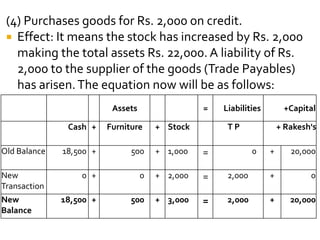
The accounting equation is a fundamental expression in accounting that equates assets to liabilities plus owner's equity. It is based on the dual aspect principle where every transaction affects at least two accounts. The accounting equation must always balance, meaning the total assets must equal the total claims on assets (liabilities plus equity). The document provides examples of transactions and their impact on the accounting equation to illustrate how it is used to track the financial activities of a business.





![Assets = Liabilities + Capital+ [(Revenue-
Expenses)- dividends]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptsonaccountingequation-240404141510-f2be3338/85/PPTs-on-Accounting-Equation-for-beginners-pptx-11-320.jpg)
