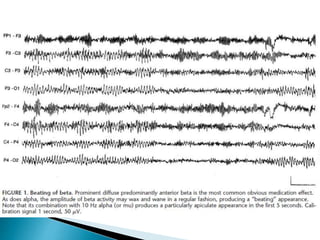
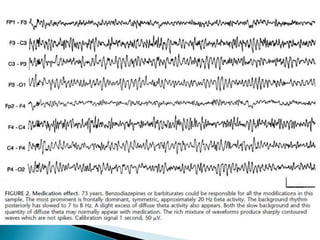
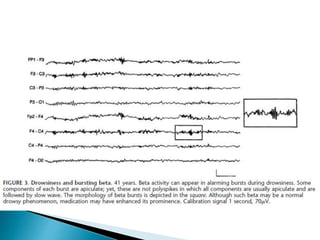
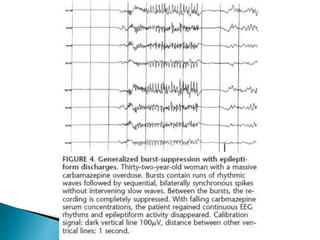
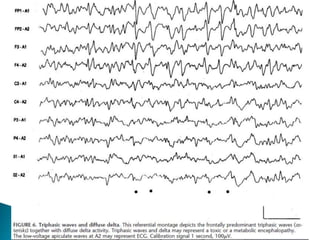
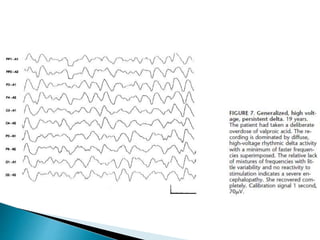
The document discusses how different drugs can affect EEG interpretation. It notes that the quantity of medication in a patient influences the EEG, depending on factors like dose and metabolism. It provides examples of specific drugs that may elicit different EEG patterns, such as background slowing with phenytoin, excess beta with GABA agonists like barbiturates and benzodiazepines, epileptiform activity, triphasic waves, theta and delta activity, and coma patterns. Certain medications are also more likely to produce beta activity in children versus adults or with acute versus chronic use. Very high doses of some medications can cause spikes or polyspikes. Diffuse delta and excess theta may indicate neurotoxicity associated with certain anti-