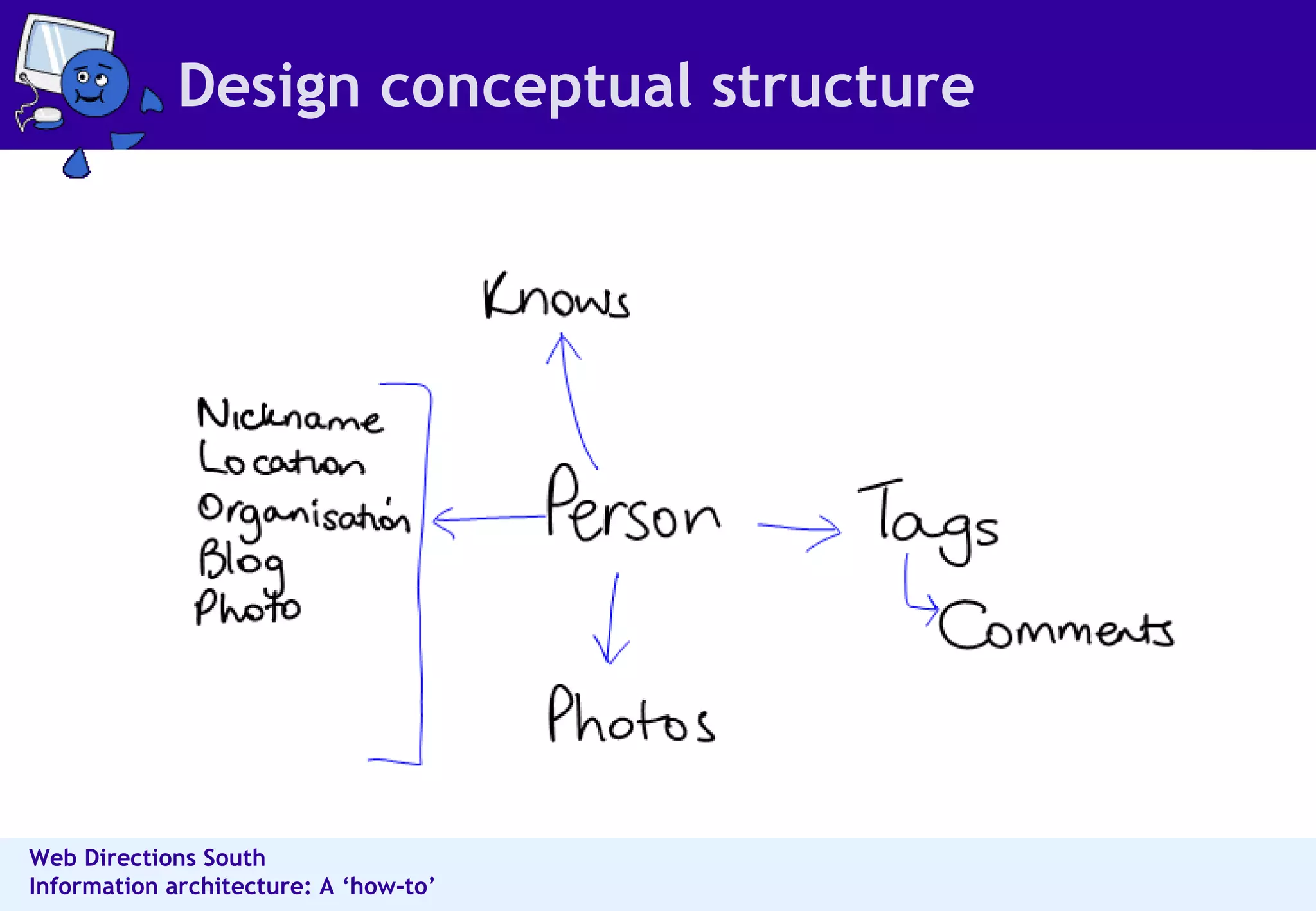
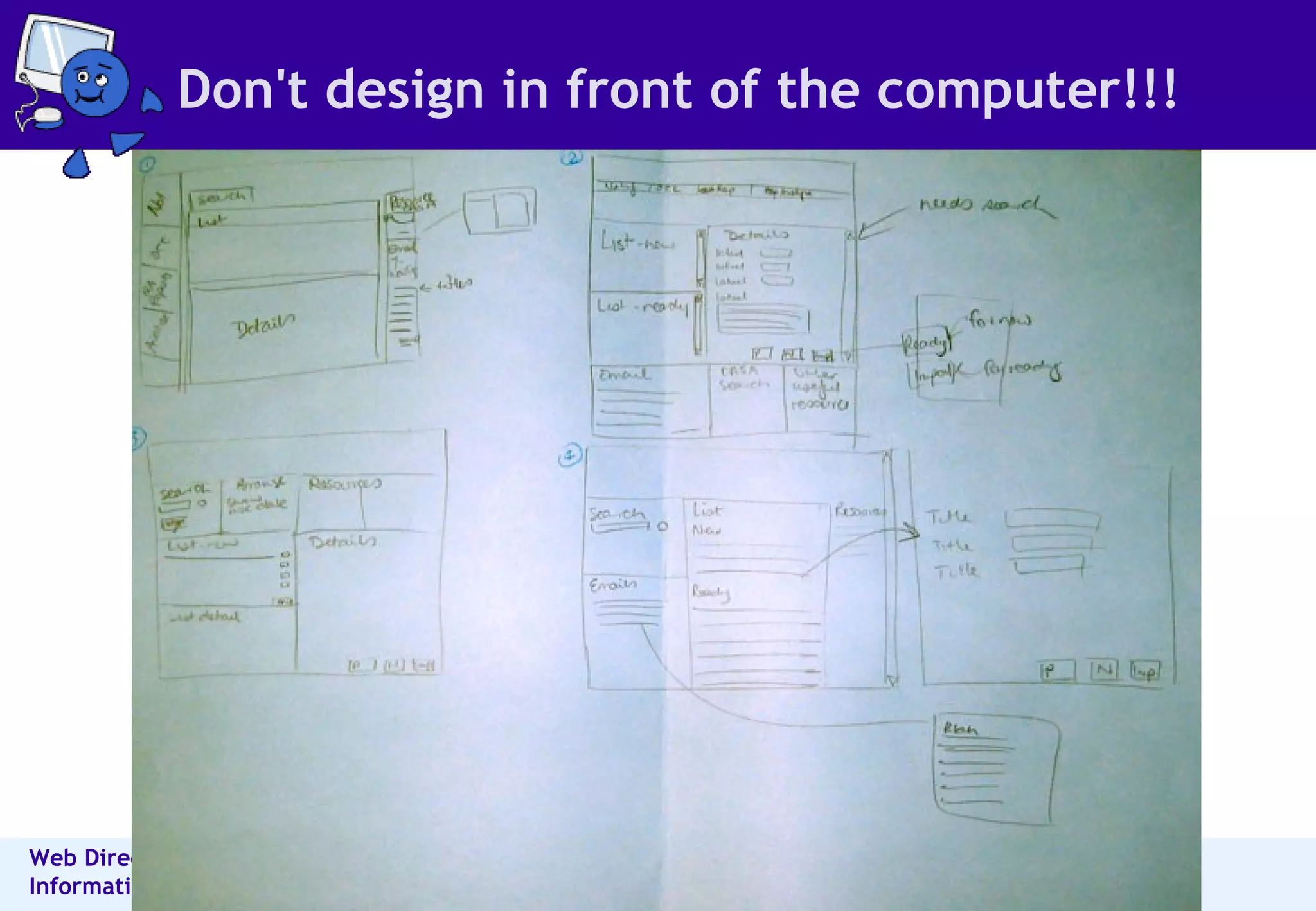
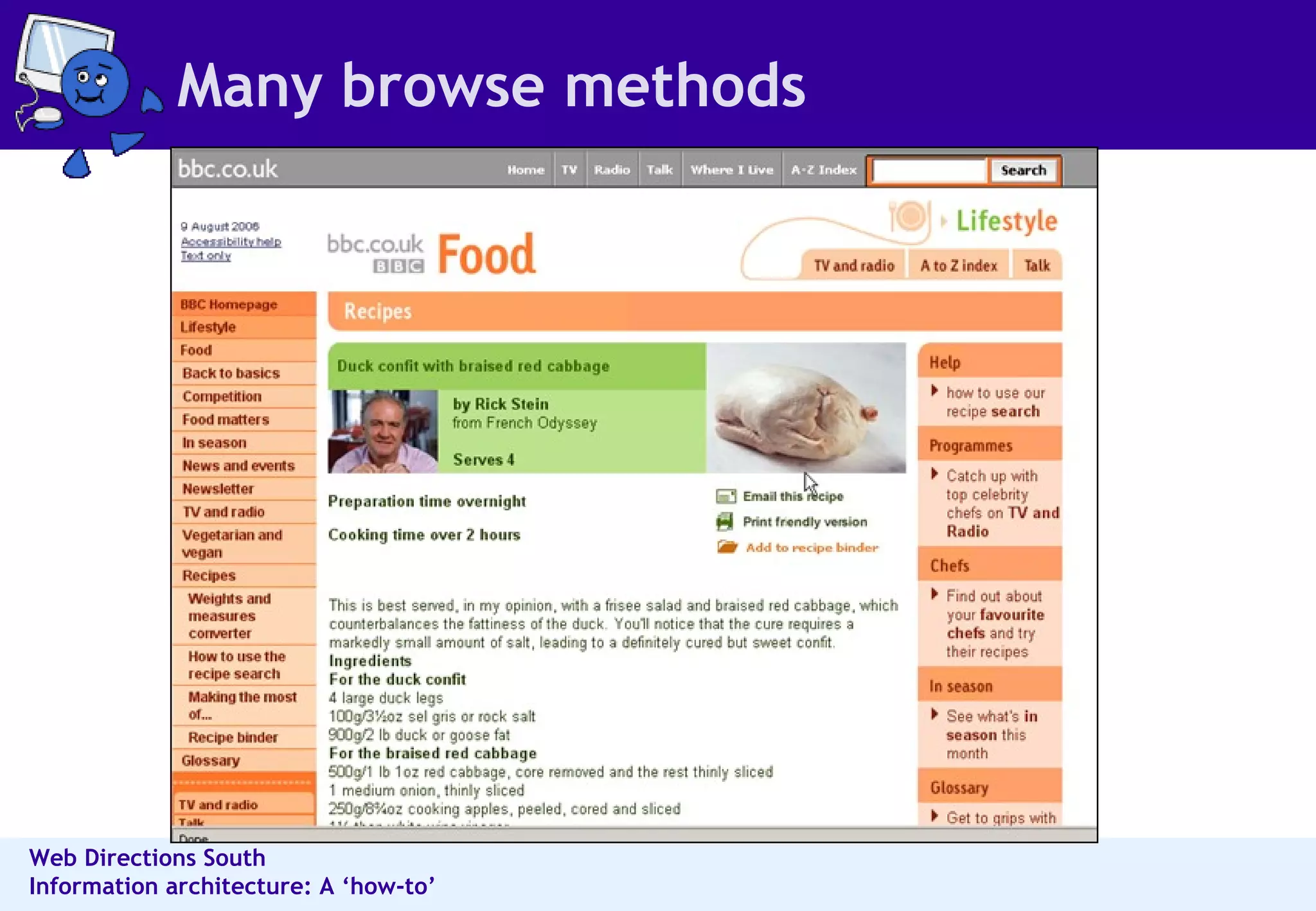
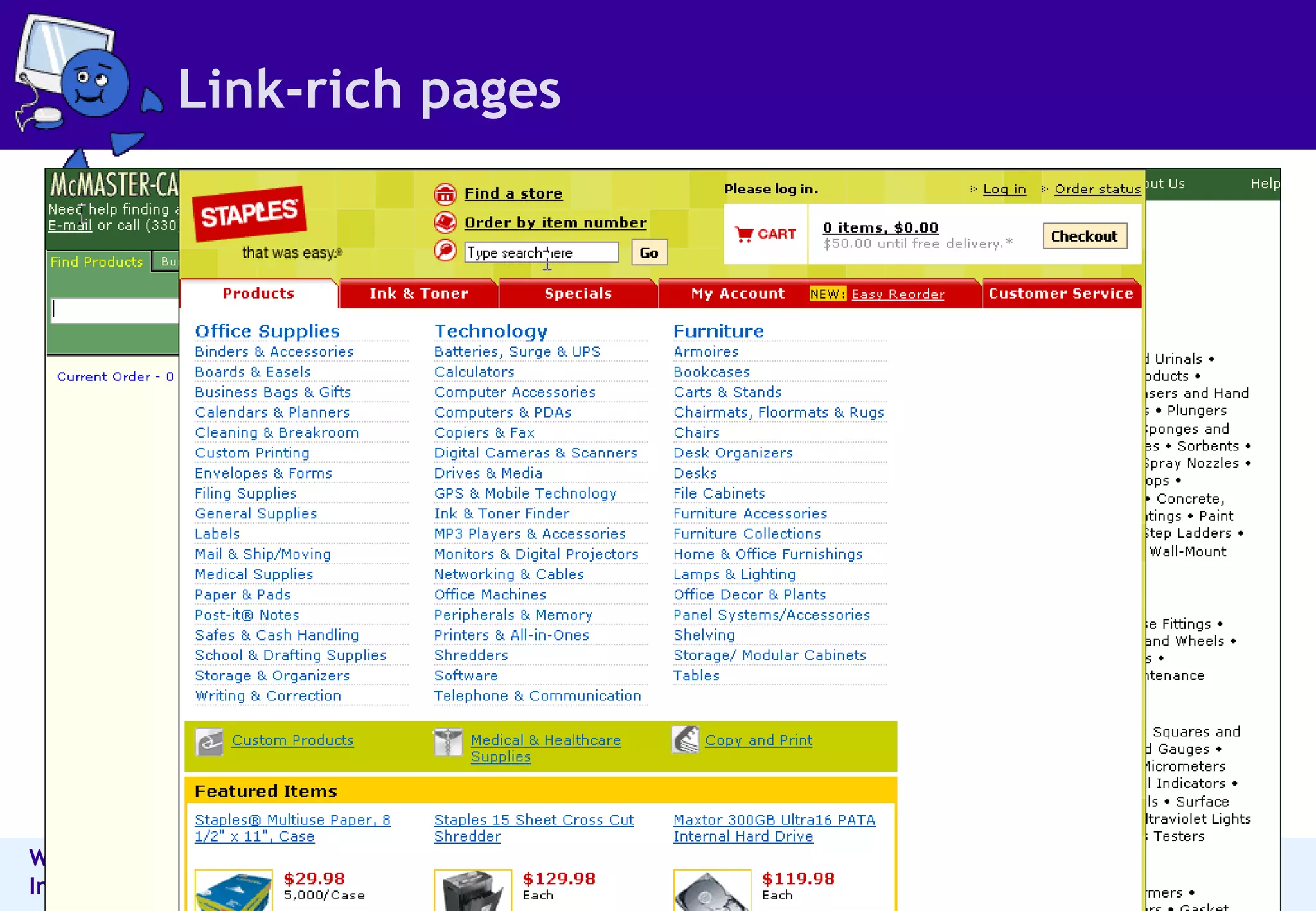
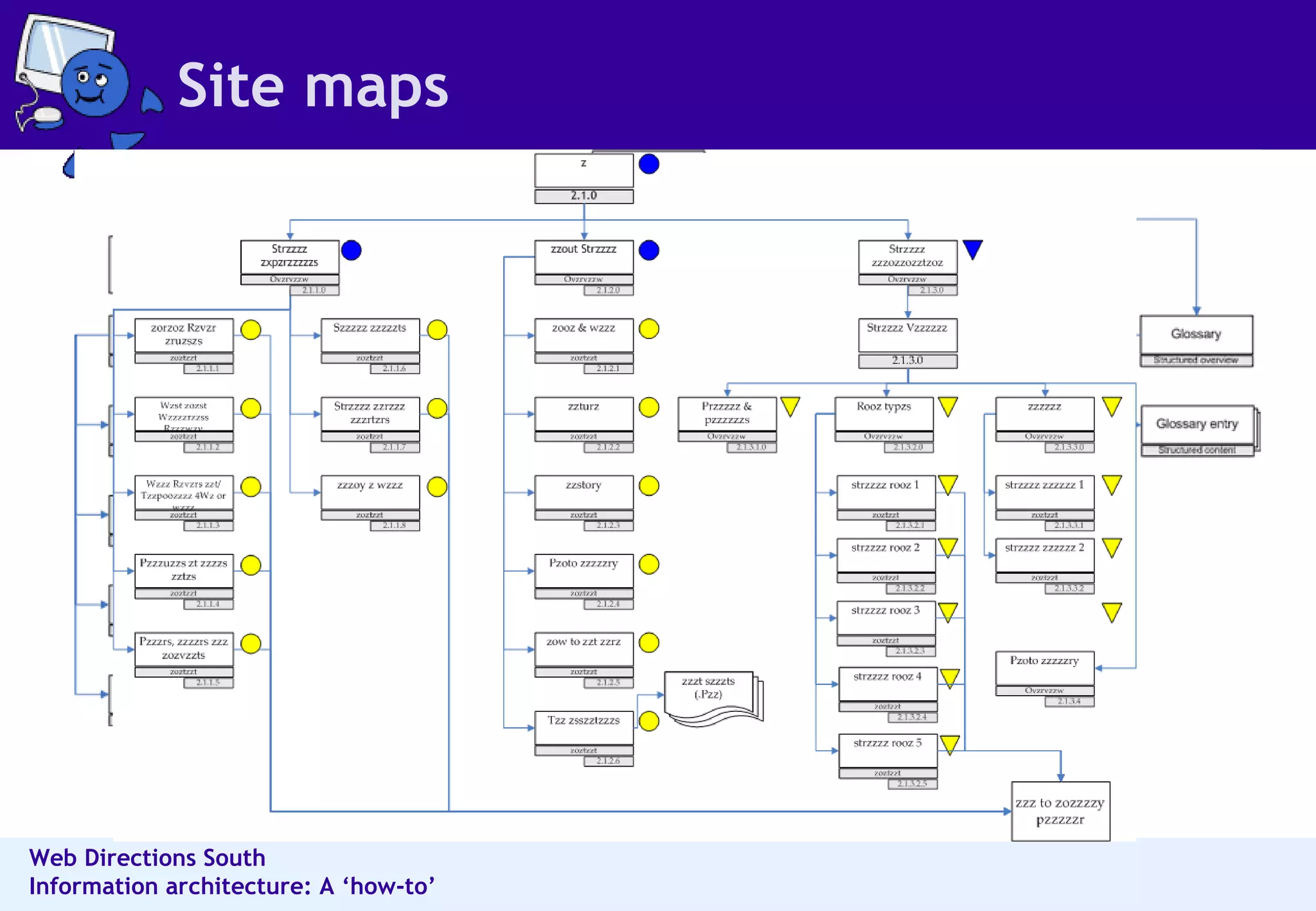
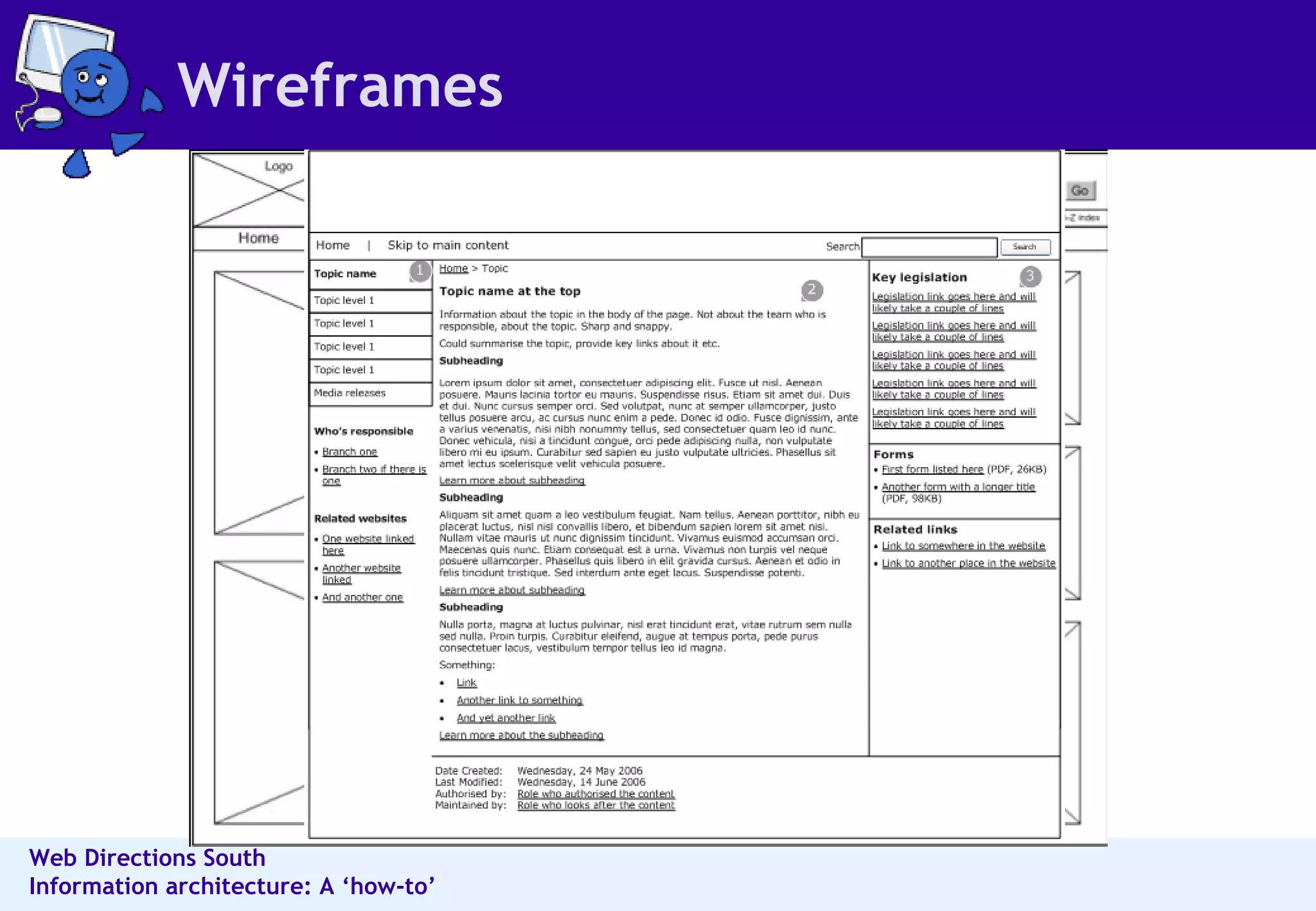
The document outlines best practices for information architecture (IA) and interaction design, emphasizing the importance of user research and content organization. It details methods such as card sorting and content analysis to enhance user experience and facilitate content discovery. The author, a freelance IA expert, shares insights on designing effective structures that balance business and user goals, and offers practical tips for executing IA projects.


















![Questions & thanks http://maadmob.net/ 0409-778-693 [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/donna-maurer-information-architecture-a-how-to-9576/75/Donna-Maurer-Information-architecture-a-how-to-33-2048.jpg)