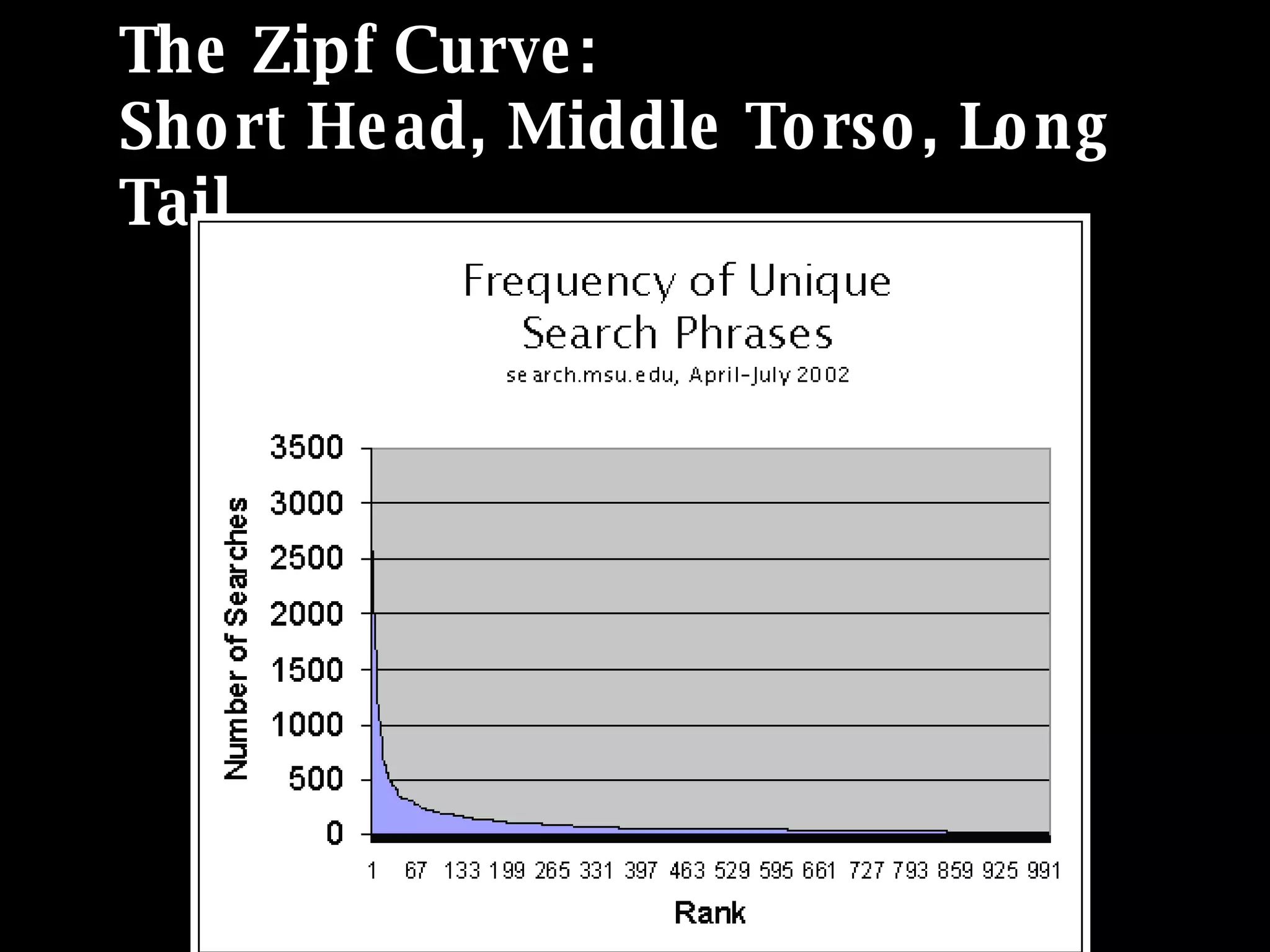
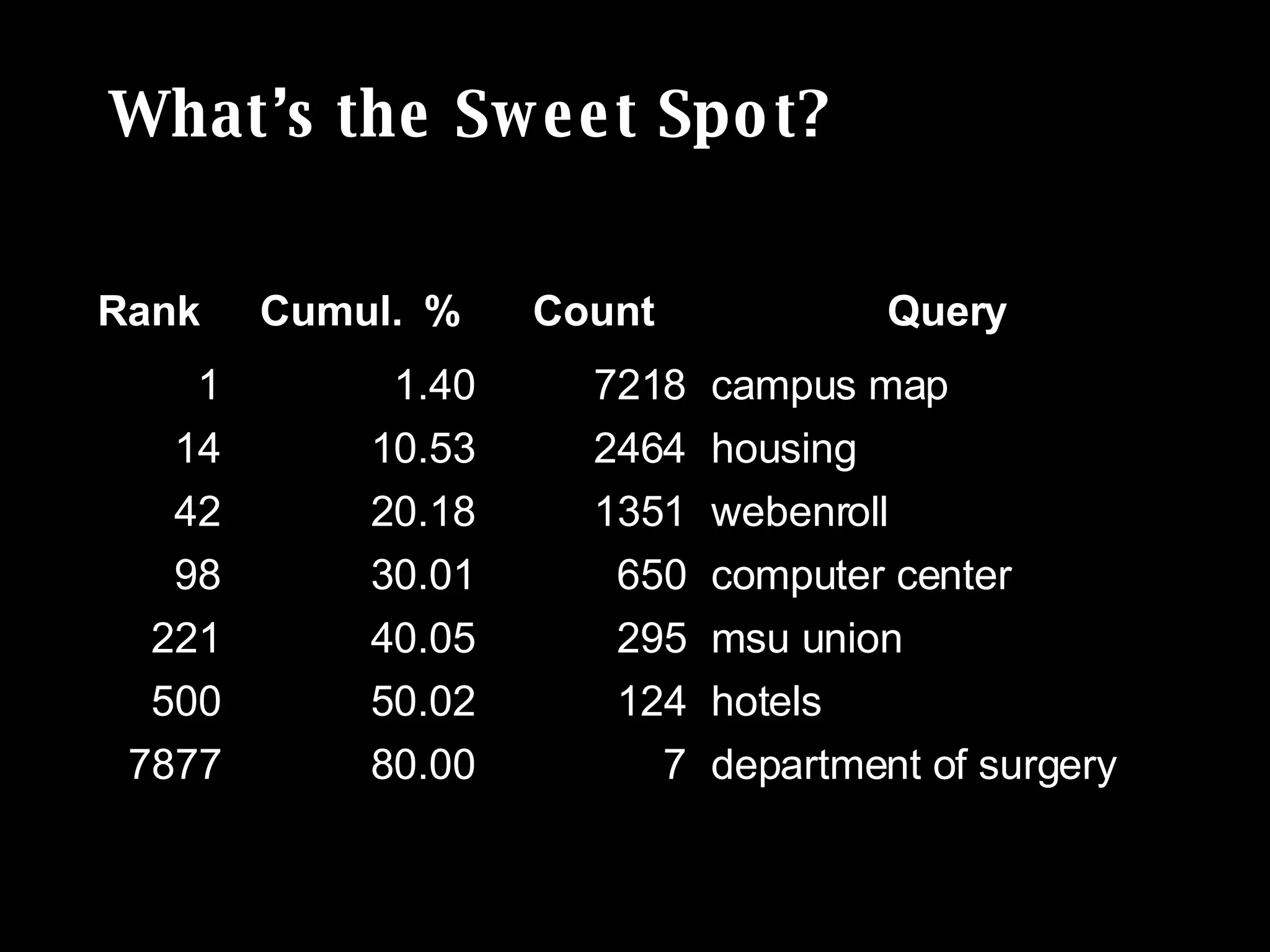
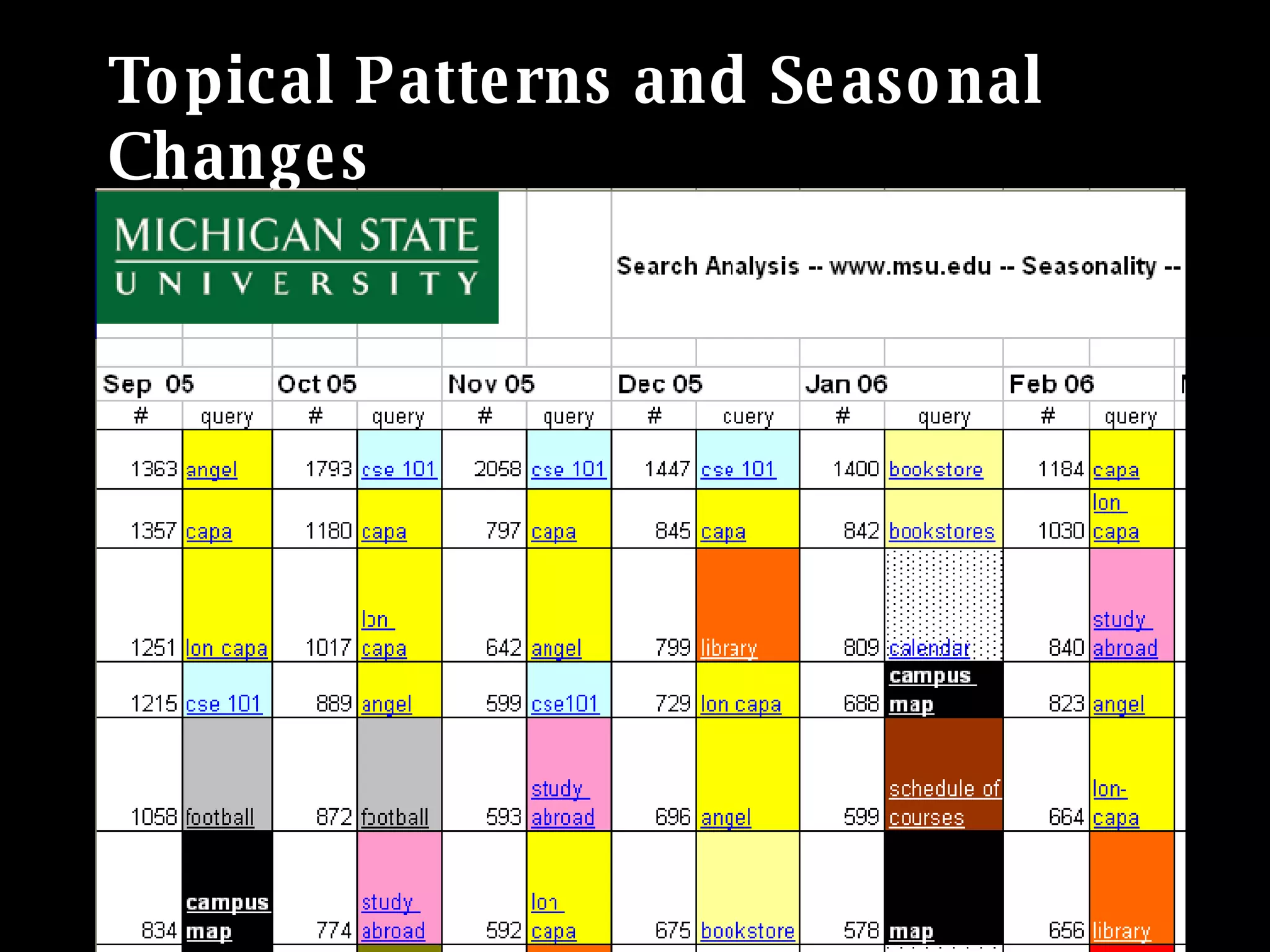
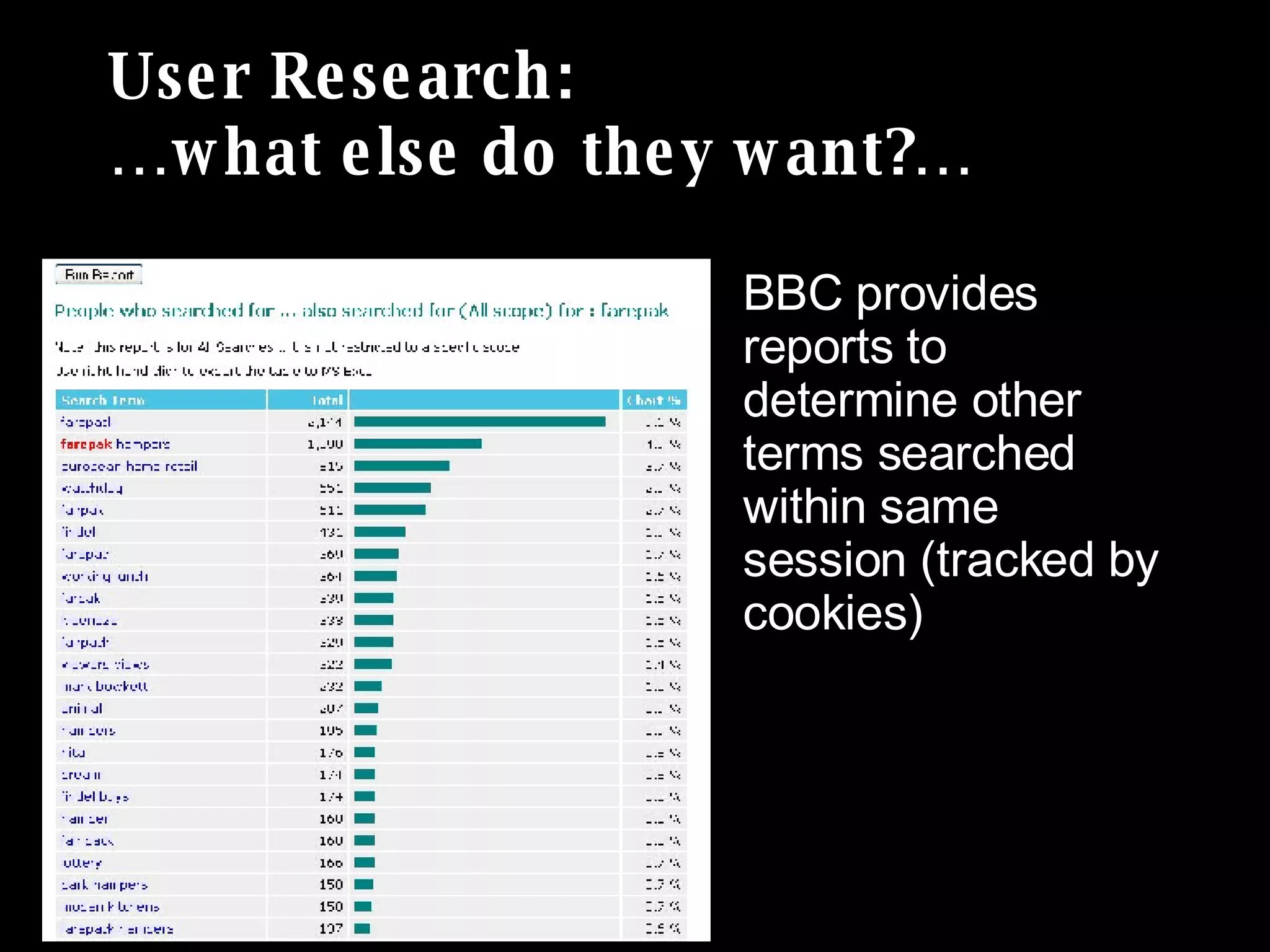
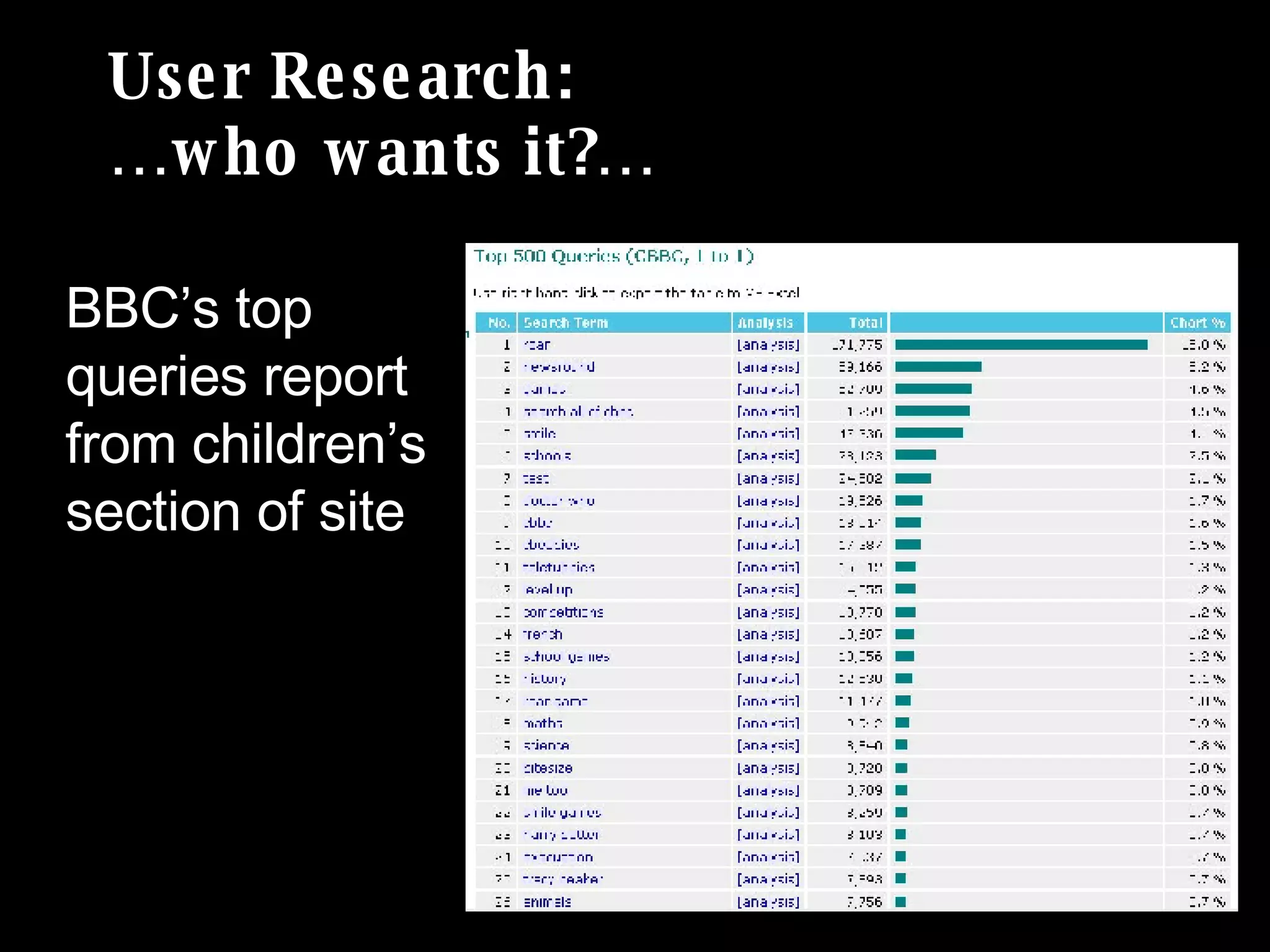
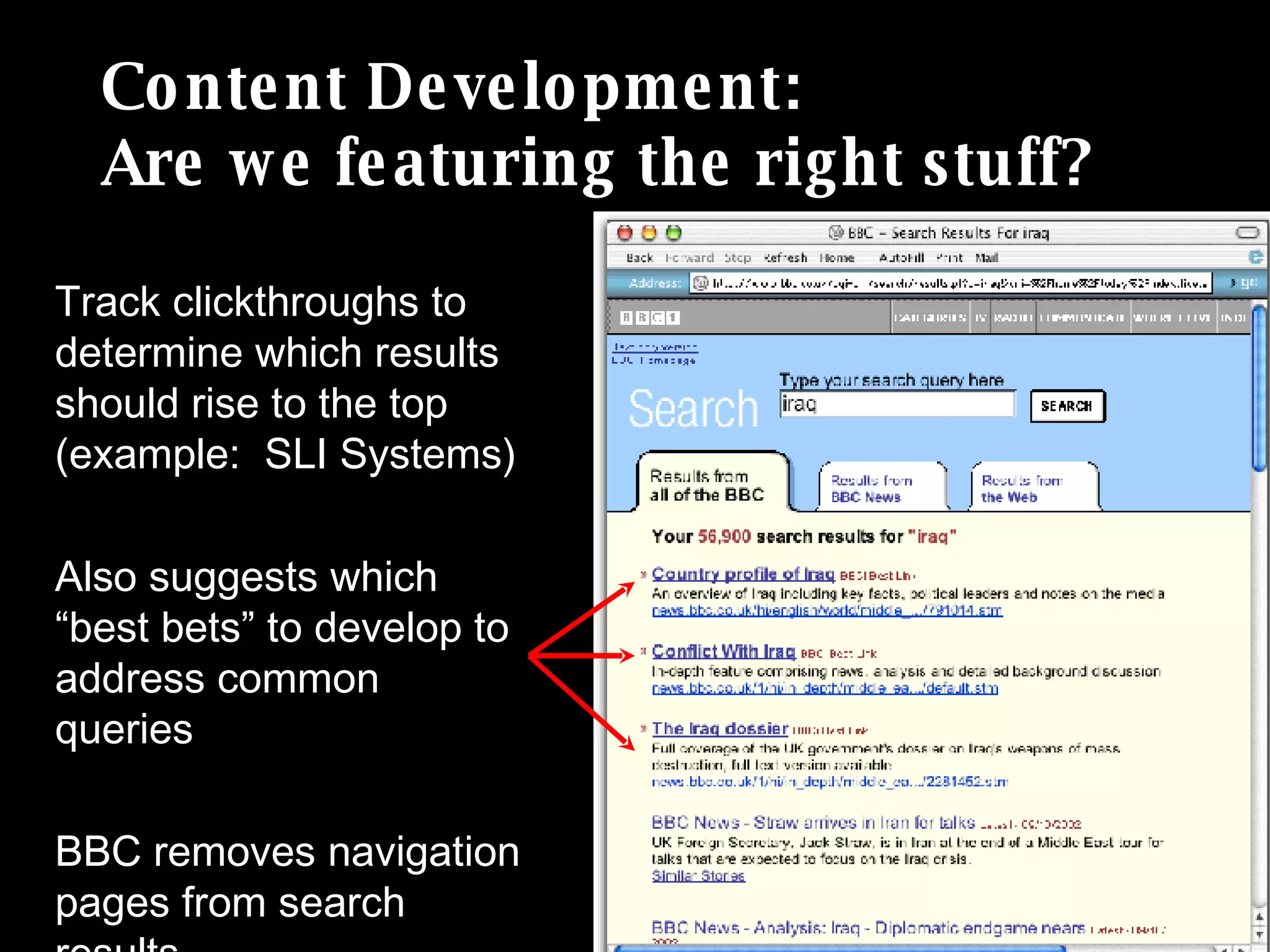
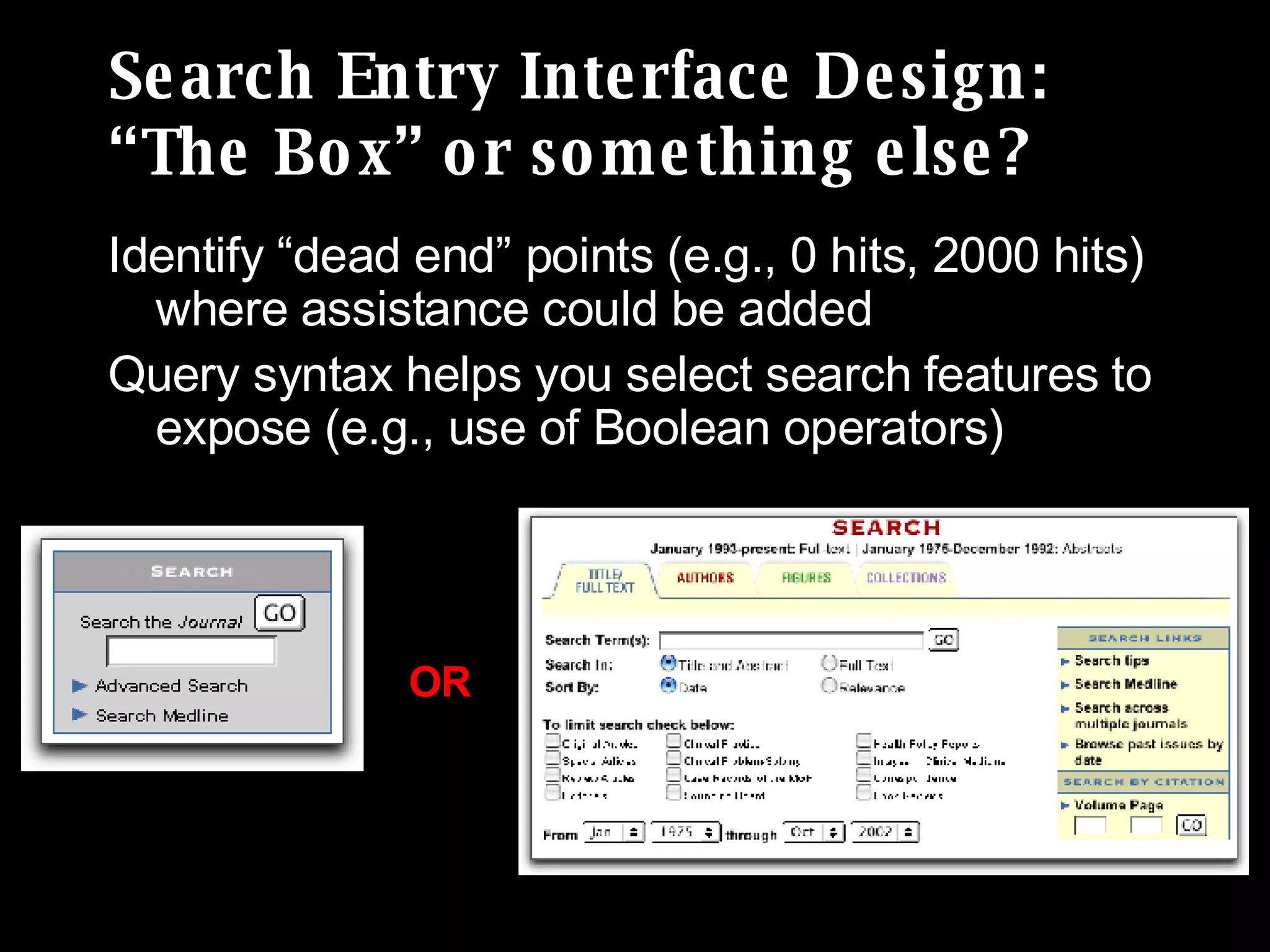
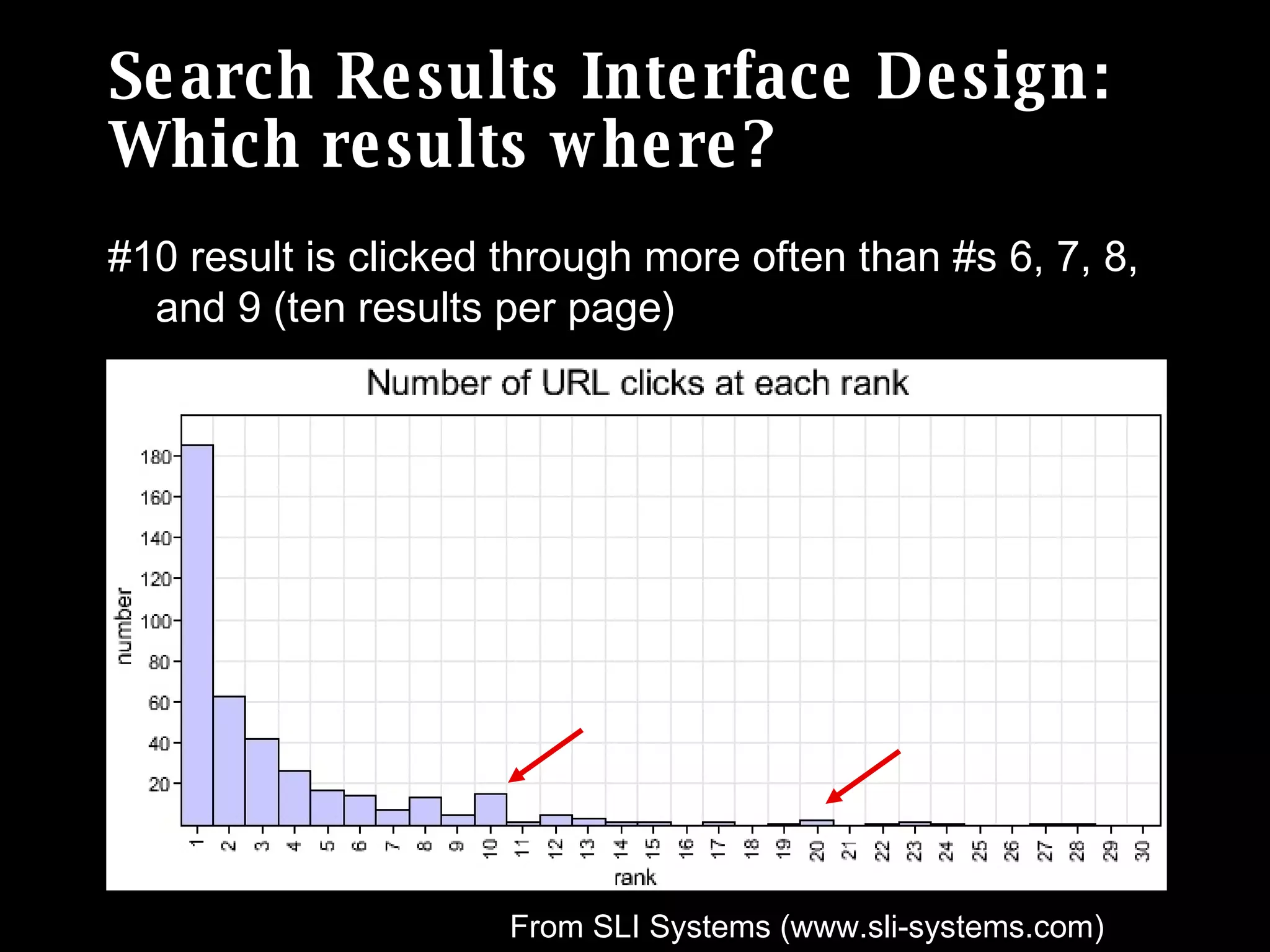
The document discusses the importance of search analytics in understanding user behavior and optimizing search systems. It covers the analysis of search logs, query patterns, and user needs, providing practical insights for improving user experience and content relevance. The author emphasizes the value of combining quantitative search data with qualitative user research to better cater to audience demands.


![Anatomy of a Search Log (from Google Search Appliance) Critical elements in pink : IP address , time/date stamp , query , and # of results: XXX.XXX.X.104 - - [ 10/Jul/2006:10:25:46 -0800] "GET /search?access=p&entqr=0&output=xml_no_dtd&sort=date%3AD%3AL%3Ad1&ud=1&site=AllSites&ie=UTF-8&client=www&oe=UTF-8&proxystylesheet=www&q= lincense+plate &ip=XXX.XXX.X.104 HTTP/1.1" 200 971 0 0.02 XXX.XXX.X.104 - - [ 10/Jul/2006:10:25:48 -0800] "GET /search?access=p&entqr=0&output=xml_no_dtd&sort=date%3AD%3AL%3Ad1&ie=UTF-8&client=www&q= license+plate &ud=1&site=AllSites&spell=1&oe=UTF-8&proxystylesheet=www&ip=XXX.XXX.X.104 HTTP/1.1" 200 8283 146 0.16 XXX.XXX.XX.130 - - [ 10/Jul/2006:10:24:38 -0800] "GET /search?access=p&entqr=0&output=xml_no_dtd&sort=date%3AD%3AL%3Ad1&ud=1&site=AllSites&ie=UTF-8&client=www&oe=UTF-8&proxystylesheet=www&q= regional+transportation+governance+commission &ip=XXX.XXX.X.130 HTTP/1.1" 200 9718 62 0.17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/search-analytics-for-fun-and-profit2922/75/Search-Analytics-for-Fun-and-Profit-3-2048.jpg)

















![Contact Information Louis Rosenfeld Rosenfeld Media, LLC 705 Carroll Street, #2L Brooklyn, NY 11215 USA +1.718.306.9396 [email_address] www.louisrosenfeld.com www.rosenfeldmedia.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/search-analytics-for-fun-and-profit2922/75/Search-Analytics-for-Fun-and-Profit-33-2048.jpg)