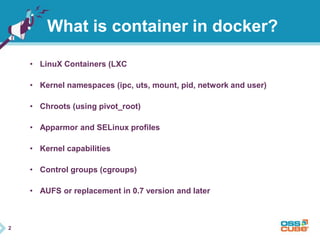
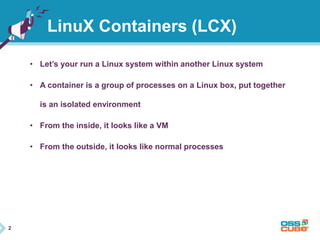
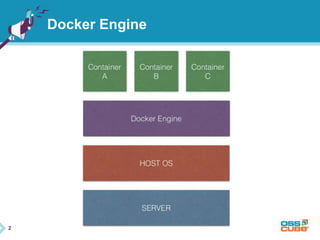
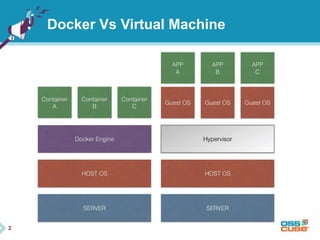
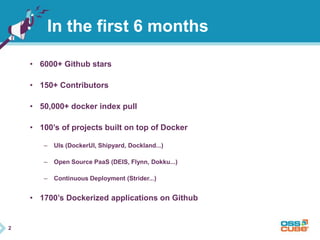
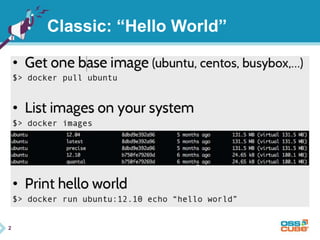
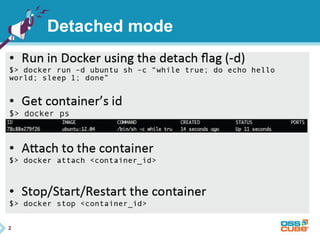
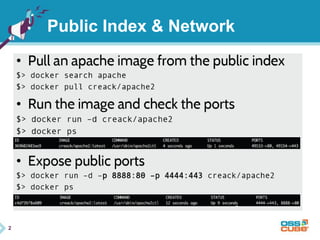
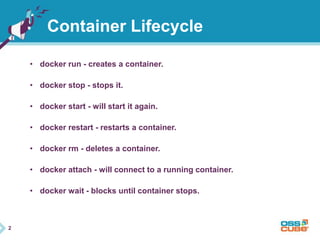
This document discusses Docker, an open-source container platform. It begins with a quick survey asking how familiar people are with Docker. It then defines Docker as allowing applications to be packaged into standardized units called containers that are portable and self-sufficient. The document outlines some benefits of containers like speed and small footprint. It compares containers to virtual machines and explains key components that enable containers like namespaces and control groups. Finally, it provides some basic Docker commands and examples of using Docker to package and run applications.
![July 14, 2014
Kaushal Kishore [ kaushal@osscube.com ]
Sr. Sofware Engineer [OSSCube]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dockerpresentation-140822061136-phpapp02/75/Docker-Presentation-1-2048.jpg)