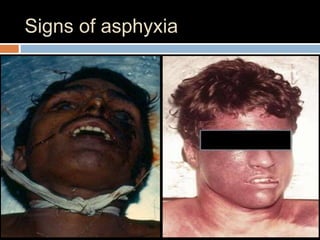
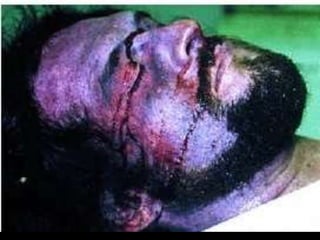
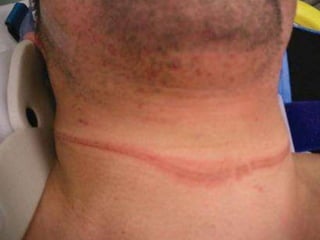
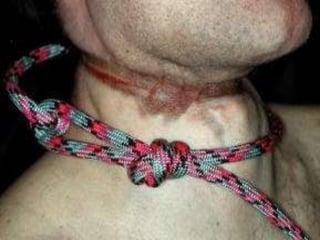
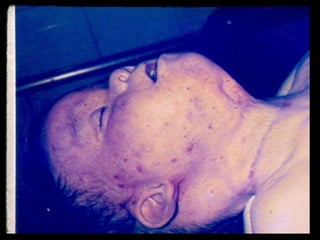
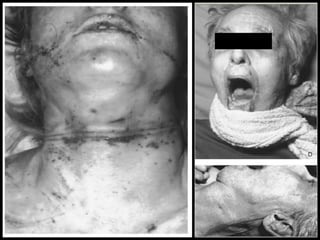
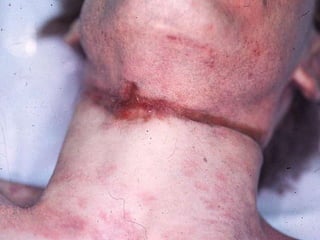
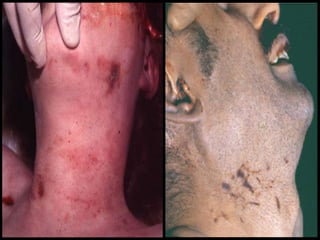
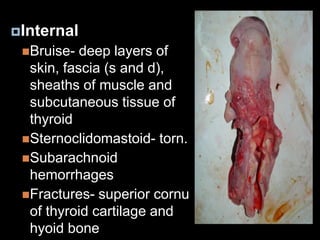
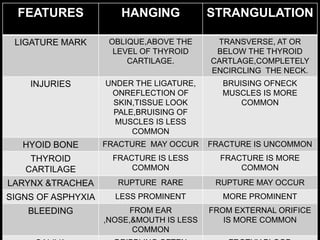
This document discusses strangulation, including definitions, types, signs of asphyxia, ligature strangulation, manual strangulation, and hyoid bone fractures. It defines mechanical asphyxia and anoxia. Types of strangulation include ligature, throttling, garroting, mugging, and bansdola. Signs of asphyxia include cyanosis, facial swelling, bulging eyes, swollen tongue, bloodstained froth, clenched hands, and ligature marks. Ligature strangulation involves external constriction of the neck by materials like rope or wire. Manual strangulation involves compression of the neck by hands, which can cause hyoid bone or thyroid cartilage fractures. The document outlines differences between