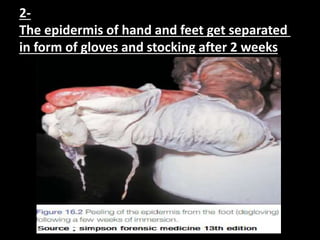
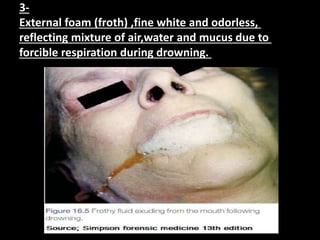
Drowning can result from natural causes, injuries, hypothermia, or true aspiration of water into the lungs. There are three main types of drowning: wet where water is inhaled, dry where water is not inhaled but laryngeal spasm occurs, and secondary where brain damage causes death hours to days later. Drowning is a major public health problem worldwide, especially in low and middle income countries, and is more common in males than females of all ages. Signs of drowning include washer-woman hands, separated skin on hands and feet, lung emphysema, and diatom presence in organs. Alcohol is frequently present in adult drowning victims and can exacerbate injuries or hasten hyp