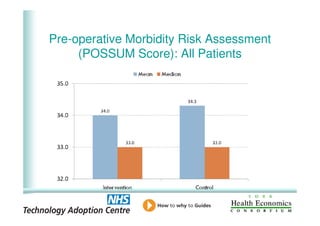
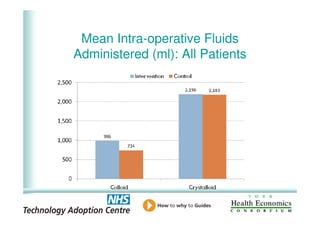
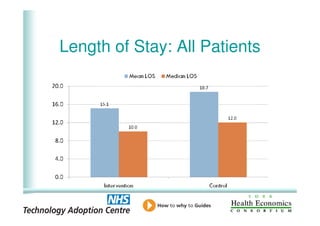
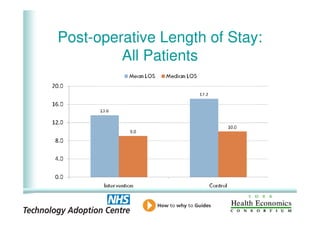
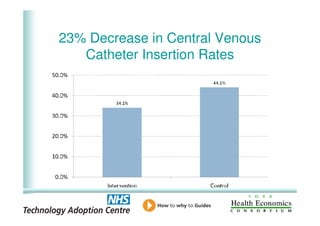
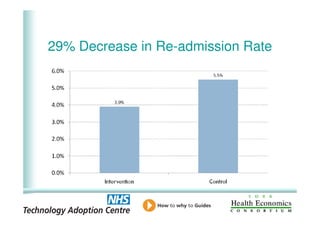
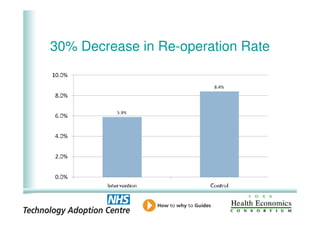
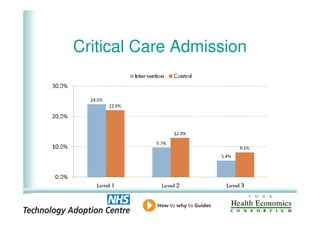
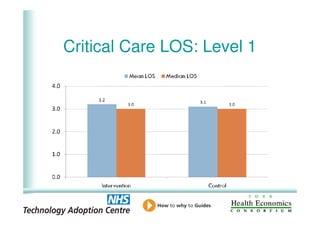
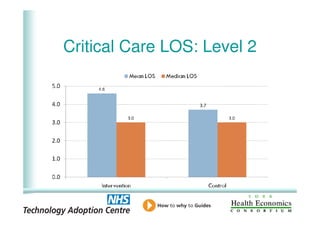
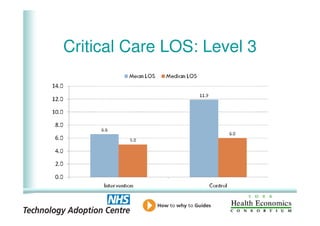
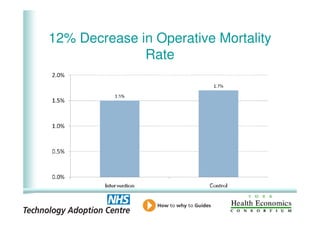
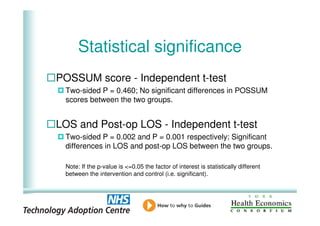
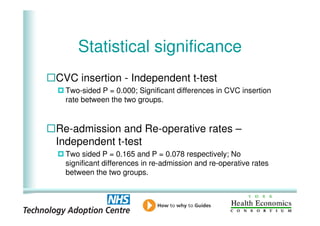
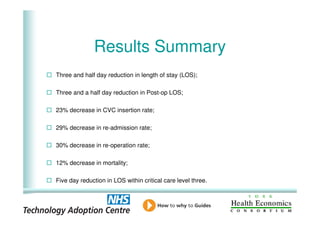
This document analyzes data from a study comparing intraoperative fluid management with Doppler guidance versus standard care without guidance between 2007-2009 across three hospitals. The Doppler-guided group (n=649) had significantly reduced length of stay, post-operative length of stay, central venous catheter insertion rates, and mortality rates compared to the control group (n=658) who received standard care. There were no significant differences between the groups in re-admission rates, re-operation rates, or critical care length of stay.