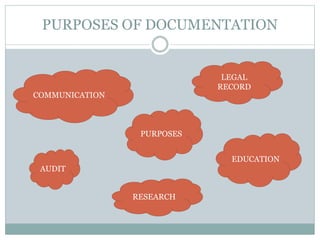
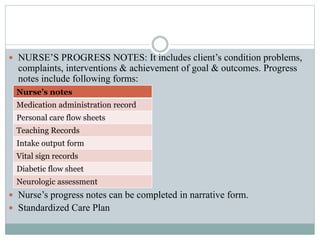
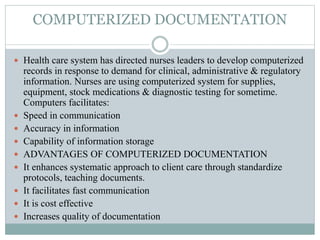
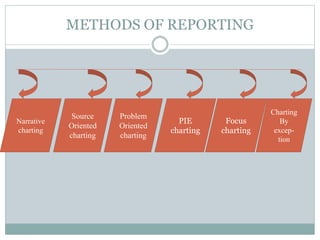
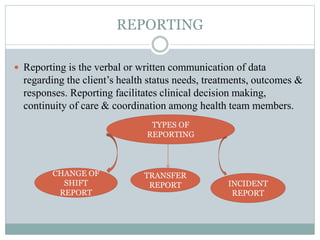
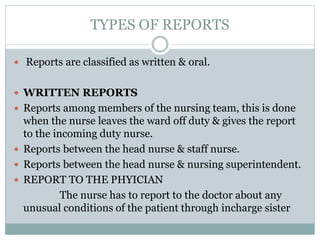
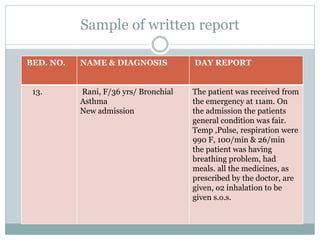
This document discusses documentation and reporting in healthcare. It covers the purposes of documentation such as communication, legal records, audits, research, and education. It describes different types of records like patient records, nursing records, and academic records. It discusses guidelines for accurate, complete, confidential, and factual documentation. It also covers various types of reports like change of shift reports, transfer reports, and incident reports. The document provides examples of documentation forms and emphasizes the importance of minimizing legal liabilities through thorough documentation.