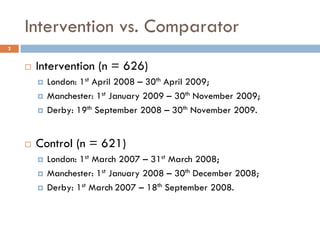
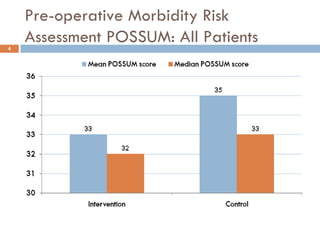
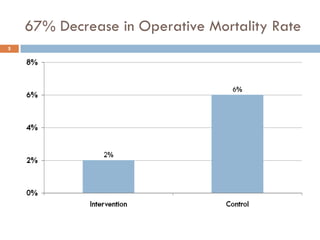
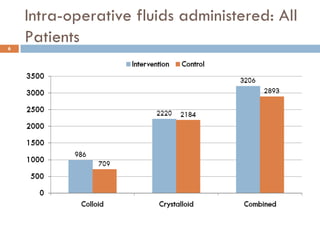
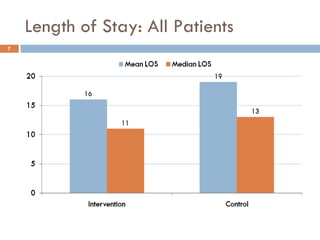
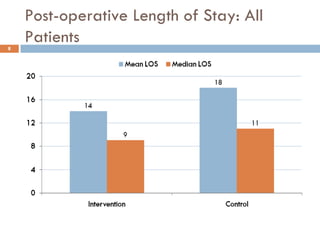
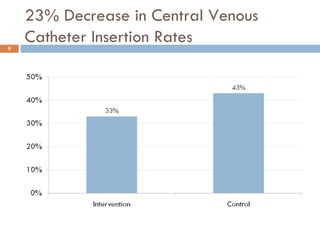
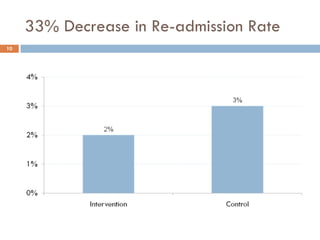
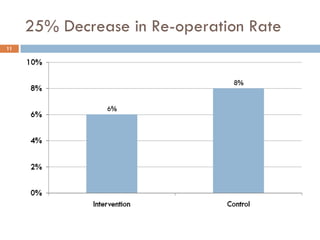
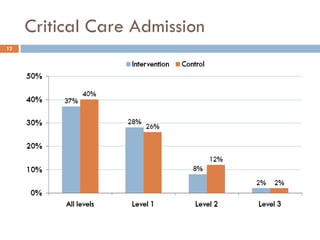
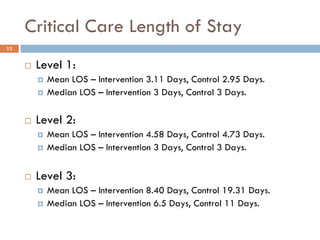
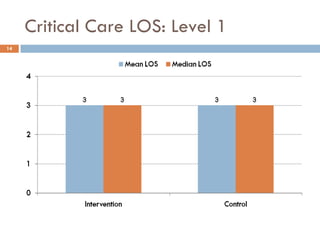
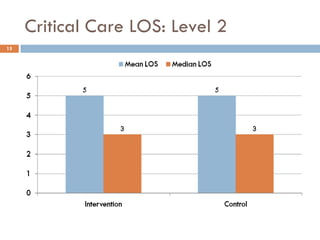
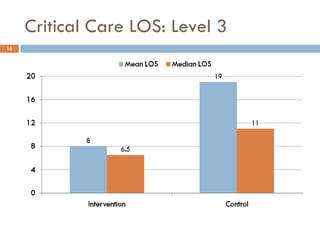
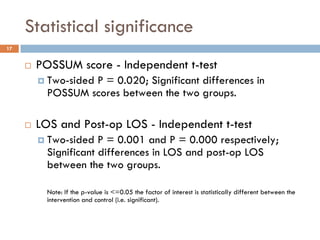
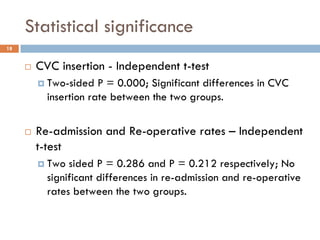
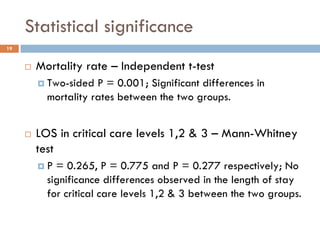
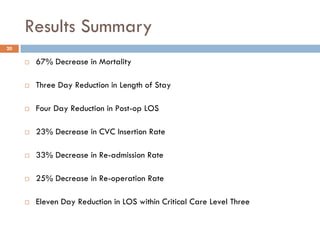
This document analyzes data from a study comparing Doppler guided intraoperative fluid management (intervention) to standard care (control) in surgical patients. Key findings include: a 67% decrease in operative mortality rate, reductions of 3 days in length of stay and 4 days in post-operative length of stay, and decreases of 23% in central venous catheter insertion rates, 33% in re-admission rates, and 25% in re-operation rates with the intervention. Length of stay in the highest level of critical care was reduced by 11 days.