
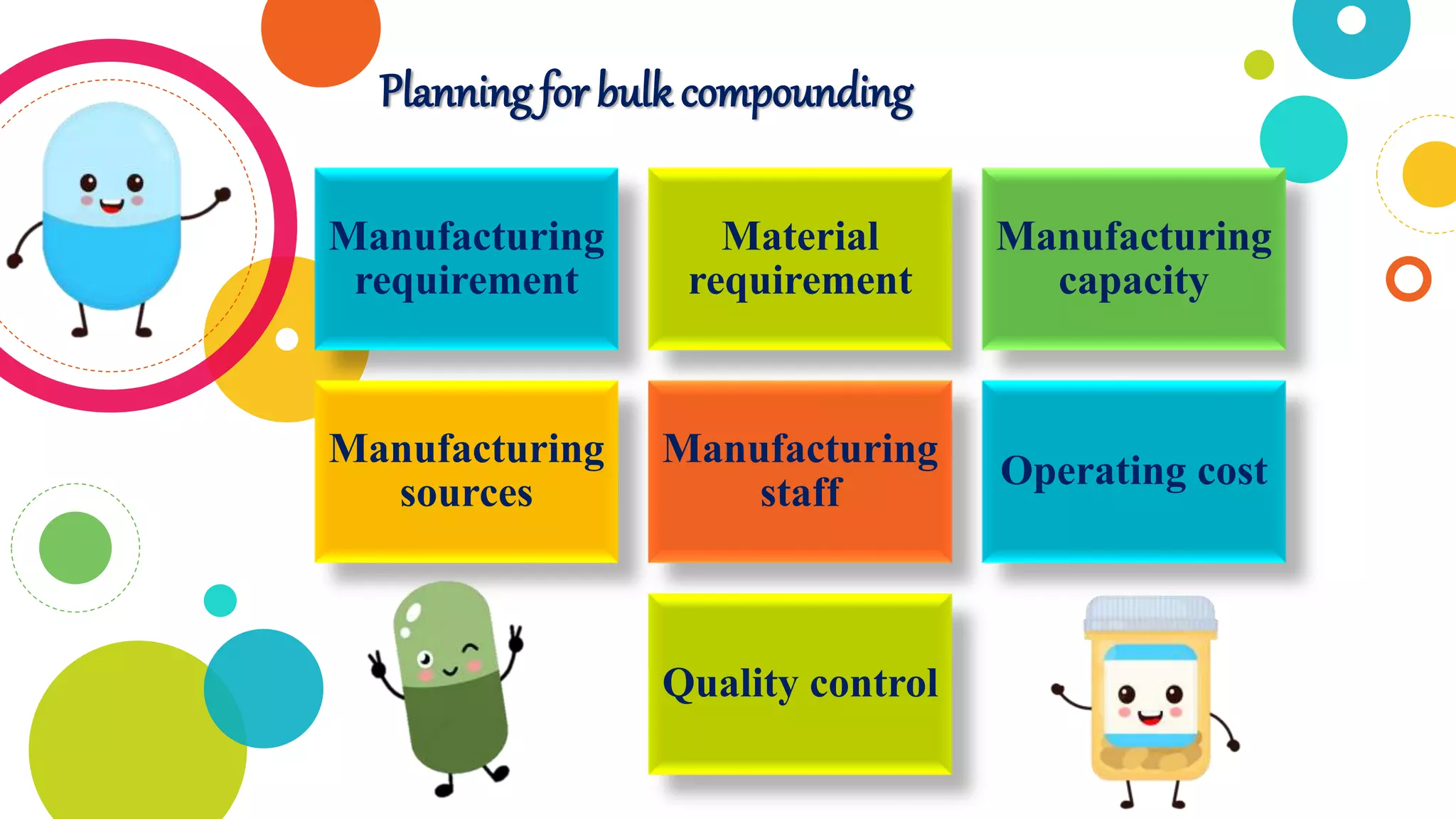
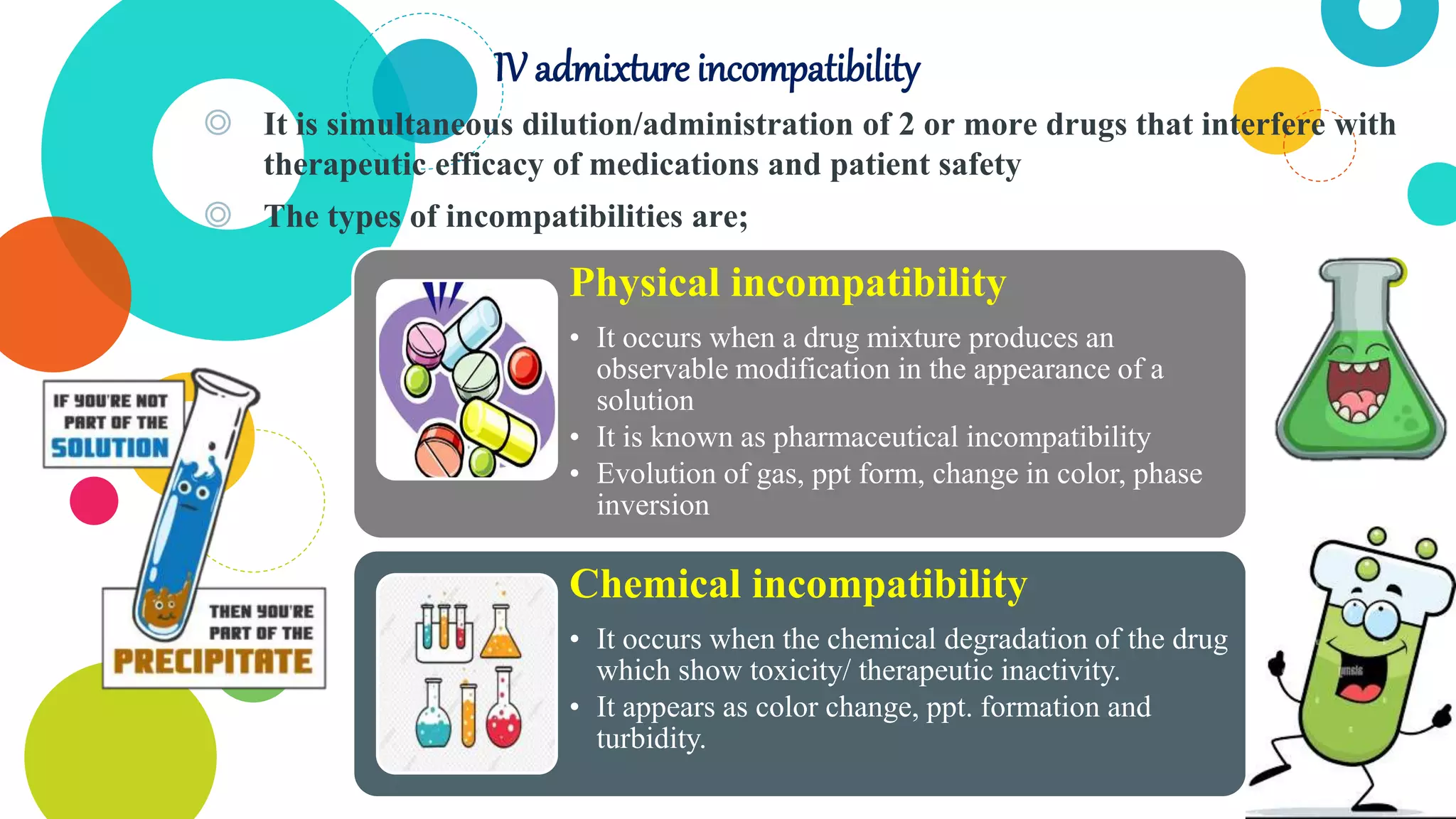
The document discusses the compounding of medications in hospital pharmacies, detailing the preparation of customized formulations for patients with unique health needs that cannot be met by commercially available products. It outlines the importance of sterile conditions for IV admixture preparations and the processes to avoid medication errors and incompatibilities. Additionally, it explains Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN) for patients unable to ingest nutrients traditionally, highlighting its components and indications for use.