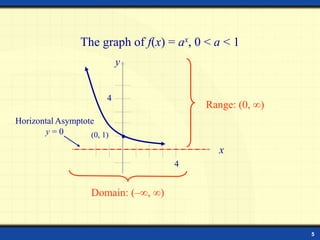
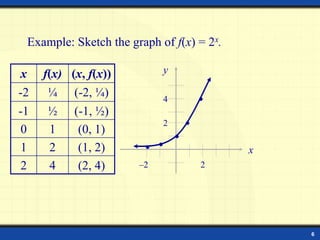
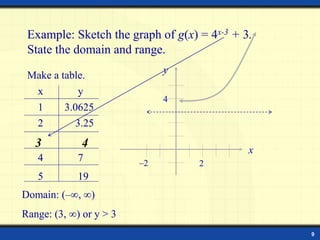
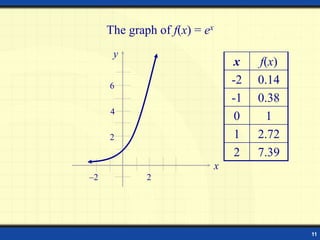
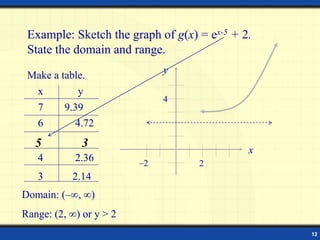
This document discusses exponential functions and their graphs. It defines the exponential function f(x) = ax and gives examples. It shows how to evaluate exponential functions at different values of x. It explains the graphs of exponential functions with bases greater than and less than 1, and how they have horizontal asymptotes at y = 0. It provides examples of sketching graphs of exponential functions and stating their domains and ranges. It introduces the irrational number e and the natural exponential function f(x) = ex. It concludes with formulas for compound interest and an example problem.