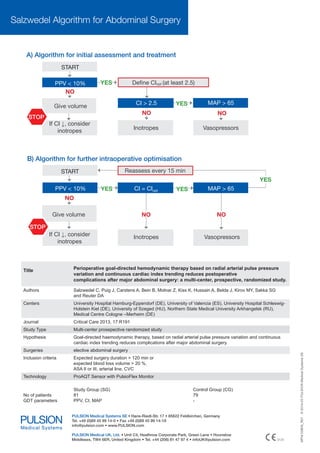
The study demonstrates that goal-directed therapy (GDT) significantly reduces complications and mortality rates in major abdominal surgeries, with a 41.7% reduction in complications observed. A meta-analysis showed that GDT leads to a 33% reduction in mortality across high-risk surgeries and a 56% decline in overall complications compared to control groups. The research emphasizes the importance of individualized treatment and perioperative optimization in improving surgical outcomes.

![Goal Directed Therapy (GDT)
– A proven concept for outcome optimisation
In 1988 Shoemaker developed the first principles of goal directed therapy and its superiority regarding
outcome(2). This concept has been adopted ever since and new perioperative indications such as general, abdominal, cardiac, orthopaedic surgery have evolved. Improved outcome through GDT was proven in several
publications.
Benefits of GDT
*
A meta-analysis of Gurgel et al. analysed the impact of
GDT on mortality reduction in high-risk surgeries.
• Over all three defined mortality subgroups: Reduction of mortality by 33% in the GDT group(3).
• Surgical procedures with a mortality from 5% to 20%
in the control group: Reduction of mortality by 35%(4).
reduced
up to
• Surgical procedures with mortality > 20% in the control group: Reduction of mortality by 68%(3).
A meta-analysis of Hamilton et al. and Dalfino et al. analysed the impact of GDT on complications
reduced
by
• In general GDT resulted in a decline of complications
by 56% compared to the control group(5).
• Especially the numbers of infections were reduced
significantly by 60%(6).
A strong cochrane review of Grocott et al. analysed the
impact of GDT on Length of Stay (LoS) (7).
• Postoperative ICU stay: mean reduction by 0.45 days,
reduced
by
• Postoperative hospital stay: mean reduction by 1.16
days
Study or Subgroup
Odds Ratio
M-H, Fixed, 95% CI
Bishop, 1995 (26)
0.38 [0.16, 0.90]
Chytra, 2007(30)
0.69 [0.31, 1.52]
Boyd, 1993 (29)
Fleming, 1992 (32)
Lobo, 2000 (17)
Lobo, 2006 (35)
Lopes, 2007 (36)
Shoemaker, 1998 (4)
Shultz, 1985 (40)
*Forest plot: Comparison of GDT vs.
conventional treatment in surgical
procedures with a mortality > 20%(3)
Odds Ratio
M-H, Fixed, 95% CI
Total (95% CI)
0.21 [0.06, 0.79]
0.41 [0.14, 1.15]
0.19 [0.04, 0.88]
0.22 [0.04, 1.21]
0.29 [0.05, 1.80]
0.07 [0.01, 0.63]
0.07 [0.01, 0.61]
0.32 [0.21, 0.47]
0.1
0.2
0.5
Faverous experimental
1
2
5
10
Faverous control](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/brosur-140308033633-phpapp02/85/Improve-Outcome-in-Major-Abdominal-Surgery-with-ProAQT-2-320.jpg)
![High Risk Abdominal Surgery
Benefits most from GDT
Despite high standards in surgical and
anaesthesiological care in Europe, the
perioperative mortality rate is still higher
than expected(8).
High blood loss (> 20%) and volume shifts during
the procedure can result in hypo- or hypervolaemia
8
6
4
2
0
6,7
Oesophagectomy
•
10
Gastrectomy
Complex procedures with high-risk of intraand post-op complications
11,8
12
Colectomy
Long surgery time (>120 min)
•
14
Mortality [ % ]
•
15,1
16
Mortality rates for procedures in abdominal surgery, 1999 (9)
PulsioFlex – Your navigator in perioperative haemodynamic management
ProAQT
CeVOX
Radial arterial trend monitoring of
Cardiac Index - simply attached to
an arterial line
Central venous oxygen
saturation - simply attached to
a standard CVC
Parameters:
Parameters:
•
Cardiac Output:
CITrend
•
Volume responsiveness:
SVV, PPV
•
Afterload:
SVRI, MAP
•
Cardiac function:
dPmx, CPI
•
Central venous oxygenation
ScvO2
Oxygenation: DO2, VO2, O2ER (ProAQT combined with CeVOX)
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
Salzwedel C et al., Perioperative goal-directed hemodynamic therapy based on radial arterial pulse pressure variation and continuous cardiac index trending reduces postoperative
complications after major abdominal surgery: a multi-center, prospective, randomized study. Crit Care 2013; 17(5): R191.
Shoemaker WC et al., Prospective trial of supranormal values of survivors as therapeutic goals in high-risk surgical patients. Chest 1988; 94(6): 1176-86.
Gurgel ST & do Nascimento P, Maintaining tissue perfusion in high-risk surgical patients: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials. Anesth Analg 2011; 112(6): 1384-91.
Cecconi M et al., Clinical review: Goal-directed therapy-what is the evidence in surgical patients? The effect on different risk groups. Crit Care 2013; 17(2): 209.
Rhodes A et al., Goal-directed therapy in high-risk surgical patients: a 15-year follow-up study. Intensive Care Med 2010; 36(8): 1327-1332.
Dalfino L et al., Haemodynamic goal-directed therapy and postoperative infections: earlier is better. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care 2011; 15(3): R154.
Grocott MP et al., Perioperative increase in global blood flow to explicit defined goals and outcomes after surgery: a Cochrane Systematic Review. Br J Anaesth 2013; 111: 535-48.
Pearse RM et al., Mortality after surgery in Europe: a 7 day cohort study. Lancet 2012; 380: 1059-1065.
Goodney PP et al., Is Surgery Getting Safer? National Trends in Operative Mortality. J Am Coll Surg 2002; 195: 219-27.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/brosur-140308033633-phpapp02/85/Improve-Outcome-in-Major-Abdominal-Surgery-with-ProAQT-3-320.jpg)