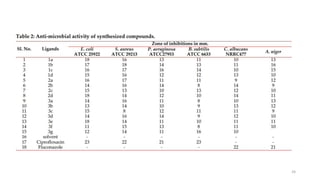
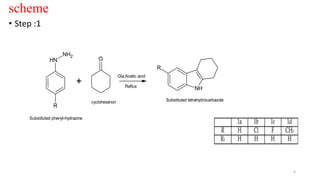
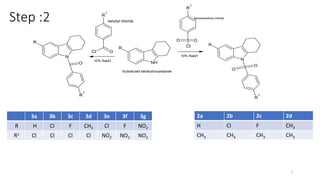
The document summarizes the synthesis and characterization of N-substituted tetrahydrocarbazole compounds and their molecular docking studies and antibacterial evaluation. Key steps included synthesizing substituted tetrahydrocarbazoles via refluxing cyclohexanone with substituted phenylhydrazines. The tetrahydrocarbazoles were then reacted with substituted acid chlorides to obtain N-substituted derivatives. The derivatives were characterized using techniques like NMR, IR and tested for antibacterial activity against pathogens using the agar cup method. Molecular docking studies of the derivatives were performed targeting the Gln-6-p enzyme to understand binding interactions.













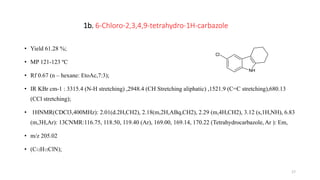
![2a: 9-[(4-methylphenyl)sulfonyl]-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1Hcarbazol
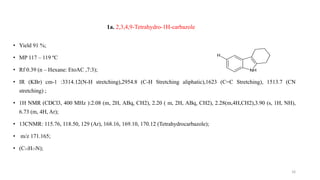
• Yield 61%;
• MP 322- 323 ºc
• Rf 0.86 (n-hexane EtoAC, 7:3) ;
• IR KBrcm-1 :3018.45(C-H aromatic Stretching) ,2856.78 (C-H aliphatic stretching),1601.78 (C=C aromatic
stretching),1346.67(O =S = O Stretching)
• 1 H NMR ( CDCl3 , 400 MHz);2.28 (m, 4H, CH2), 2.08 (m, 2H, ABq, CH2), 1.35 (t, 3H, CH3), 2.20 (m, 2H,
ABq, CH2), 6.83 (m, 4H, Ar), 7.95(m, 4H, Ar); 13CNMR (CDCl3, 125MHz); 17.30, 18.90, (CH3), 21.96,
22.30, 30.15 (aliphatic), 114.76, 117.89, 127.10 (Ar), 167.13, 170.12, 171.14 (Tetrahydracarbazole Ar).
• m/z 328.76 (C19H19NO2S);
20
N
H
S
O
O
CH3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/journalclub2presentation-230603050051-f0b10ae3/85/Journal-Club-Presentation-20-320.jpg)
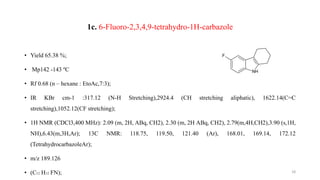
![2b: 6-chloro-9-[(4-methylphenyl)sulfonyl]-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole
• Yield 61%;
• MP : 338-340 ºC
• Rf 0.91 (n-hexane EtoAC,7:3)
• IR KBr cm-1 : 2950.68 (C-Haromatic stretching), 2876.98 (C-H aliphatic stretching), 1627.34 (C=C aromatic
stretching), 1334.74 (O=S=O Stretching), 735.78(C-Cl stretching) :
• 1H NMR (CDCl3 , 400 M Hz);2.21(m,4H,CH2), 2.08 ( m,2H, ABq ,CH2) 1. 25 (t,3 H, CH3), 2.10
(m,2H,ABq,CH2), 6.23 (m 3H , Ar ), 7.85 (m, 4H,Ar).13C NMR ( CDCl3,125 M Hz)16.90,17.56, 18.30
(CH3), 22.30,30.15( aliphatic), 114.96, 116.89, 128.10 (Ar) 166.13, 169.12, 171.15 ( Tetrahydracarbazole Ar).
• m/z 358.76 (C19H18 ClNO2S);
21
N
Cl
S
O
O
CH3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/journalclub2presentation-230603050051-f0b10ae3/85/Journal-Club-Presentation-21-320.jpg)
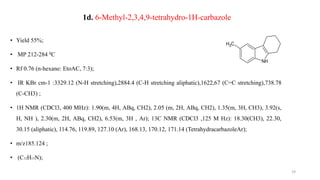
![2d: 6-methyl-9-[(4-methylphenyl)sulfonyl]-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole
• Yield 61%;
• MP 346- 348ºC
• Rf 0.91(n-hexane EtoAC 7:3);
• IR KBrcm-1 :3111.18(C-H aromatic Stretching), 2956.13 (C-H aliphatic stretching), 1537.98 (C=C aromatic
stretching),1426.87(O=S=OStretching),924.24(CCH3Stretching);
• 1HNMR (CDCl3, 400MHz); 2.35(m,4H,CH2), 2.38(m,2H,ABq ,CH2)1.72(t,3H,CH3),1. 25 (t,3 H, CH3) ,
2.20 (m, 2H, ABq, CH2), 6.73 (m 3H , Ar ), 7.35 (m, 4H,Ar) 13C NMR (CDCl3 , 125 M Hz)17.34,19.30
(CH3), 22.30, 24.37, 30.15(aliphatic), 114.76, 124.89, 127.10 (Ar), 168.13, 169.12, 171.14 (
Tetrahydracarbazole Ar).
• m/z 339.76 (C20 H21FNO2S);
22
N
C
H3
S
O
O
CH3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/journalclub2presentation-230603050051-f0b10ae3/85/Journal-Club-Presentation-22-320.jpg)