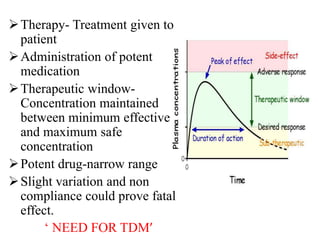
This document discusses therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM), which involves measuring drug concentrations in patients to optimize drug therapy and dosing. TDM is needed because treatment involves potent drugs with narrow therapeutic windows, and patient factors can cause pharmacokinetic variability. Drugs that often require TDM include cardiac drugs, antiepileptics, bronchodilators, immunosuppressants, anti-cancer drugs, and psychiatric drugs. TDM helps manage therapy by identifying non-compliance or toxicity issues based on a patient's drug concentration levels. Factors like dosage, impairment, interactions, and individual pharmacokinetics must be considered when interpreting TDM results.