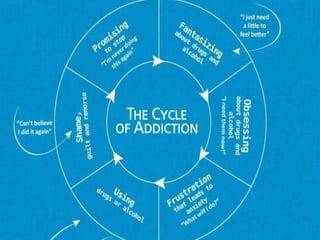
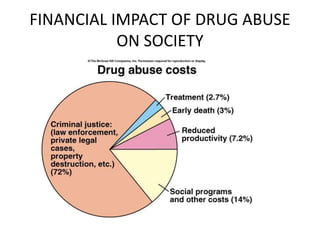
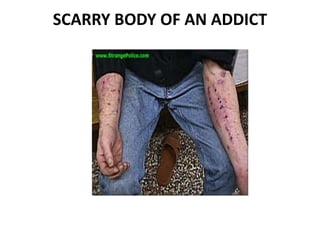
People use drugs for several reasons, including peer pressure, thrill-seeking, and to self-medicate emotional needs. Addiction is now recognized as a chronic relapsing brain disease, characterized by compulsive drug use despite negative consequences. It progresses through stages as tolerance increases and brain changes persist for years after drug use. While drugs can have medical benefits when properly used, drug abuse has significant health and social costs, including increased crime and family problems. Education and treatment aim to prevent misuse and support recovery from addiction.