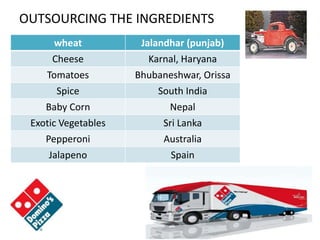
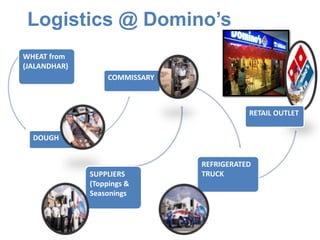
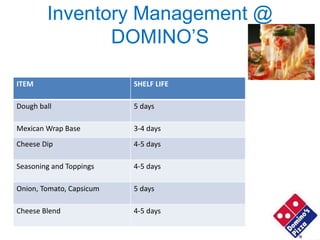
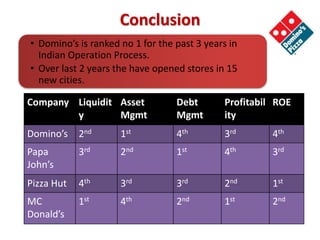
Domino's opened its first store in India in 1996 and has since expanded to over 700 stores across India. The document discusses Domino's logistics and inventory management model. It established centralized commissaries to process ingredients like dough, which are then distributed to stores in refrigerated trucks. This allows for cheaper bulk procurement of ingredients from specific regions. The model also aims to reduce transportation costs by using trucks to transport products for other companies on return routes. Precise inventory management and shelf life tracking of ingredients further improves efficiency.