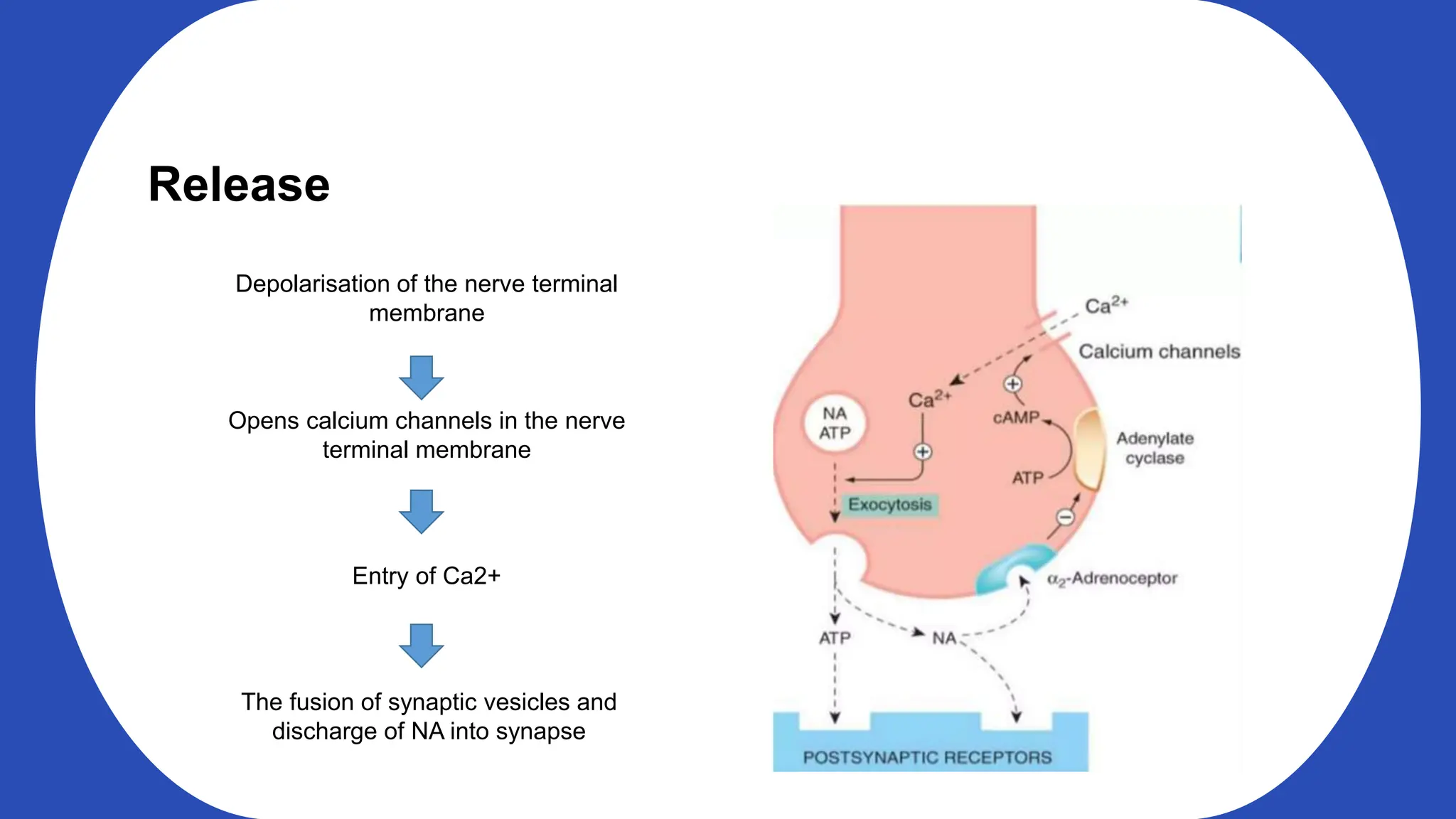
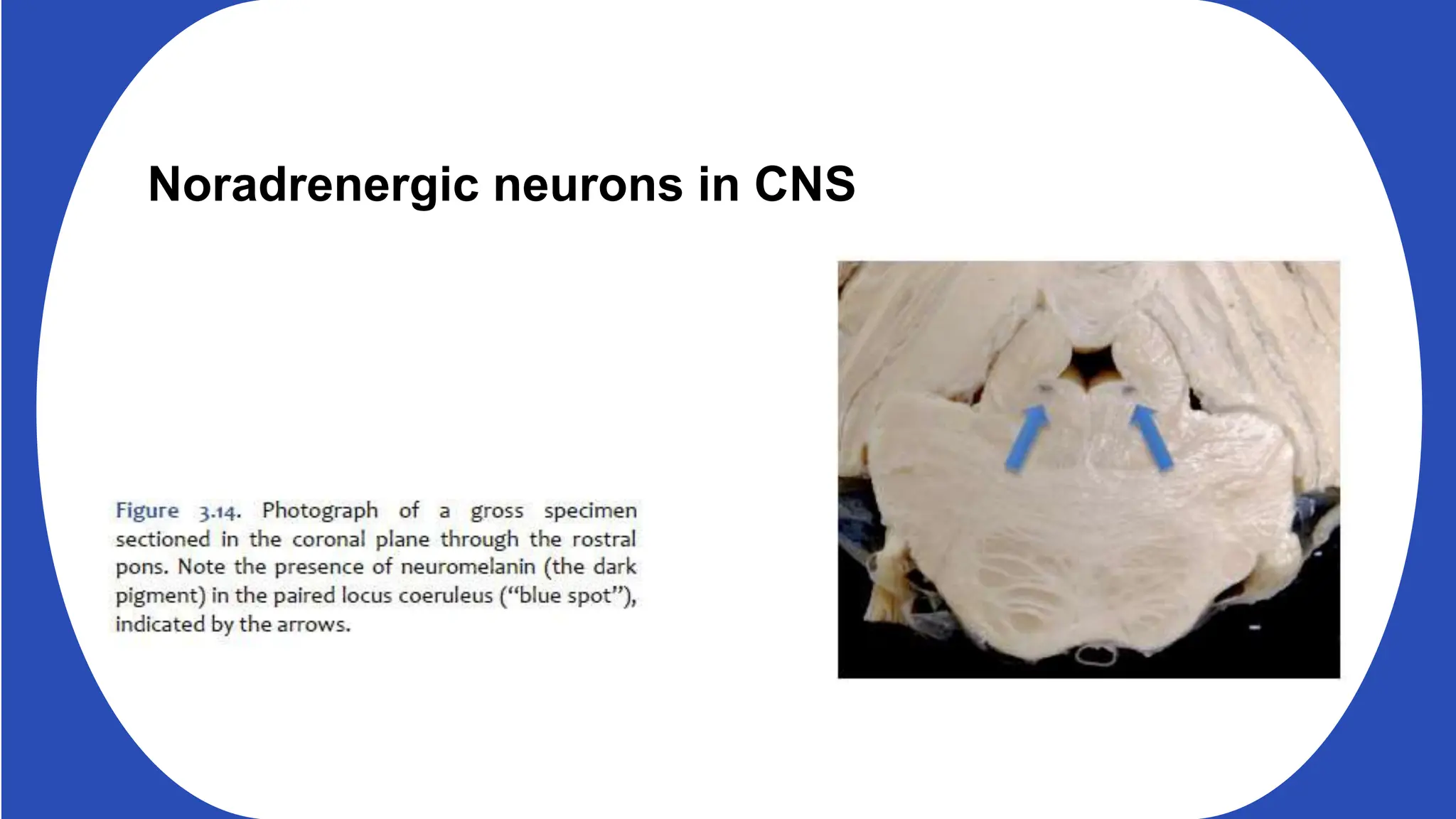
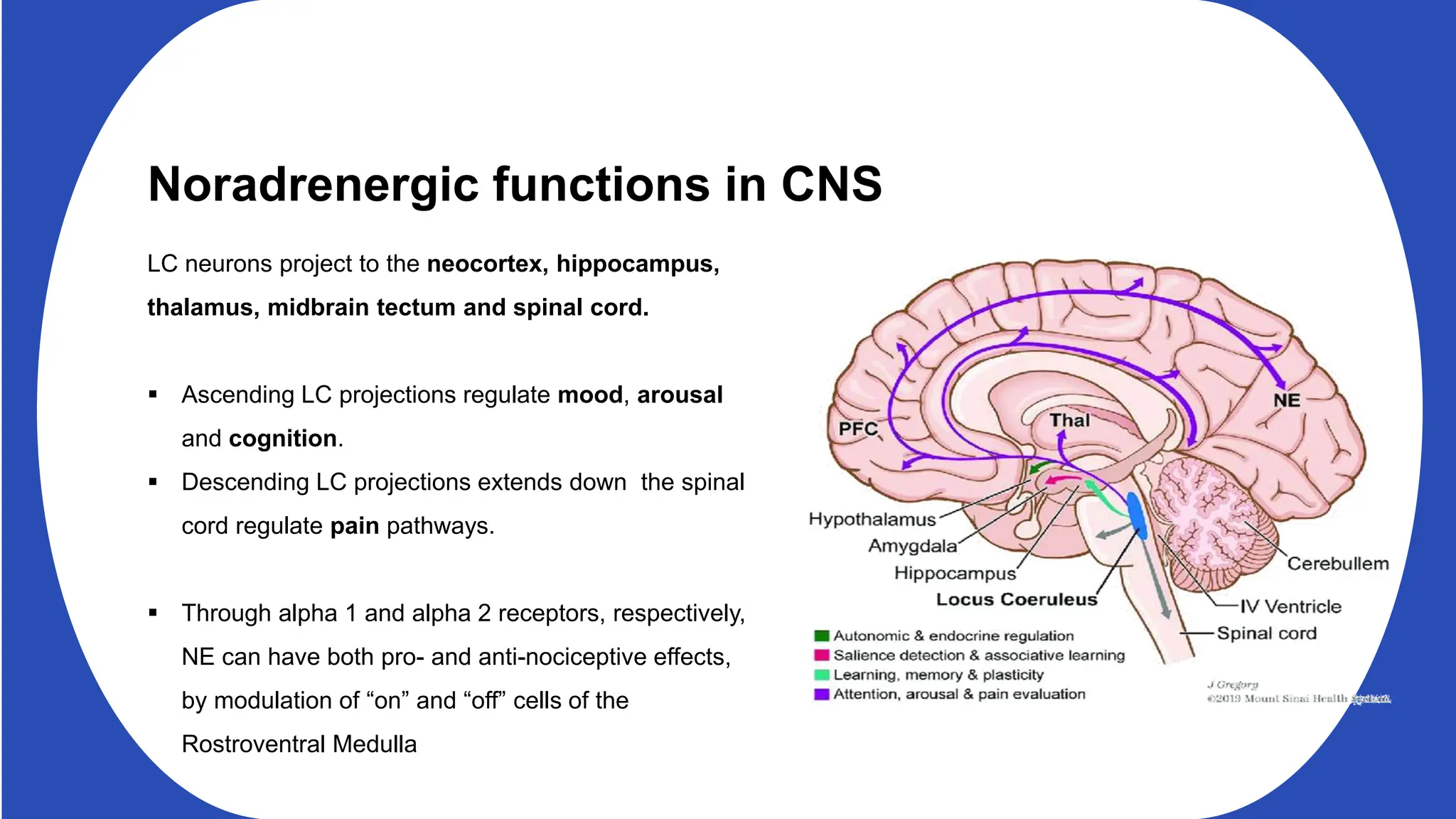
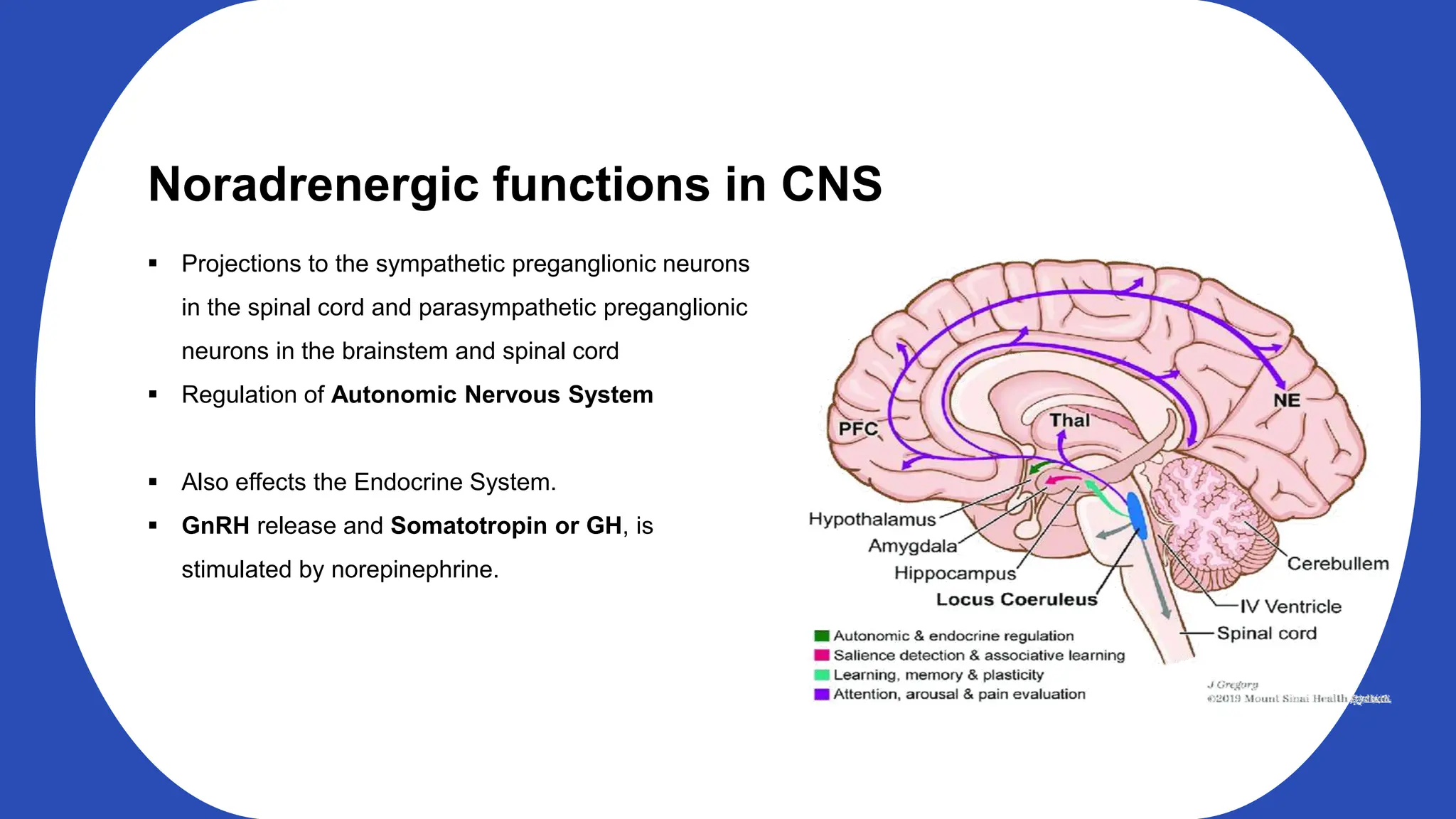
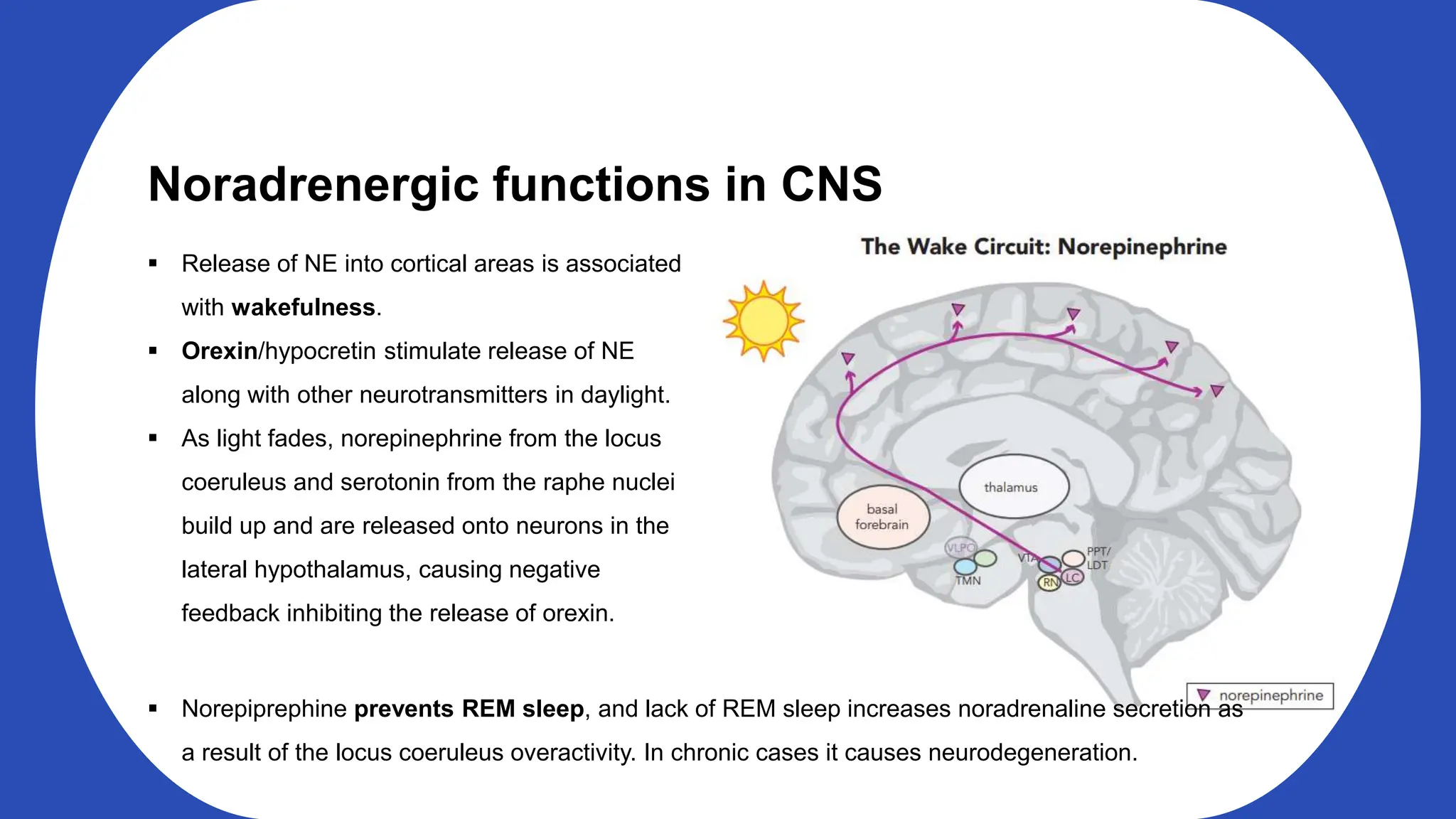
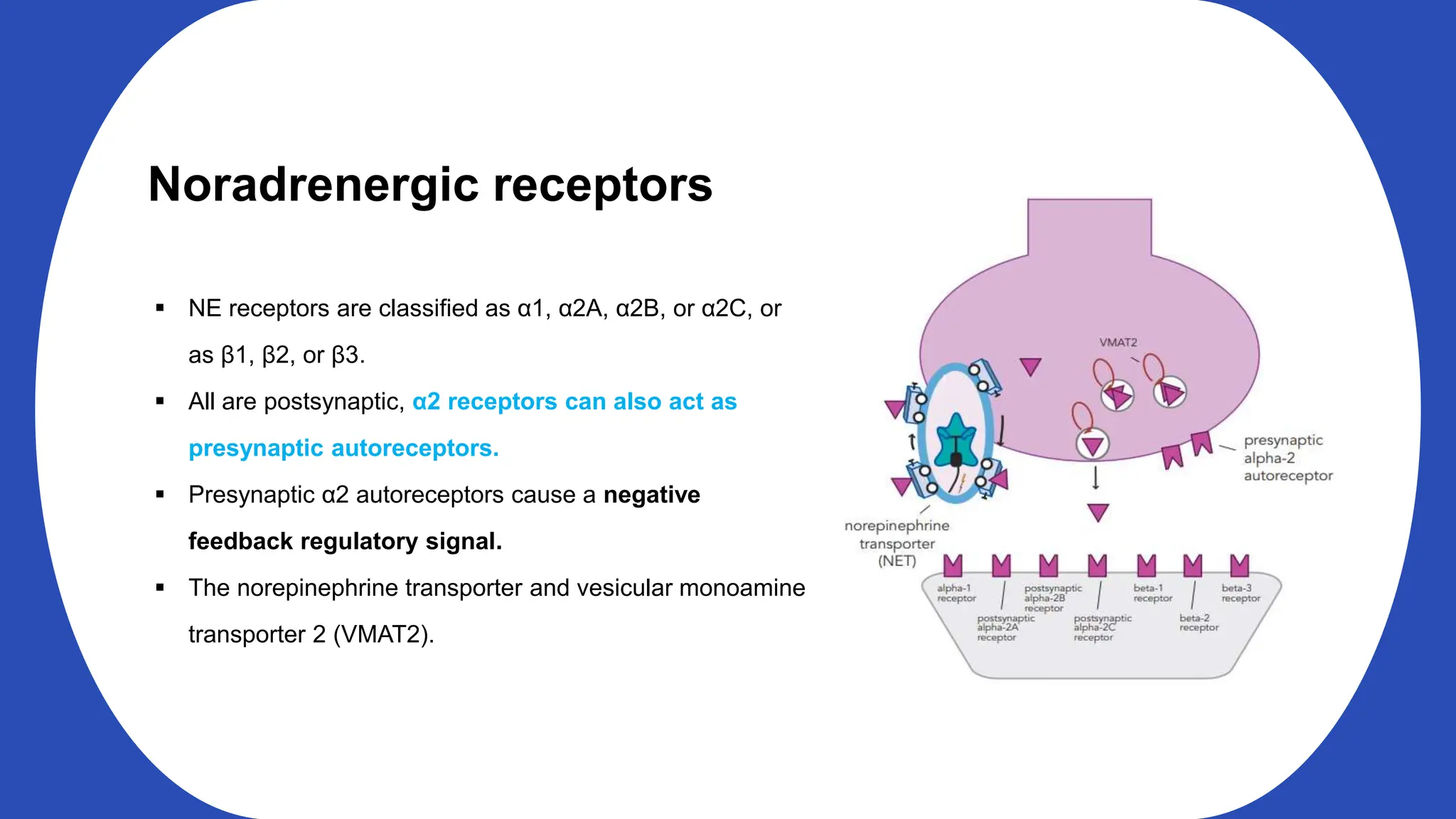
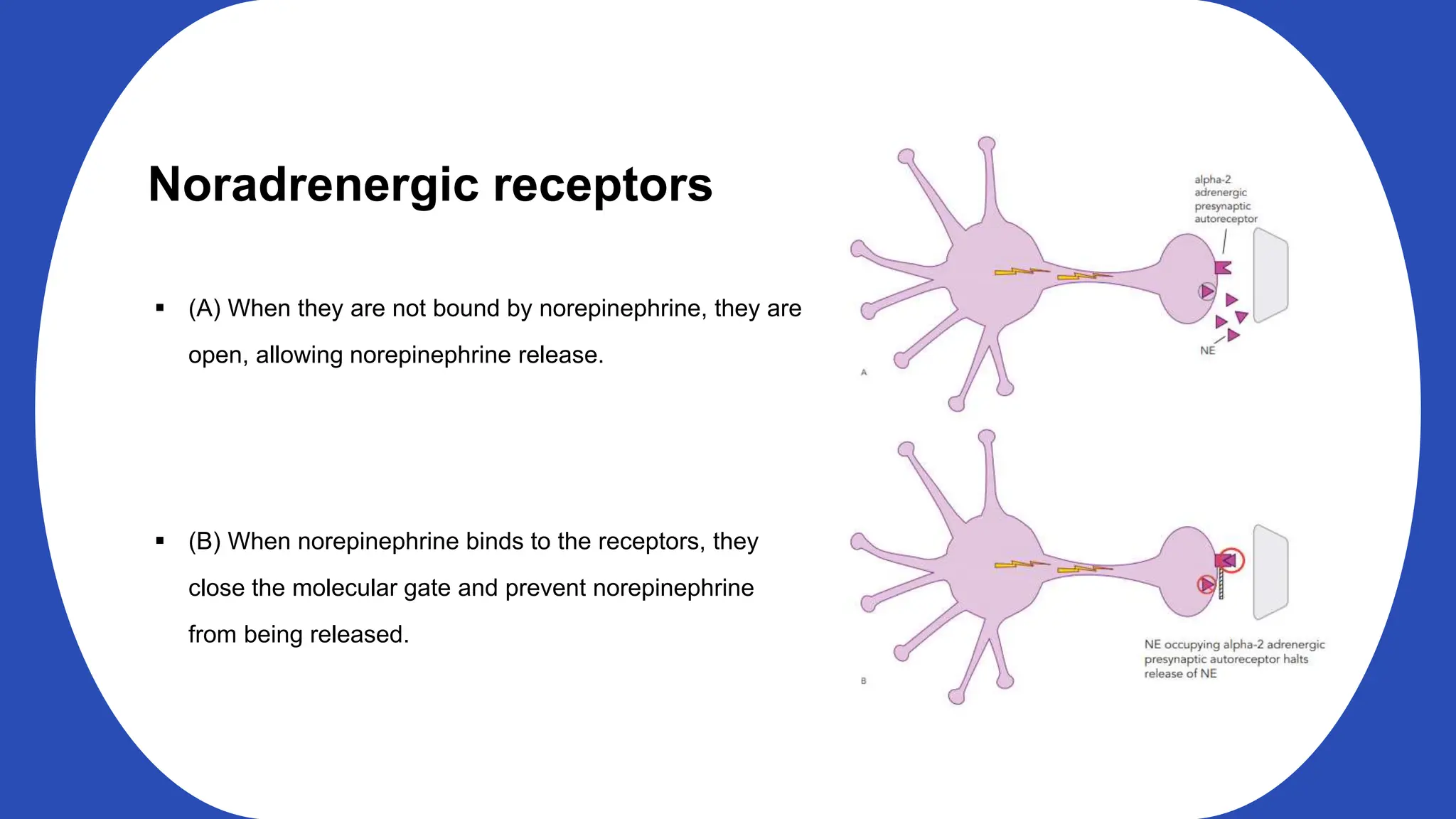
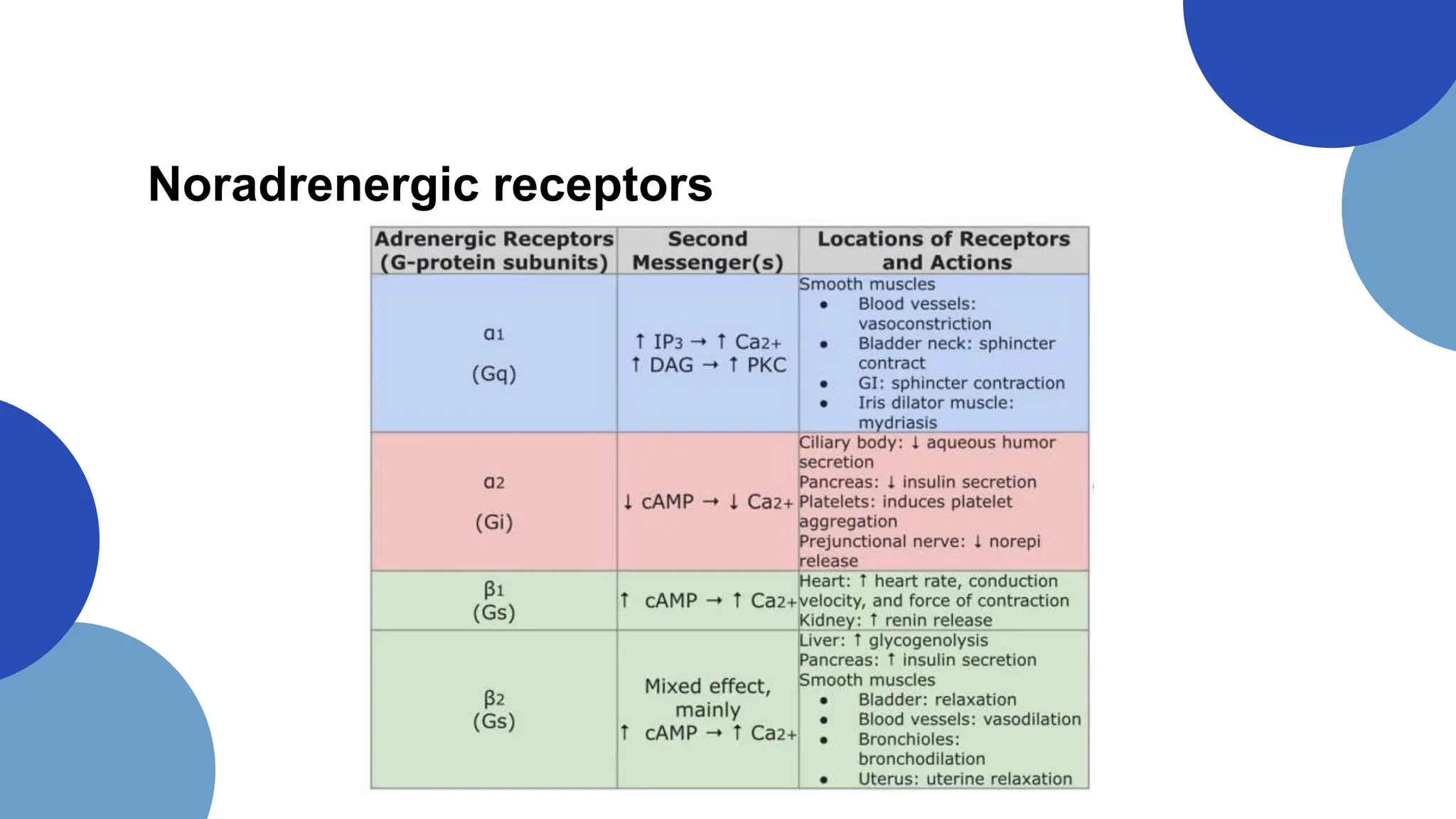
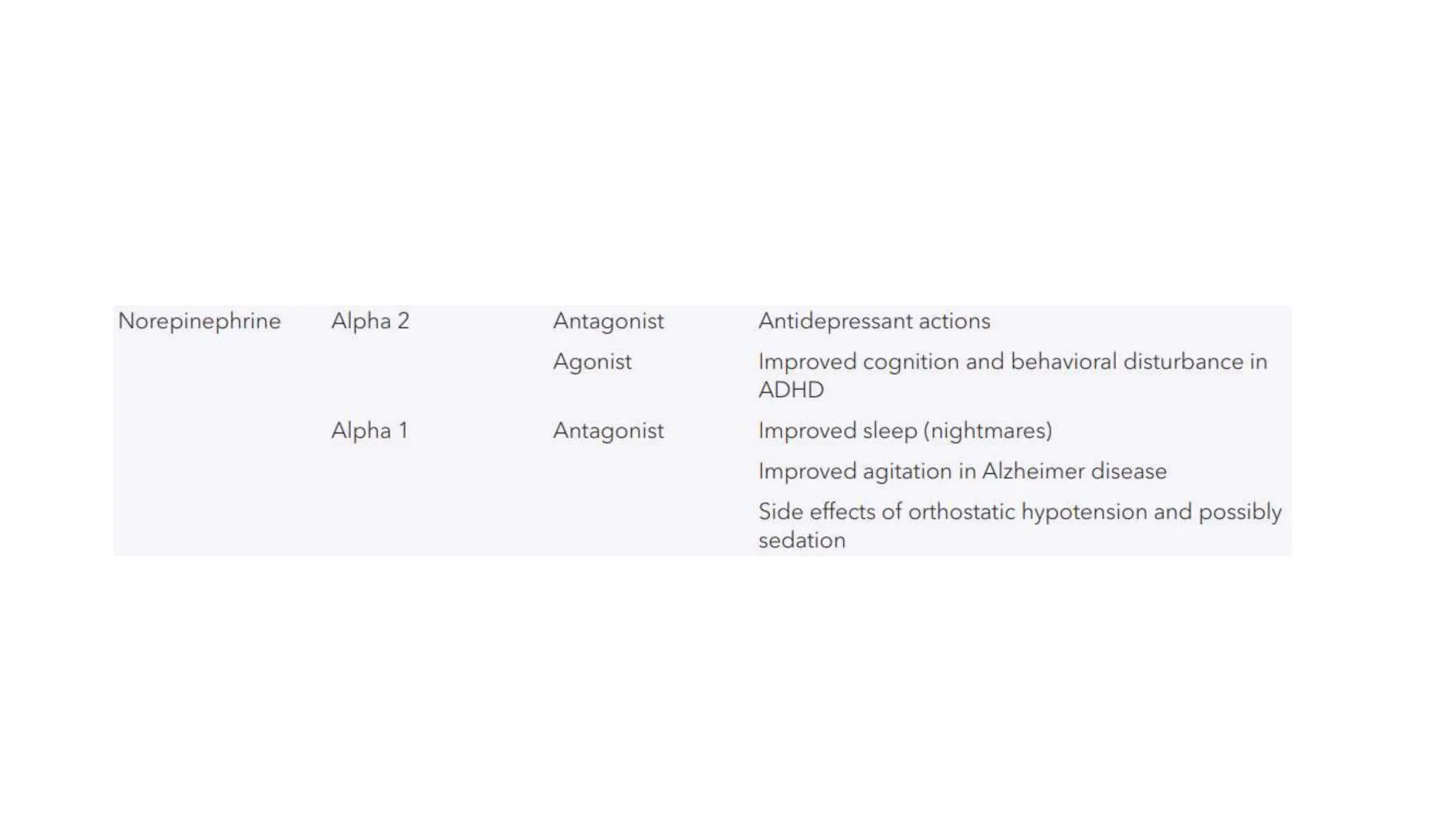
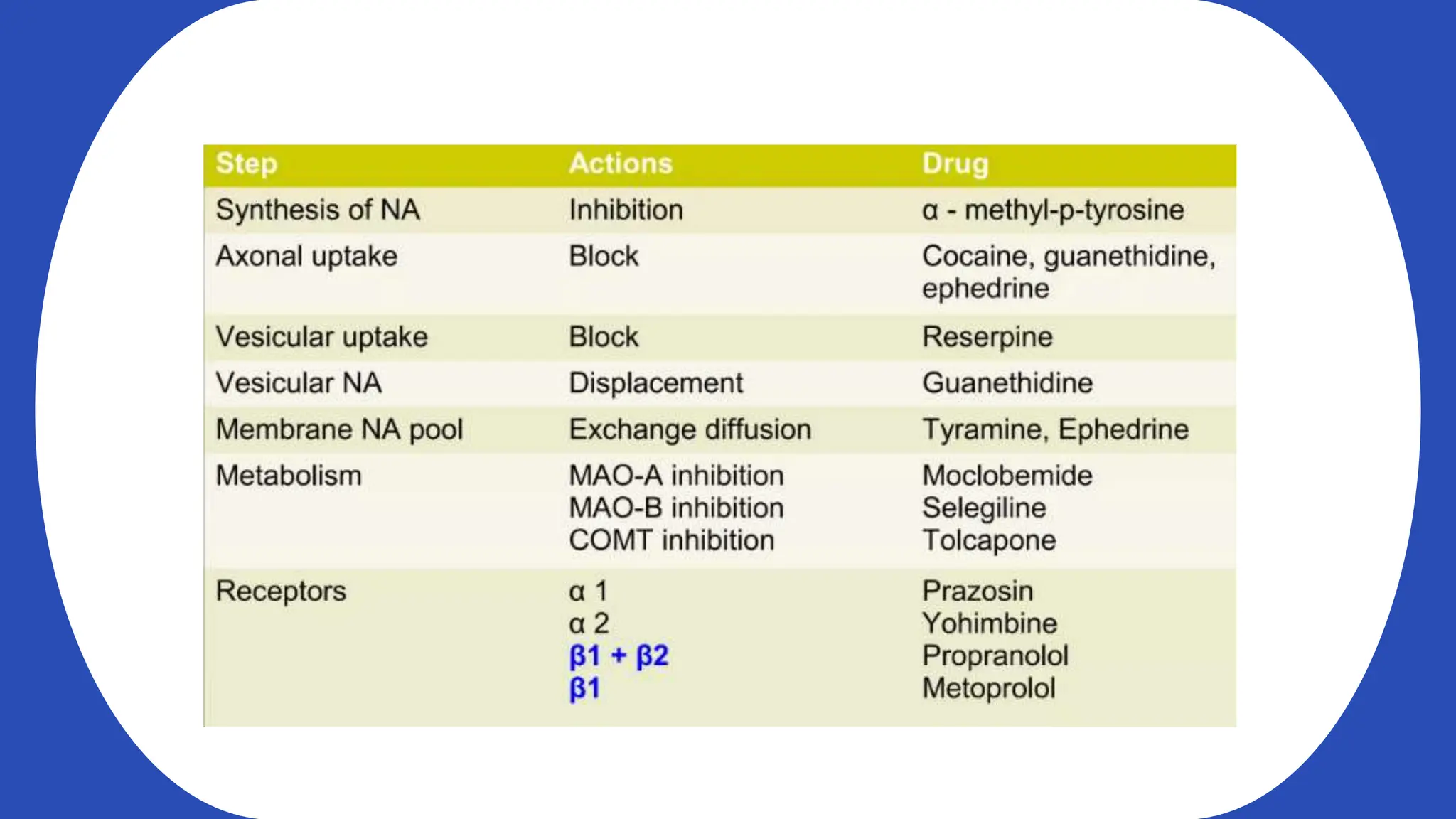
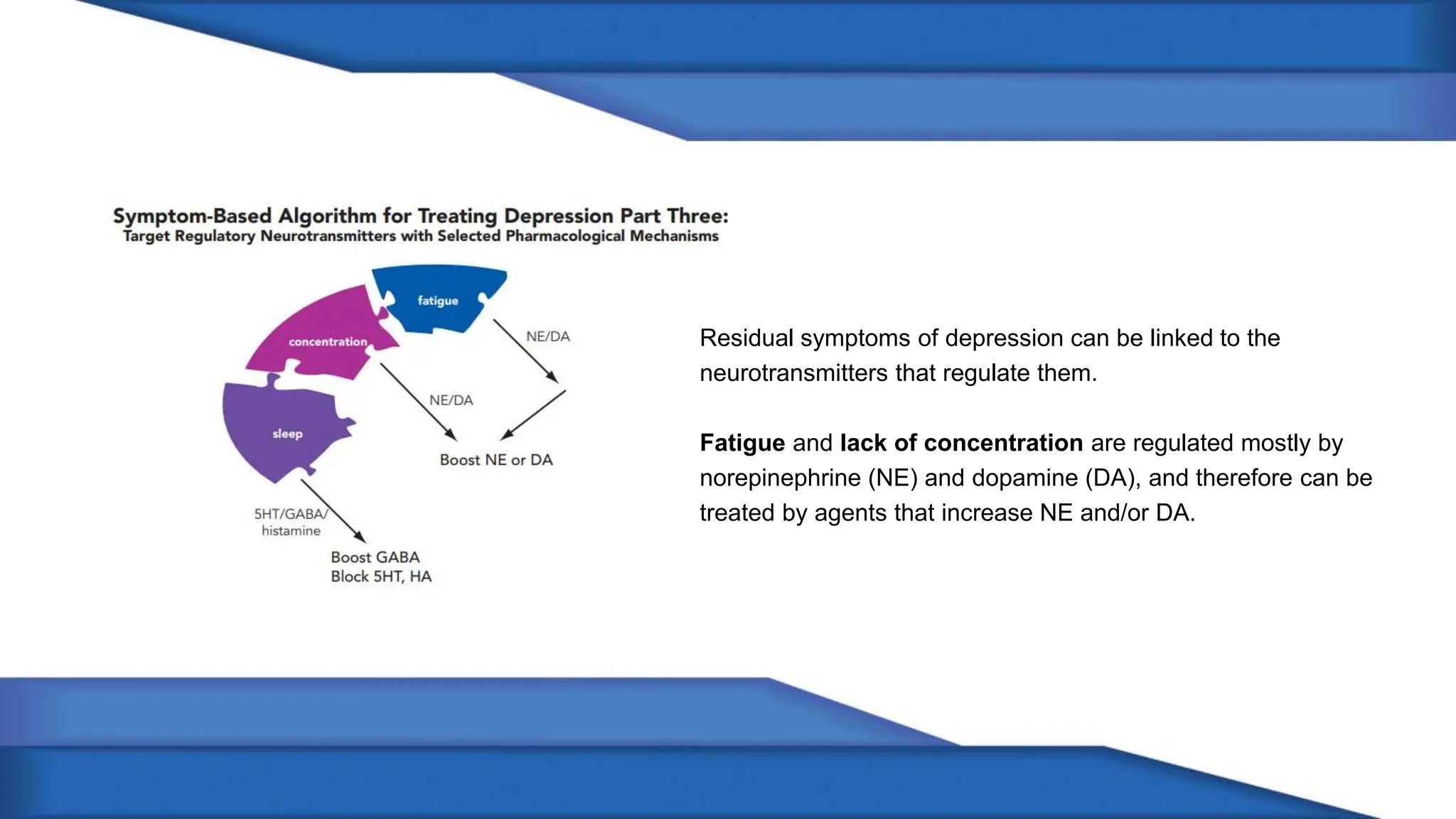
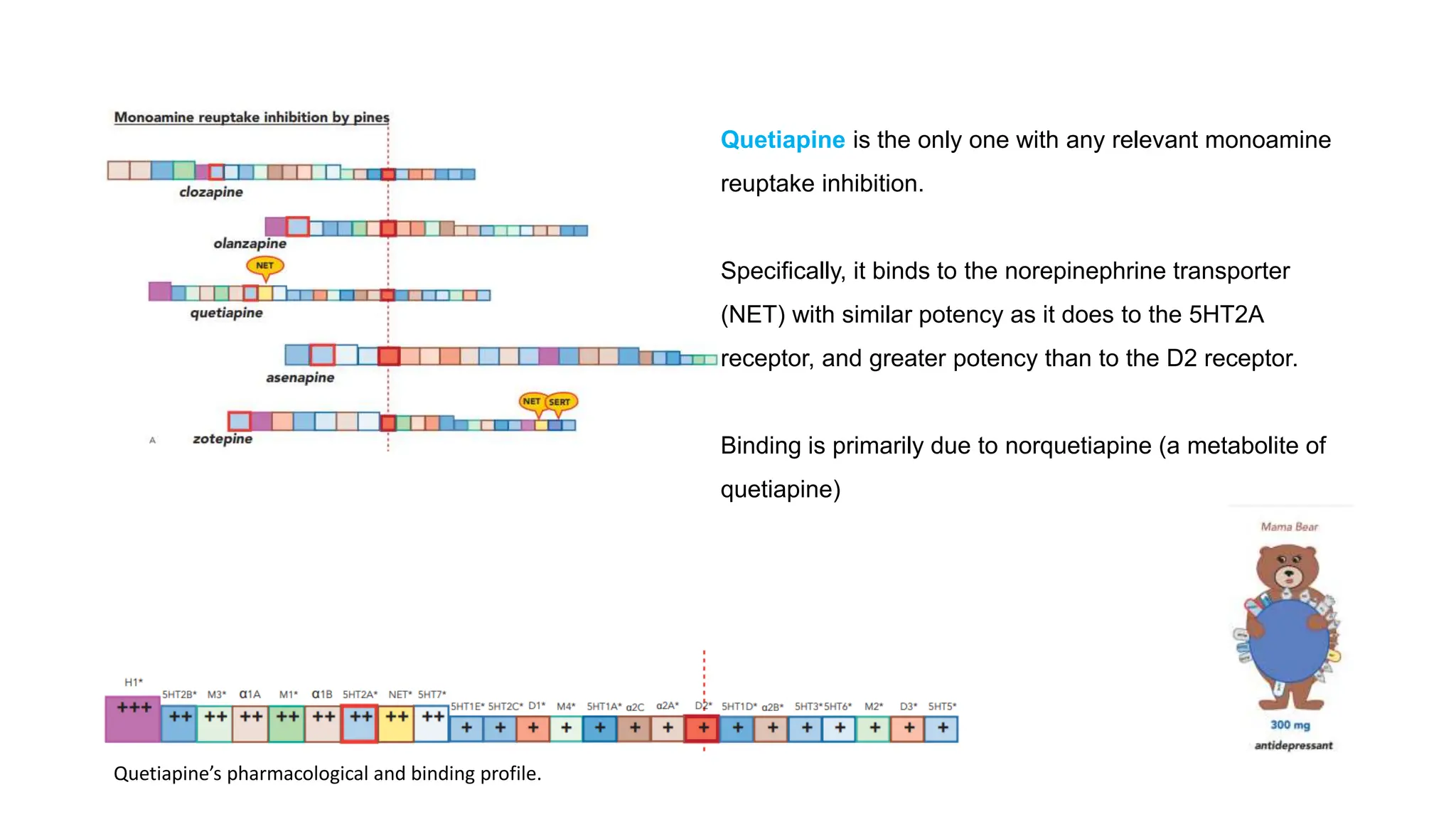
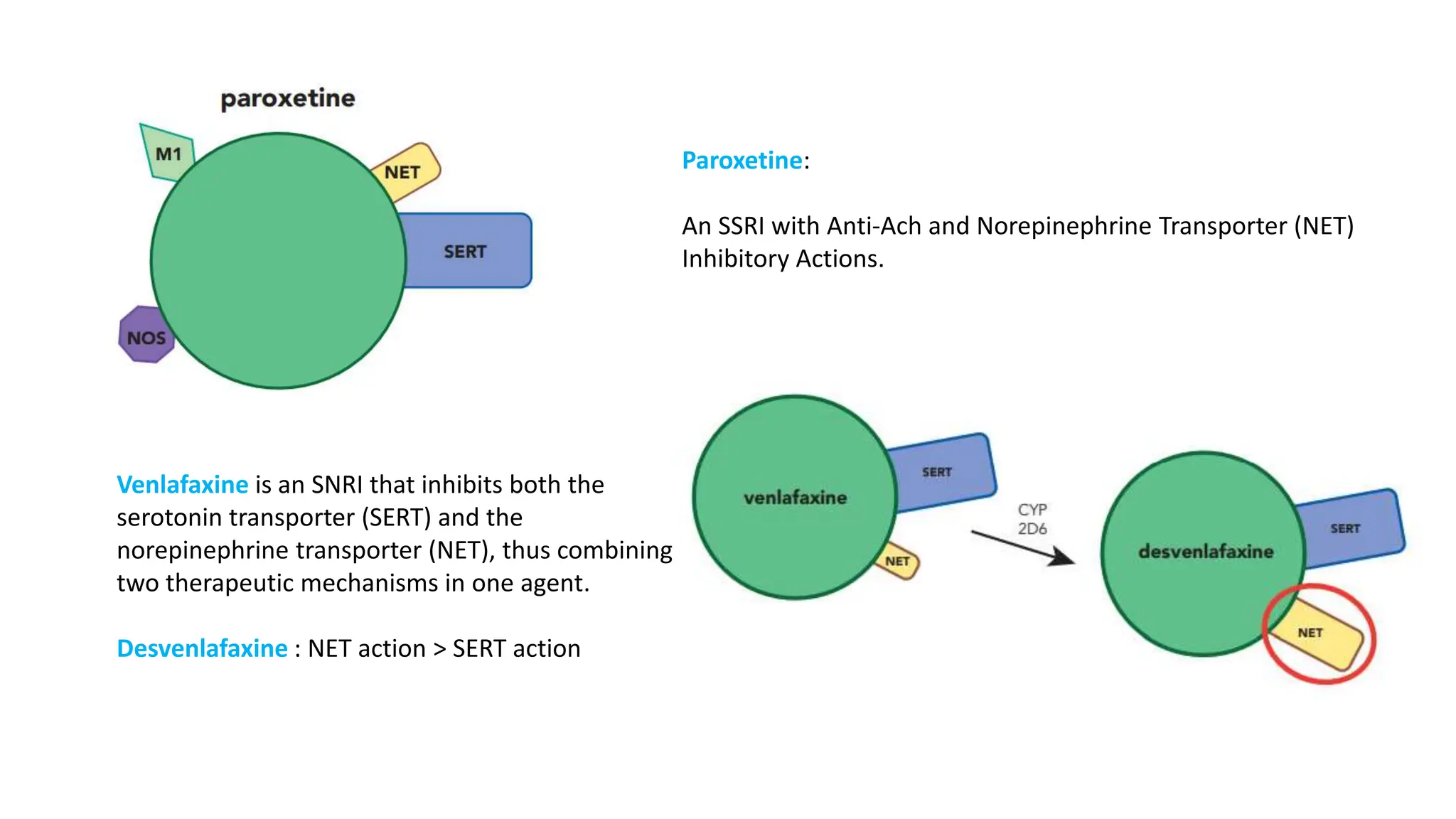
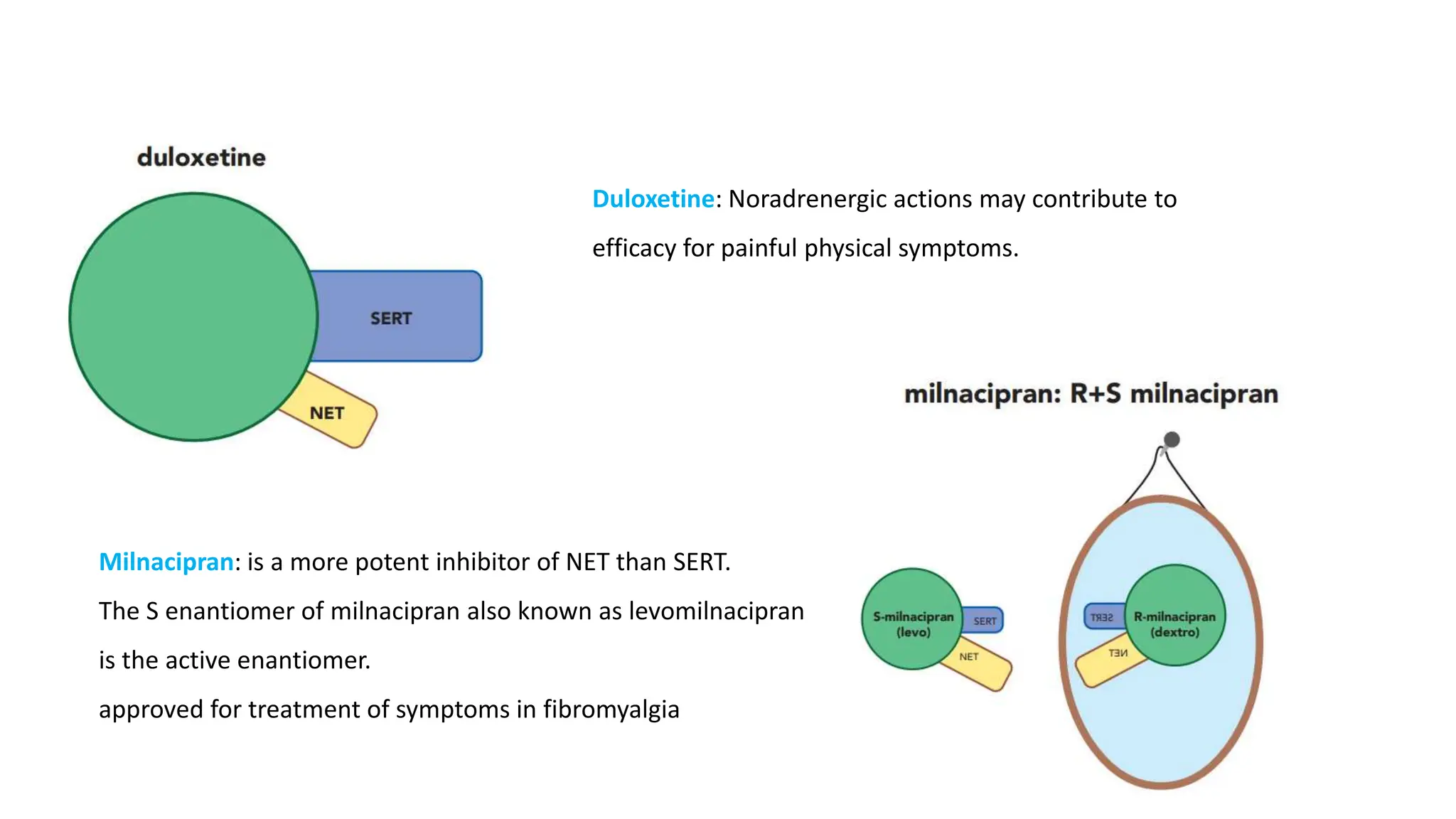
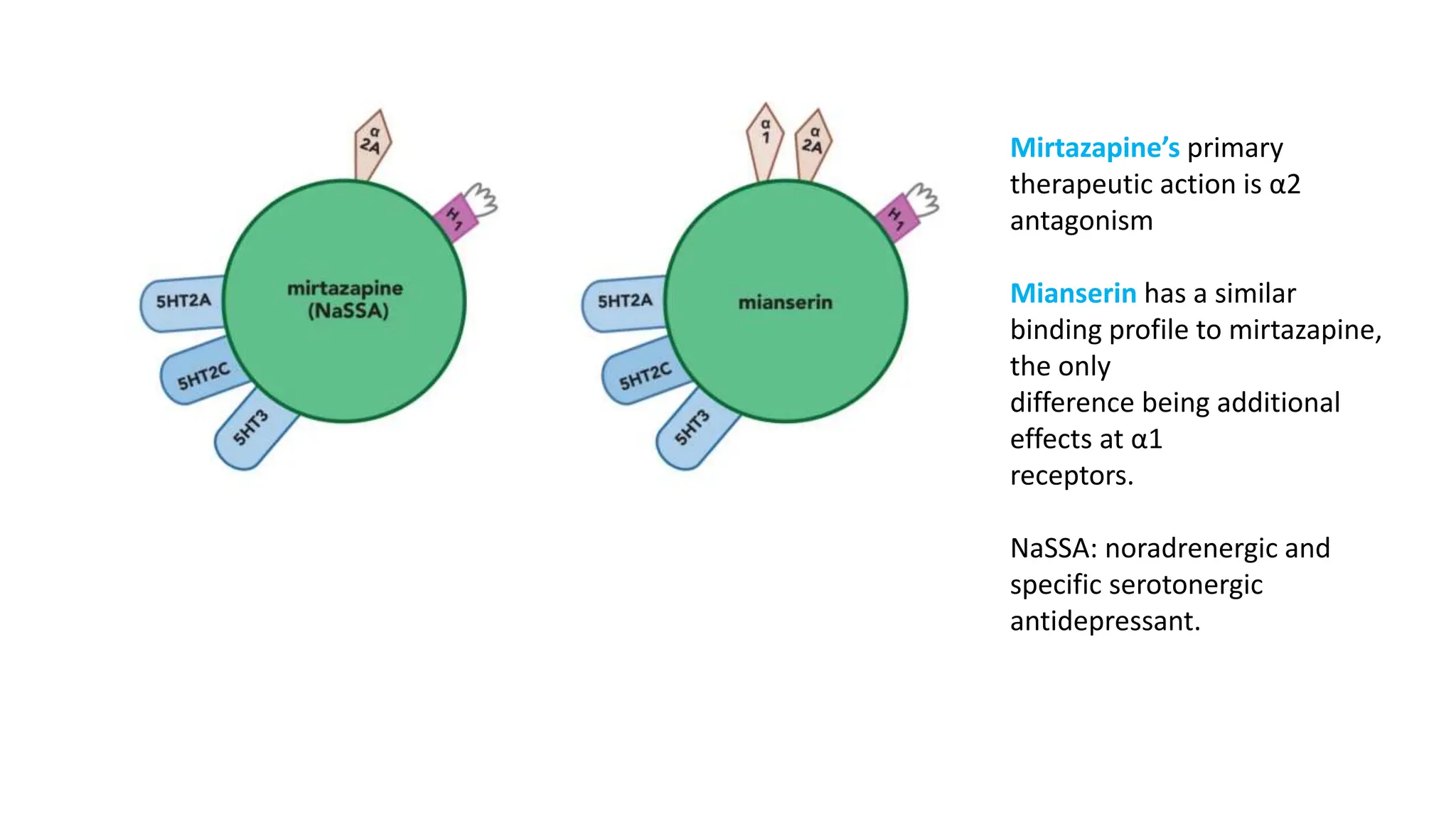
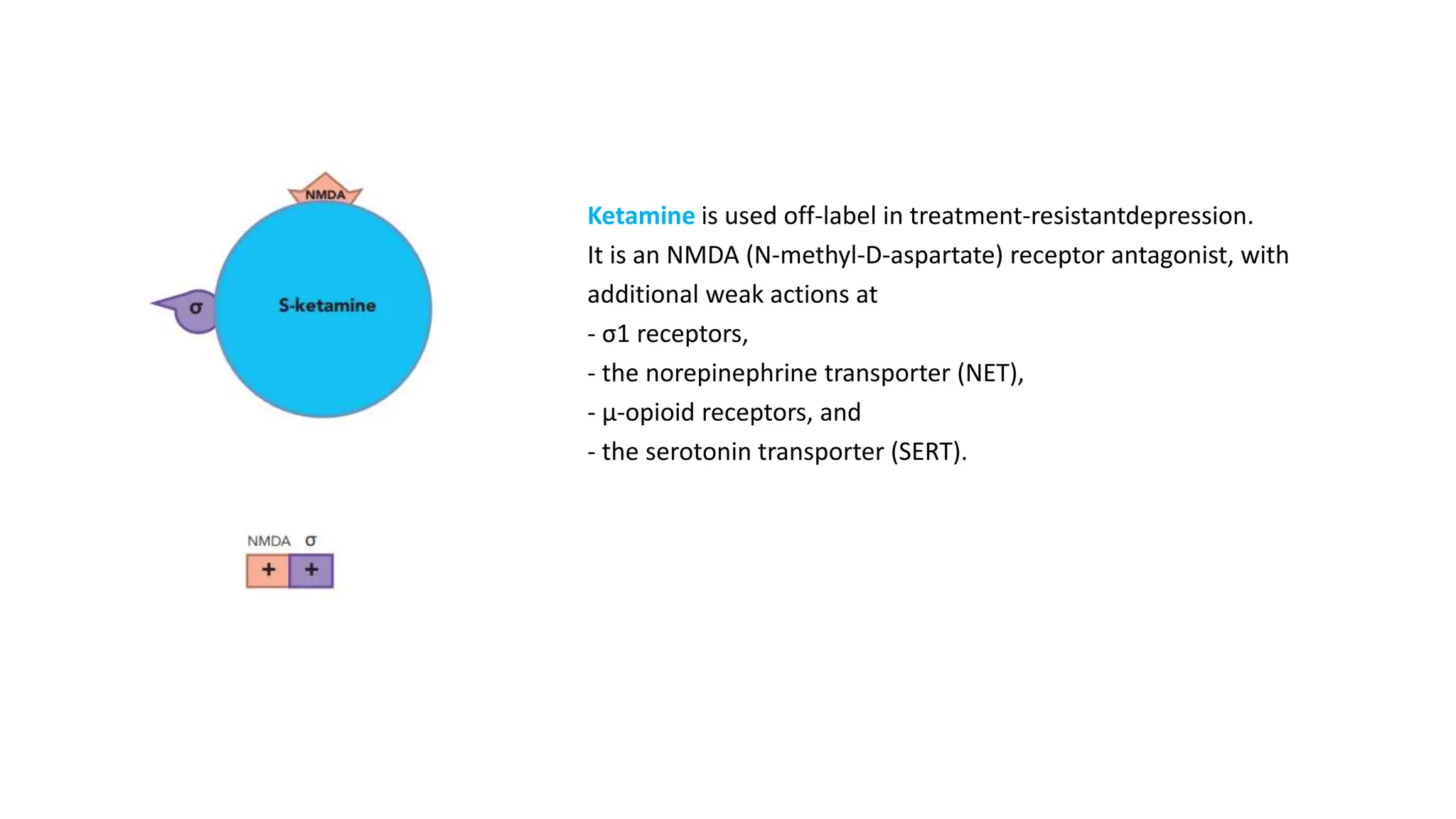
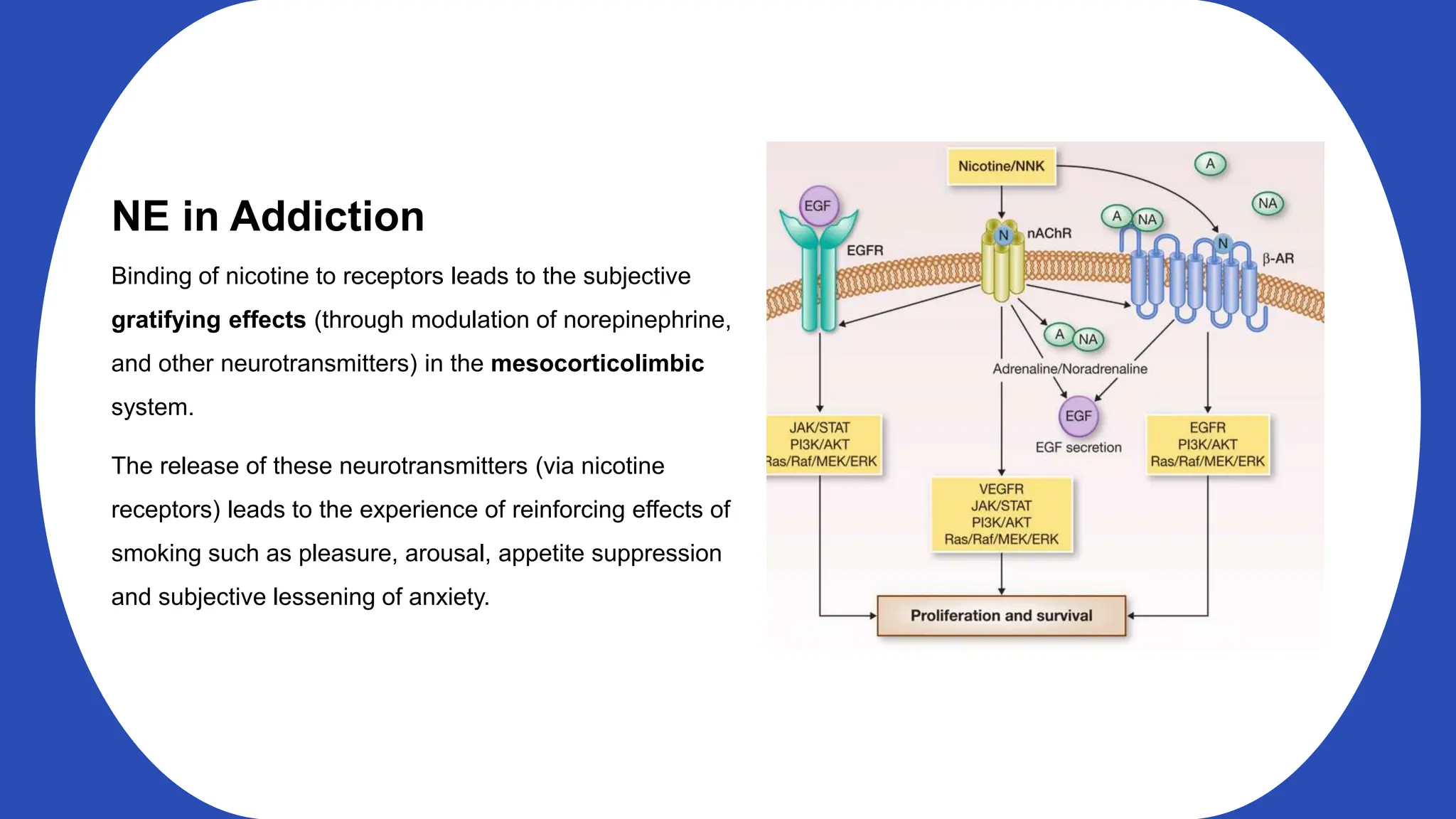
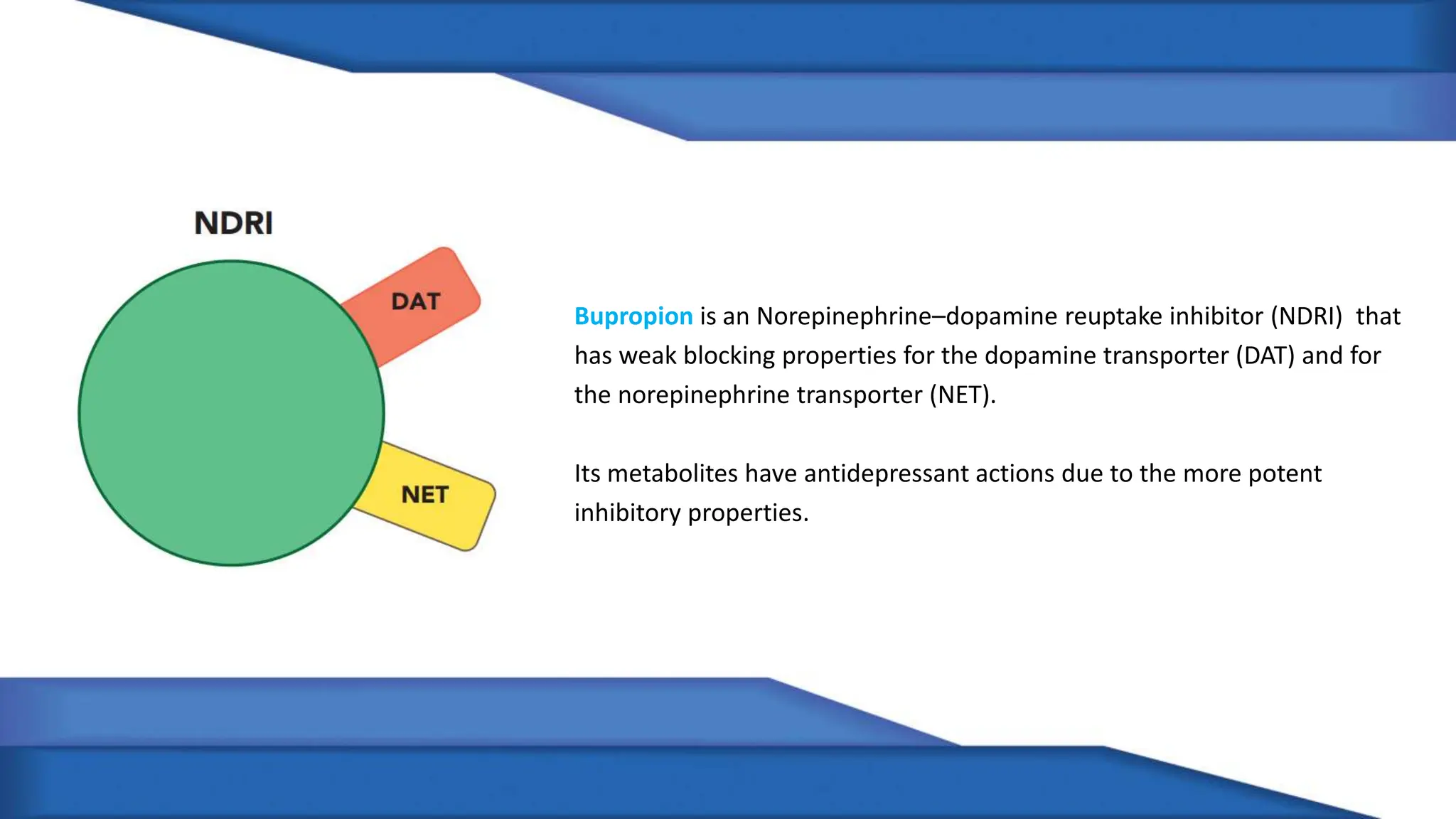
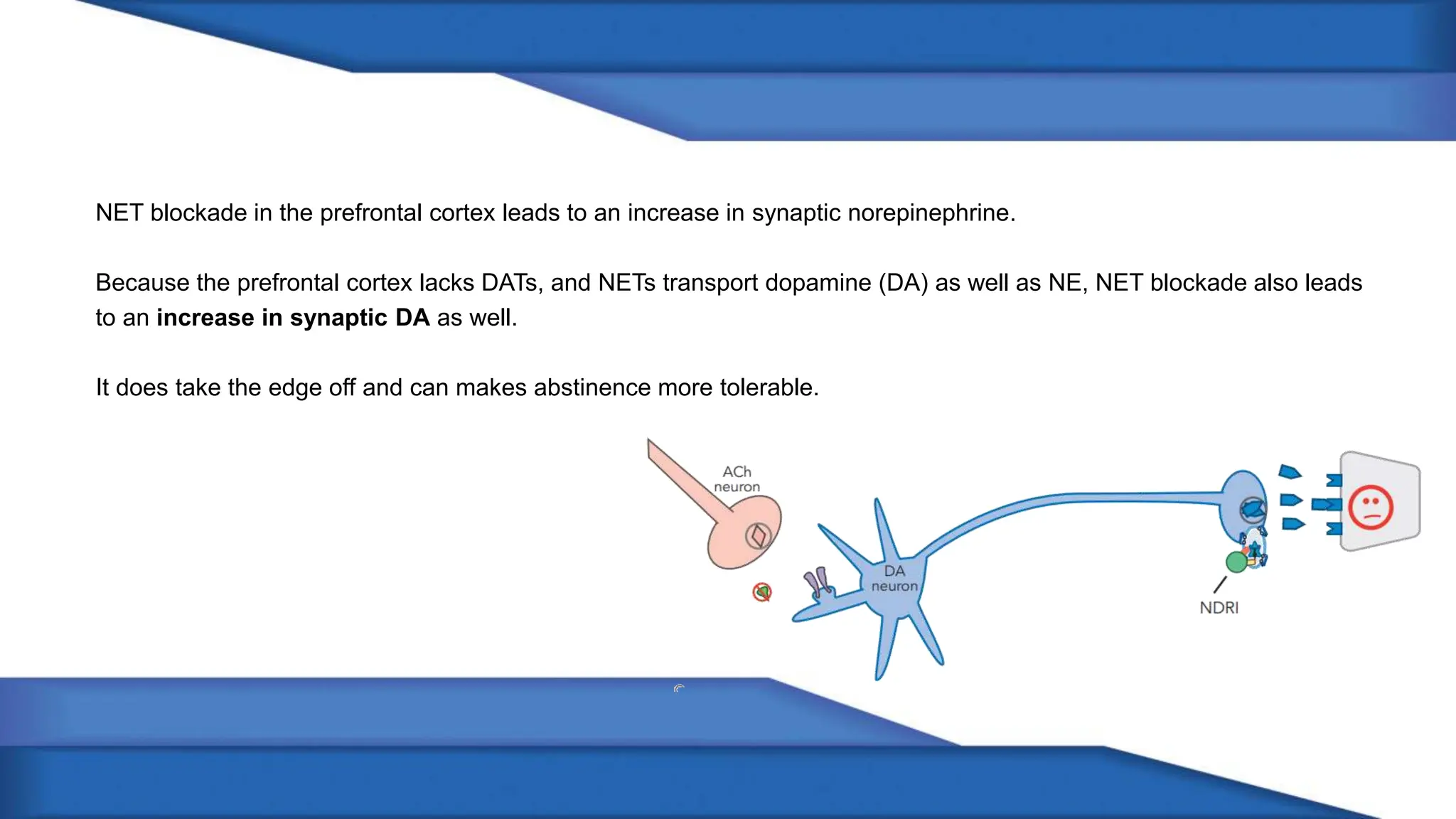
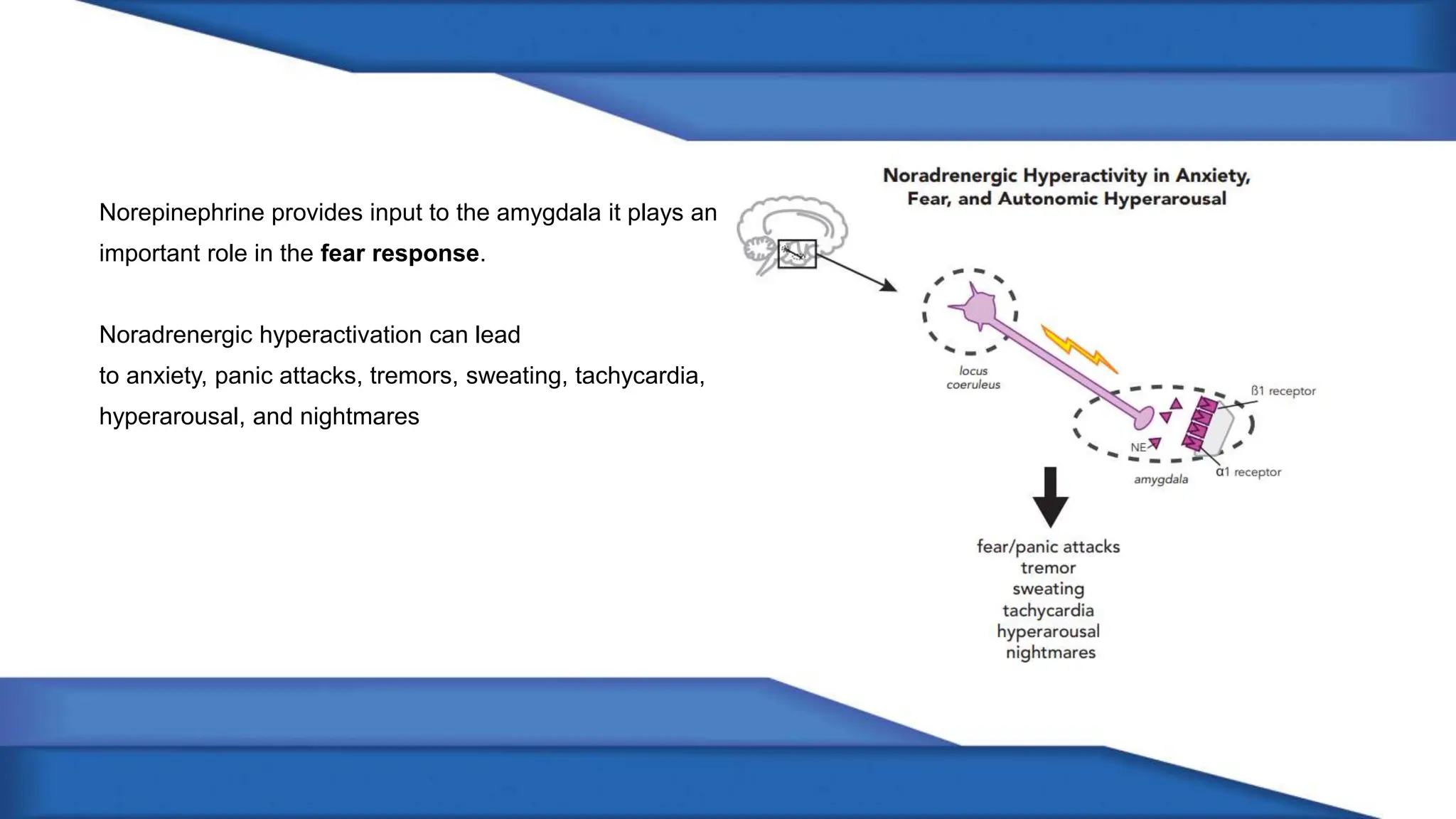
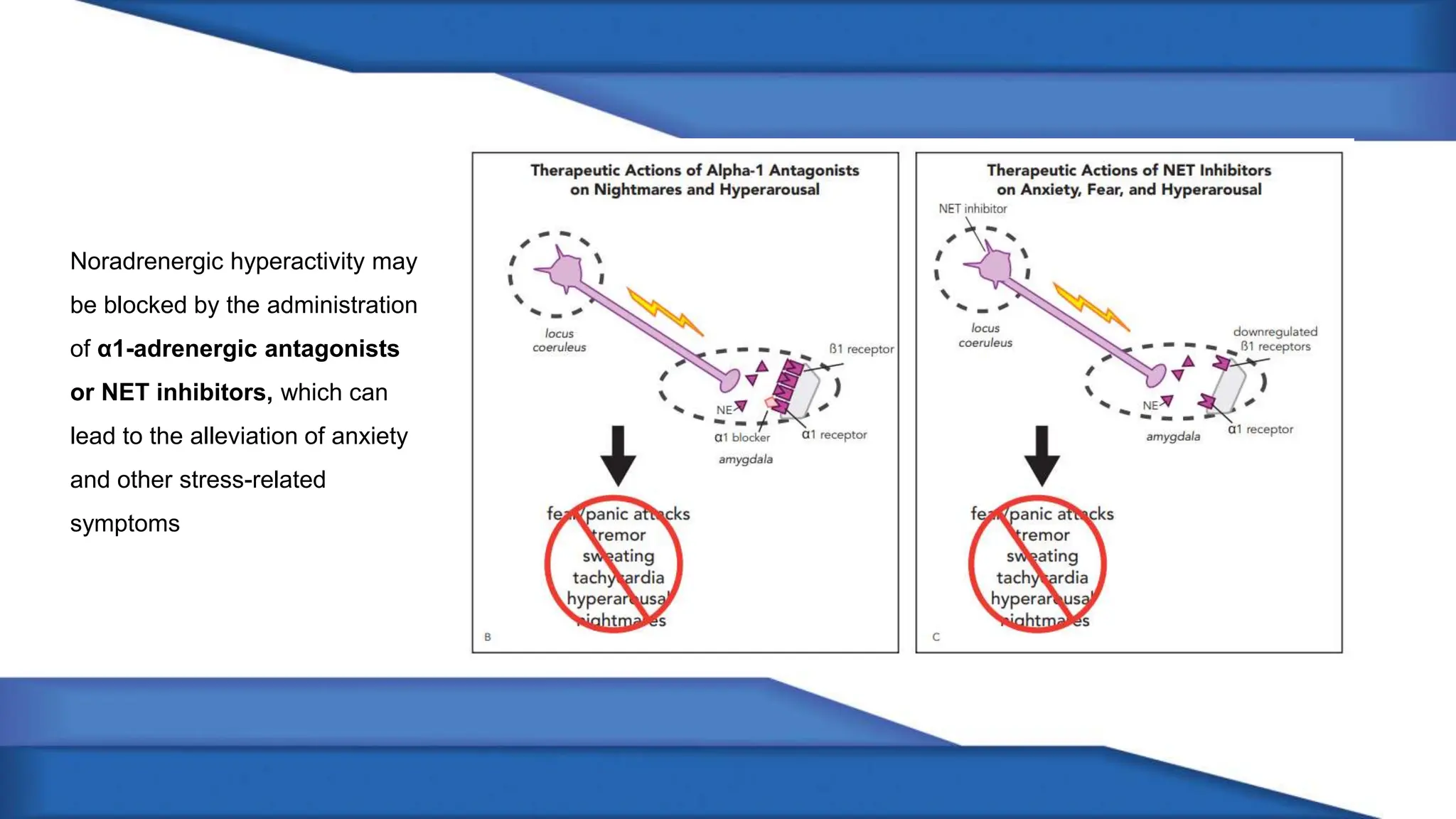
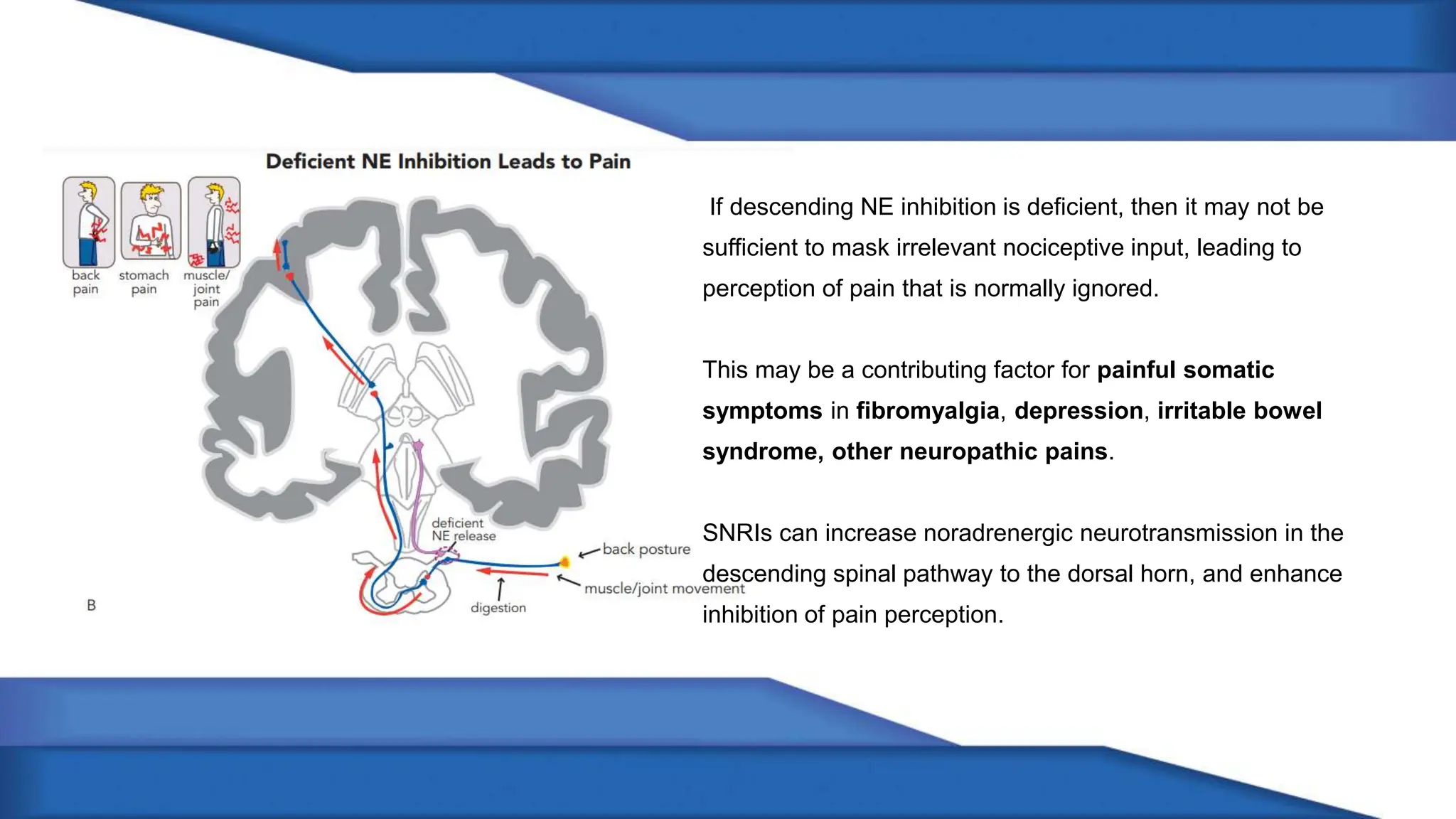
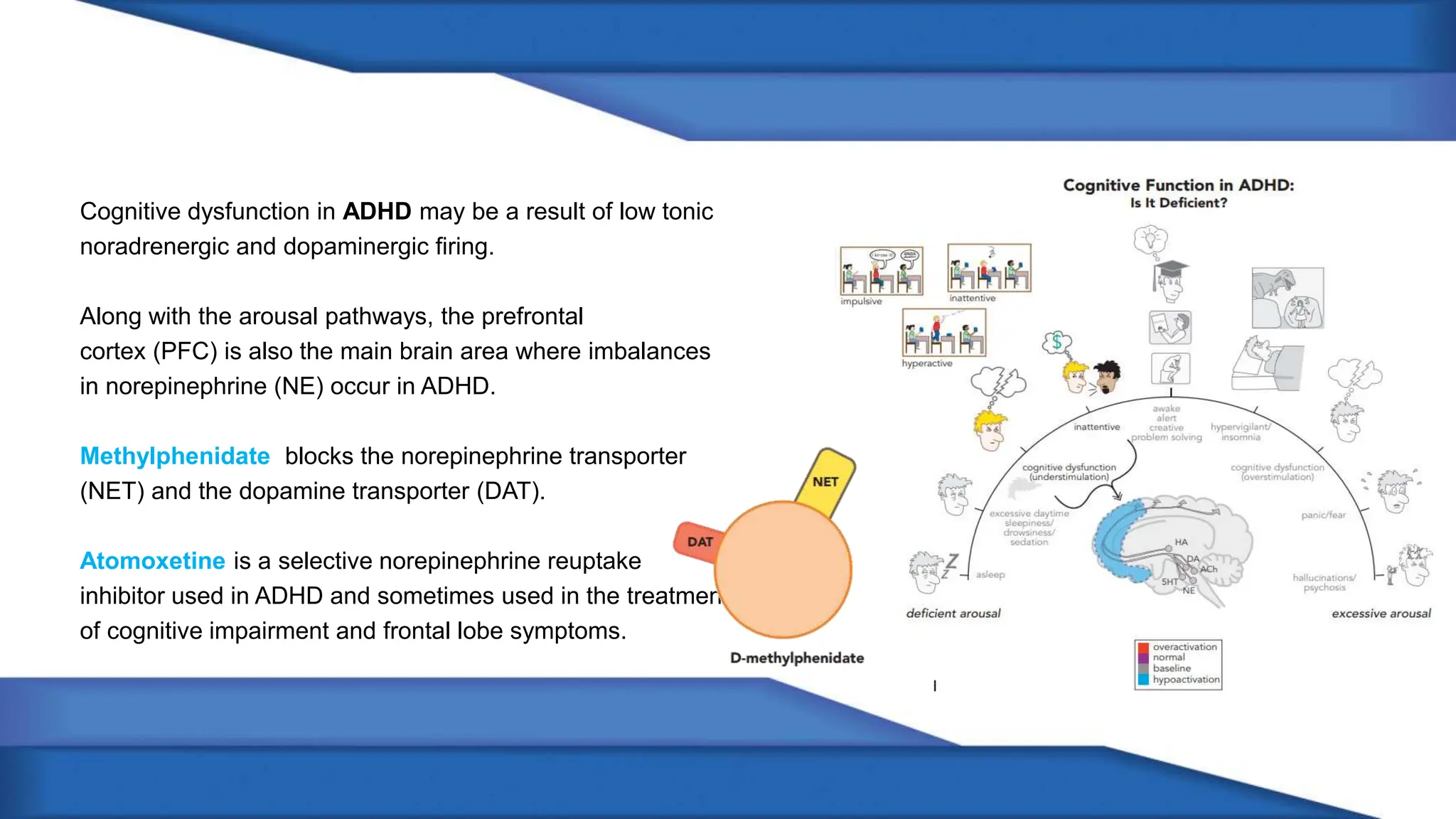
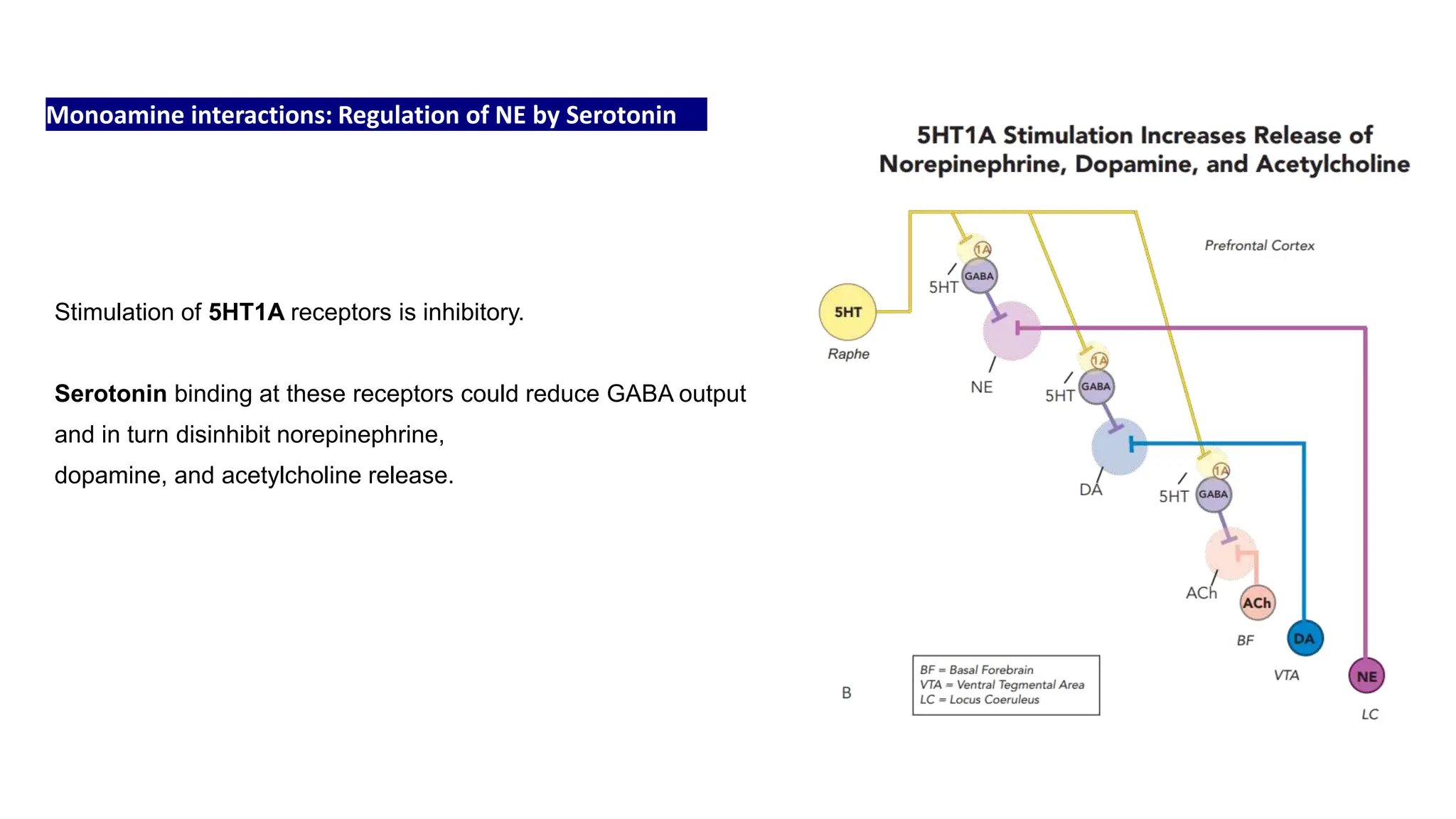
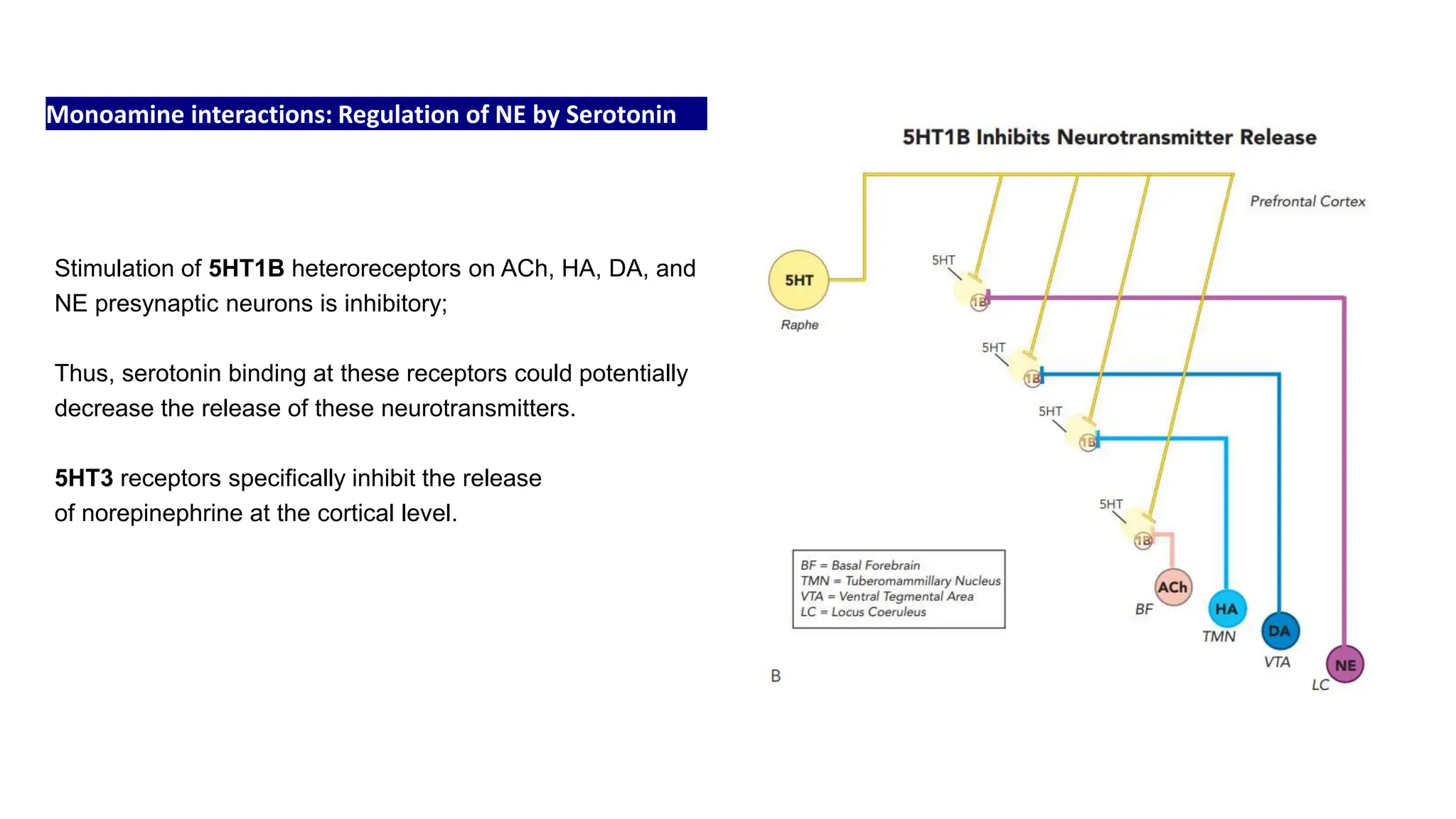
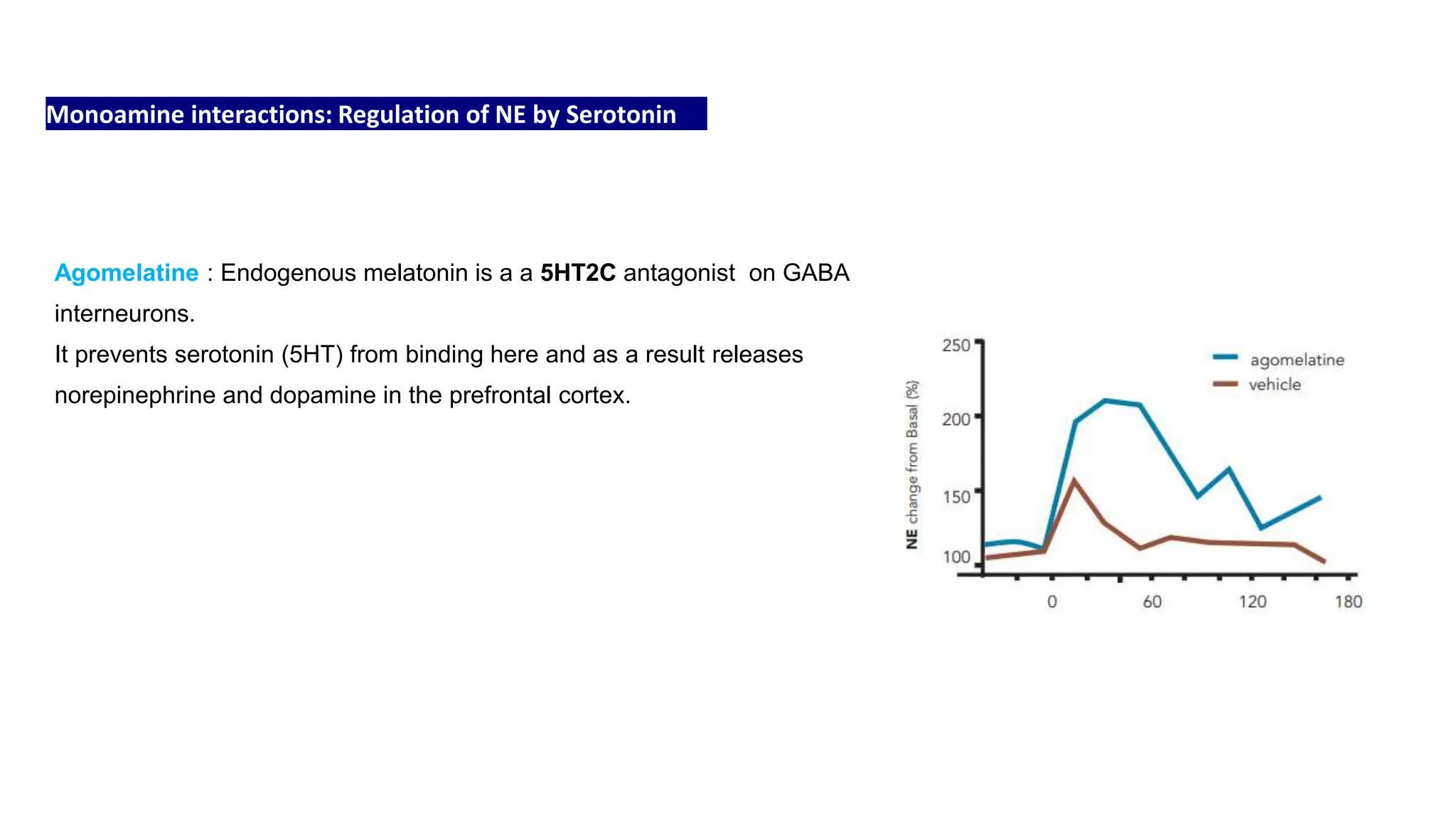
Norepinephrine, a critical neurotransmitter and hormone, is synthesized from tyrosine and plays roles in the central nervous system (CNS) and stress responses. Its regulation involves transporters and enzymes, with therapeutic implications for mental health conditions through drugs that affect norepinephrine reuptake. The neurotransmitter is linked to several conditions like anxiety, ADHD, and PTSD, and is influenced by other monoamines such as serotonin.