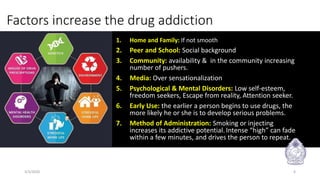
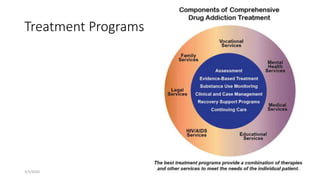
Dr. Chamendra Ranasinghe presented information on drug addiction and its consequences over 25 slides. The document discusses how drug addiction affects the brain and behavior, outlines the phases of drug addiction from experimentation to regular use, and examines the medical, social, economic, and legal impacts of drug addiction at both individual and community levels. It also addresses myths about addiction and recovery, risk factors for youth, and the importance of treatment programs, education, legislation, and community support in preventing and addressing drug abuse issues.