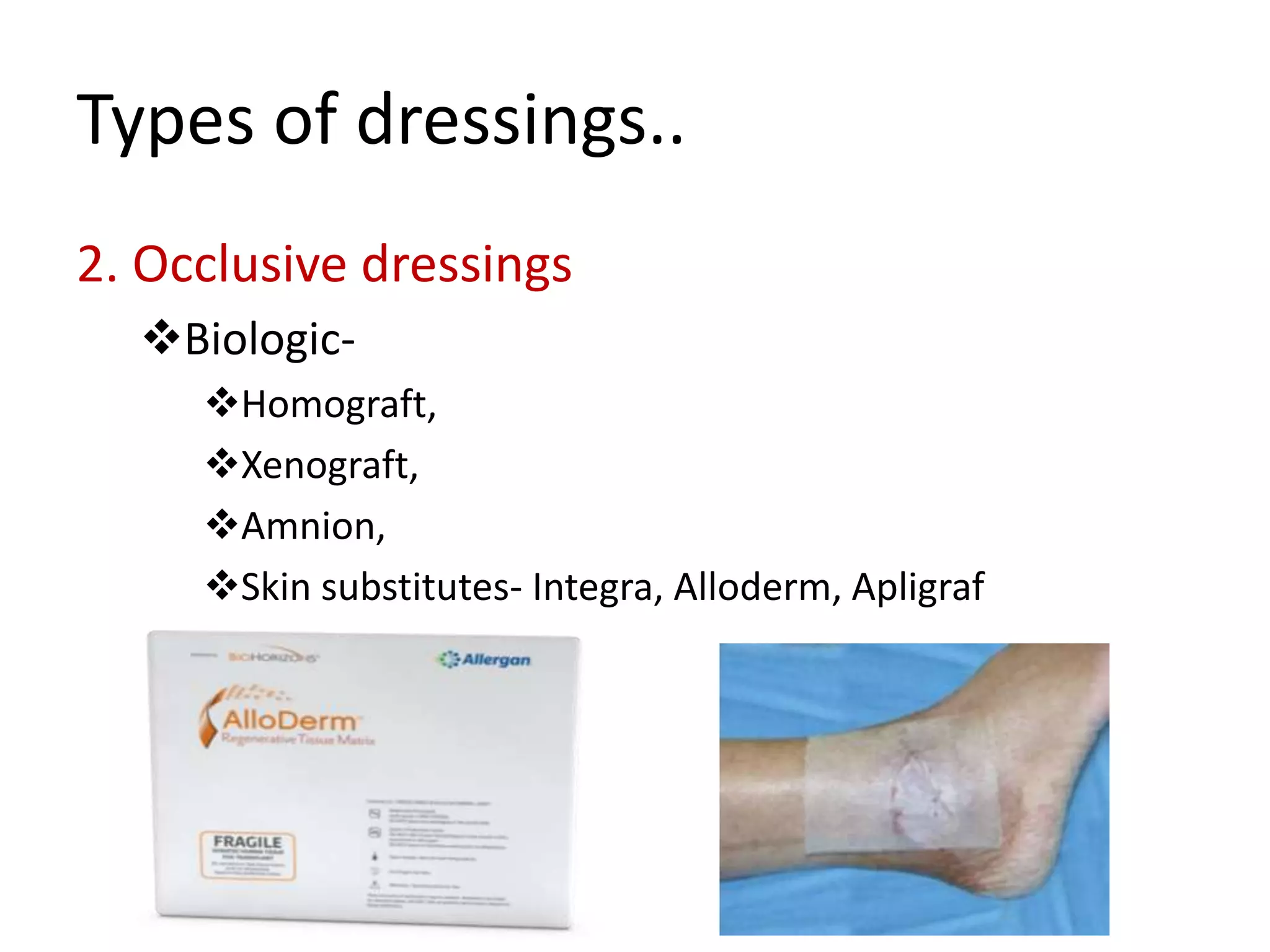
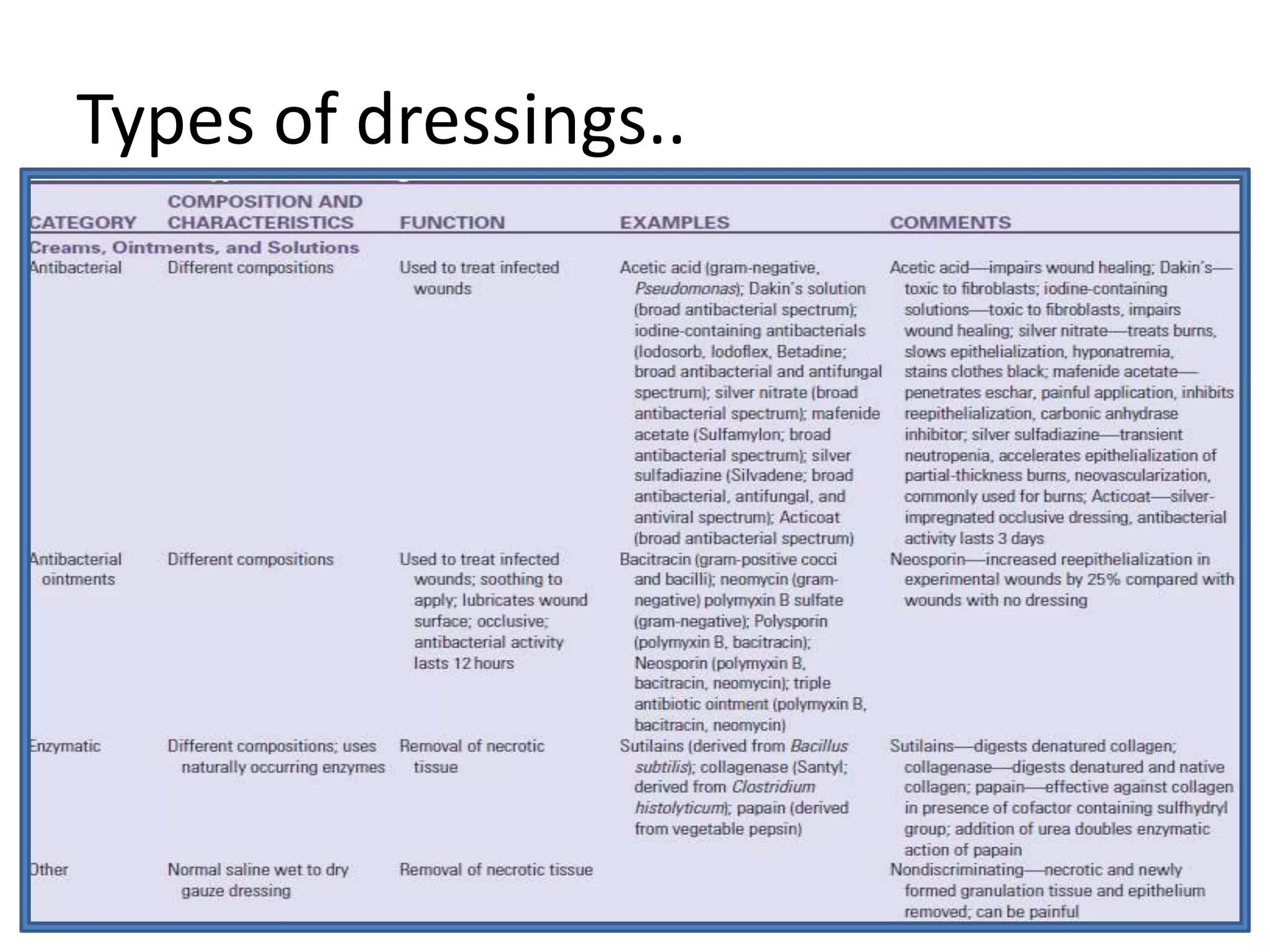
Surgical dressings are sterile pads or compresses applied to wounds to promote healing. Their history dates back to ancient Egyptians using honey and Greeks using vinegar and fig leaves. Joseph Lister introduced antiseptic dressings in the 1860s. Ideal dressings create a moist environment, remove exudate, allow gas exchange, and protect from contamination. Selection depends on whether occlusion or absorption is needed. Dressings are classified as simple like gauze or composite with layers. Common types include non-adherent fabrics, absorptive foams and gauzes, and occlusive films, hydrocolloids, alginates, and hydrogels. Creams, ointments and solutions are also